Tilt sensors detect angular displacement relative to gravity, measuring how much an object inclines, while yaw sensors monitor rotational movement around a vertical axis, essential for determining directional heading. Explore the detailed differences and applications of these sensors to understand how your projects can benefit from their unique capabilities.
Table of Comparison
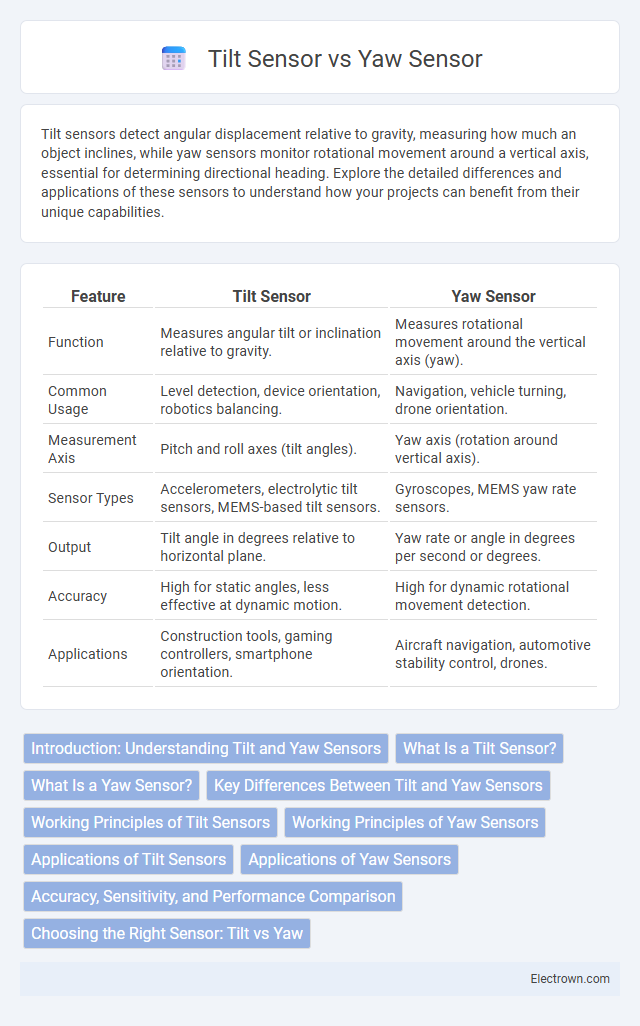
| Feature | Tilt Sensor | Yaw Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures angular tilt or inclination relative to gravity. | Measures rotational movement around the vertical axis (yaw). |
| Common Usage | Level detection, device orientation, robotics balancing. | Navigation, vehicle turning, drone orientation. |
| Measurement Axis | Pitch and roll axes (tilt angles). | Yaw axis (rotation around vertical axis). |
| Sensor Types | Accelerometers, electrolytic tilt sensors, MEMS-based tilt sensors. | Gyroscopes, MEMS yaw rate sensors. |
| Output | Tilt angle in degrees relative to horizontal plane. | Yaw rate or angle in degrees per second or degrees. |
| Accuracy | High for static angles, less effective at dynamic motion. | High for dynamic rotational movement detection. |
| Applications | Construction tools, gaming controllers, smartphone orientation. | Aircraft navigation, automotive stability control, drones. |
Introduction: Understanding Tilt and Yaw Sensors
Tilt sensors measure the angle of inclination or tilt relative to gravity, providing precise data on an object's orientation in one or two axes. Yaw sensors detect rotational movement around a vertical axis, essential for determining heading or directional changes in navigation systems. Both sensors play crucial roles in applications such as robotics, automotive stability control, and aerospace guidance by offering complementary orientation and motion data.
What Is a Tilt Sensor?
A tilt sensor measures the angle of an object relative to the force of gravity, detecting changes in orientation along one or more axes. Unlike a yaw sensor that monitors rotational movement around the vertical axis, a tilt sensor provides critical data for applications requiring precise inclination measurement. You can use tilt sensors in devices like smartphones, drones, and industrial equipment to ensure accurate position control and stability.
What Is a Yaw Sensor?
A yaw sensor measures the rotational movement around a vehicle's vertical axis, providing critical data for stability control systems by detecting changes in your vehicle's direction or orientation. Unlike a tilt sensor, which detects angular displacement relative to gravity, a yaw sensor specifically monitors lateral rotation to enhance traction and prevent skidding. Understanding the function of a yaw sensor helps optimize your vehicle's safety and handling performance during sharp turns or sudden maneuvers.
Key Differences Between Tilt and Yaw Sensors
Tilt sensors measure angular displacement relative to the gravitational axis, providing precise data on an object's inclination or tilt angle. Yaw sensors detect rotational movement around the vertical axis, crucial for determining directional orientation or heading changes. Your choice between tilt and yaw sensors depends on whether you need to monitor linear inclination or rotational orientation for accurate motion tracking.
Working Principles of Tilt Sensors
Tilt sensors operate based on the principle of detecting changes in orientation relative to gravity, using components such as electrolytic fluids, mercury switches, or MEMS accelerometers to measure angular displacement. These sensors convert the physical tilt angle into an electrical signal that can be processed to determine the device's inclination. Your choice between tilt and yaw sensors depends on whether you need to measure linear tilt angles or rotational orientation around a vertical axis.
Working Principles of Yaw Sensors
Yaw sensors operate by detecting angular velocity around the vertical axis using gyroscopic principles, often employing microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology to measure rotational movement precisely. These sensors convert mechanical rotation into electrical signals, enabling accurate monitoring of a vehicle's or device's heading changes. Unlike tilt sensors that measure inclination relative to gravity, yaw sensors focus specifically on rotational dynamics crucial for navigation and stability control systems.
Applications of Tilt Sensors
Tilt sensors are widely used in construction equipment, automotive systems, and consumer electronics for measuring the angle of inclination or slope. These sensors enhance the safety and stability of machinery by detecting changes in orientation, helping prevent accidents caused by excessive tilting. Your devices benefit from tilt sensors in applications like gaming controllers, mobile phones, and robotics, where precise angle measurement improves user experience and device functionality.
Applications of Yaw Sensors
Yaw sensors are widely used in automotive safety systems such as electronic stability control (ESC) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to detect the vehicle's rotational movement and prevent skidding or loss of control. In aerospace, yaw sensors help maintain directional stability and enable precise navigation by measuring the aircraft's angular velocity around the vertical axis. Robotics and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) also rely on yaw sensors to improve orientation, navigation, and maneuverability under various operating conditions.
Accuracy, Sensitivity, and Performance Comparison
Tilt sensors typically offer high accuracy in detecting angular displacement relative to gravity, making them ideal for precise inclination measurements, while yaw sensors excel in tracking rotational movement around the vertical axis with enhanced sensitivity to directional changes. Sensitivity in tilt sensors is primarily influenced by gravitational pull variations, yielding consistent performance in static or slow-moving environments; yaw sensors, often incorporating gyroscopic technology, provide rapid responsiveness to dynamic rotational movements. Performance comparison reveals tilt sensors as more stable and reliable for orientation detection, whereas yaw sensors outperform in applications requiring real-time rotational awareness and motion tracking.
Choosing the Right Sensor: Tilt vs Yaw
Choosing the right sensor depends on your specific measurement needs: tilt sensors detect angular displacement relative to gravity, making them ideal for monitoring slopes or elevation changes, while yaw sensors measure rotational movement around a vertical axis, essential for tracking directional heading or orientation. Your application involving stability control or vehicle navigation will dictate whether tilt or yaw sensors provide more accurate and relevant data. Understanding these key functional differences ensures optimal sensor selection for precise motion and angle detection.
Tilt sensor vs Yaw sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com