BLDC motors offer simplified control and cost-effective solutions ideal for various applications, while PMSM motors provide higher efficiency, smoother operation, and better performance at high speeds due to their sinusoidal back-EMF waveform. Discover how understanding the differences between BLDC and PMSM can optimize Your motor selection by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
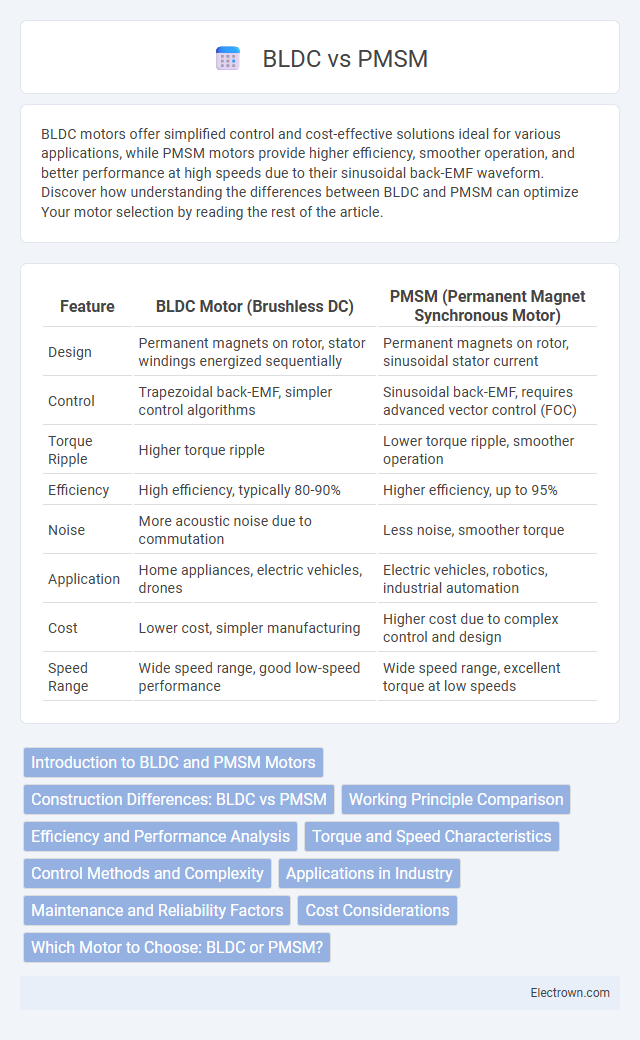
| Feature | BLDC Motor (Brushless DC) | PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Permanent magnets on rotor, stator windings energized sequentially | Permanent magnets on rotor, sinusoidal stator current |
| Control | Trapezoidal back-EMF, simpler control algorithms | Sinusoidal back-EMF, requires advanced vector control (FOC) |
| Torque Ripple | Higher torque ripple | Lower torque ripple, smoother operation |
| Efficiency | High efficiency, typically 80-90% | Higher efficiency, up to 95% |
| Noise | More acoustic noise due to commutation | Less noise, smoother torque |
| Application | Home appliances, electric vehicles, drones | Electric vehicles, robotics, industrial automation |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler manufacturing | Higher cost due to complex control and design |
| Speed Range | Wide speed range, good low-speed performance | Wide speed range, excellent torque at low speeds |
Introduction to BLDC and PMSM Motors
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are electromechanical devices that use electronic commutation to eliminate brushes, enhancing efficiency and reducing maintenance. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) feature a rotor embedded with permanent magnets, providing high torque density and precise control. Both motor types are widely used in applications requiring reliable, efficient, and compact motor designs.
Construction Differences: BLDC vs PMSM
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) feature a rotor with permanent magnets and a stator with wound coils arranged to produce trapezoidal back EMF, while permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) have a rotor embedded with permanent magnets and a stator designed to generate sinusoidal back EMF. BLDC motors typically use surface-mounted magnets on the rotor, whereas PMSMs may employ either surface-mounted or interior magnets, influencing their flux distribution and torque characteristics. The construction differences lead to distinct electromagnetic performance, where PMSMs often provide smoother torque and higher efficiency due to their sinusoidal excitation and optimized magnet placement.
Working Principle Comparison
BLDC (Brushless DC) motors operate using a trapezoidal back-EMF waveform controlled by electronic commutation, where the rotor position is sensed to switch stator windings sequentially. PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors) use a sinusoidal back-EMF, producing smooth and continuous torque by synchronizing the rotor's permanent magnets with a sinusoidal stator current. The main difference lies in BLDC's discrete commutation steps versus PMSM's continuous, sinusoidal excitation for higher efficiency and quieter operation.
Efficiency and Performance Analysis
BLDC motors offer high efficiency with simpler control algorithms, making them suitable for applications requiring cost-effective and reliable performance. PMSM motors, however, deliver superior torque density and smoother operation due to their sinusoidal back-EMF, resulting in higher efficiency at variable speeds and improved dynamic response. Performance analysis reveals PMSM's advantage in precision and energy savings, especially in high-performance industrial and automotive applications.
Torque and Speed Characteristics
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) exhibit trapezoidal back-EMF and deliver consistent torque with efficient speed control, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed regulation. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) feature sinusoidal back-EMF, offering higher torque density and smoother torque output across varied speed ranges. PMSMs generally outperform BLDCs in high-speed applications due to their superior torque-speed characteristics and reduced torque ripple.
Control Methods and Complexity
BLDC motors use trapezoidal control, which is simpler and relies on Hall sensors for rotor position detection, making the control method less complex and cost-effective. PMSM motors require sinusoidal control with field-oriented control (FOC) algorithms, enabling smoother torque and higher efficiency but demanding more complex control systems and processing power. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity and lower cost (BLDC) or refined performance and precise control (PMSM).
Applications in Industry
BLDC motors are widely used in applications requiring high reliability and efficiency, such as electric vehicles, robotics, and HVAC systems, due to their simple control and maintenance advantages. PMSM motors are preferred in high-precision industrial automation, CNC machines, and aerospace systems because of their superior torque density and accuracy. Both motor types contribute significantly to modern industrial processes by optimizing performance in different operational contexts.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
BLDC motors generally require less maintenance due to their simpler rotor design without permanent magnets, reducing the risk of demagnetization and the need for frequent inspections. PMSM motors offer higher reliability in precision applications because their permanent magnets ensure consistent torque and efficiency, but they may require occasional checks for magnet integrity and winding insulation. Your choice between BLDC and PMSM should consider the maintenance demands of your application environment and the long-term reliability needed for optimal performance.
Cost Considerations
BLDC motors generally offer lower initial costs due to simpler construction and widespread manufacturing, making them favorable for budget-sensitive applications. PMSM motors, while more expensive upfront because of their sophisticated design and higher-quality permanent magnets, provide increased efficiency and performance that can reduce long-term operational expenses. Evaluating lifecycle costs, including energy savings and maintenance, is essential when choosing between BLDC and PMSM motors.
Which Motor to Choose: BLDC or PMSM?
BLDC motors offer higher efficiency and simpler control, making them ideal for cost-sensitive applications requiring reliable performance, such as electric scooters and household appliances. PMSM motors provide superior torque density and precision control, favored in high-performance settings like robotics and electric vehicles where smooth operation is critical. Selecting between BLDC and PMSM depends on specific requirements for efficiency, control complexity, and application environment.
BLDC vs PMSM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com