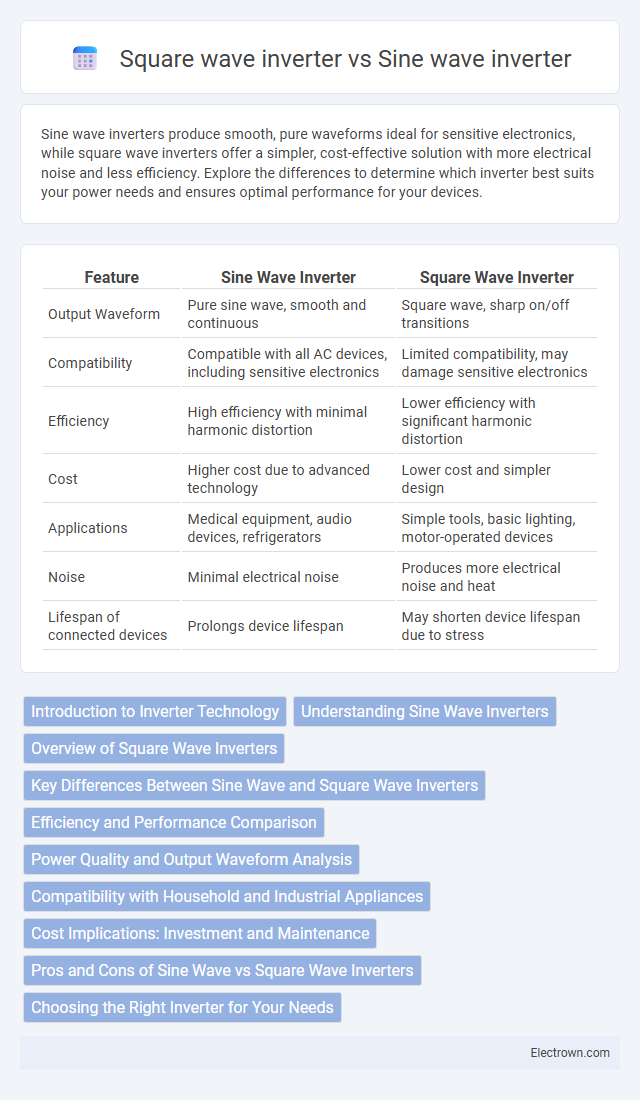
Sine wave inverters produce smooth, pure waveforms ideal for sensitive electronics, while square wave inverters offer a simpler, cost-effective solution with more electrical noise and less efficiency. Explore the differences to determine which inverter best suits your power needs and ensures optimal performance for your devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sine Wave Inverter | Square Wave Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Output Waveform | Pure sine wave, smooth and continuous | Square wave, sharp on/off transitions |
| Compatibility | Compatible with all AC devices, including sensitive electronics | Limited compatibility, may damage sensitive electronics |
| Efficiency | High efficiency with minimal harmonic distortion | Lower efficiency with significant harmonic distortion |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost and simpler design |
| Applications | Medical equipment, audio devices, refrigerators | Simple tools, basic lighting, motor-operated devices |
| Noise | Minimal electrical noise | Produces more electrical noise and heat |
| Lifespan of connected devices | Prolongs device lifespan | May shorten device lifespan due to stress |
Introduction to Inverter Technology
Inverter technology converts DC power from sources like batteries or solar panels into AC power for household appliances. Sine wave inverters produce a smooth, continuous waveform closely matching utility-supplied electricity, ensuring compatibility with sensitive electronics and efficient operation. Square wave inverters generate a simpler, stepped waveform that may cause noise and reduced performance in some devices, making sine wave inverters a better choice for reliable power conversion.
Understanding Sine Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters produce a smooth, pure sine wave output that closely mimics the natural AC power from electrical grids, making them ideal for sensitive electronics and appliances. Unlike square wave inverters, which generate a choppy and less efficient waveform, sine wave inverters reduce harmonic distortion and minimize interference with audio and video equipment. Your choice of a sine wave inverter ensures compatibility, efficiency, and longevity for devices requiring stable and clean power.
Overview of Square Wave Inverters
Square wave inverters convert DC power into a basic AC waveform characterized by sharp, abrupt voltage transitions, resulting in a simple, low-cost design ideal for less sensitive electrical devices. These inverters produce higher harmonic distortion compared to sine wave inverters, which can cause noise in audio equipment and reduce the efficiency and lifespan of motors. Your choice between square wave and sine wave inverters should consider the quality of power needed and the compatibility with your electronic devices.
Key Differences Between Sine Wave and Square Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters produce a smooth, sinusoidal AC output that closely mimics utility power, resulting in optimal performance and compatibility with sensitive electronic devices. Square wave inverters generate a simpler, stepped output that is less efficient and may cause humming, overheating, or damage in certain appliances. The key differences lie in waveform quality, device compatibility, and overall efficiency, with sine wave inverters offering superior power quality and broader application use.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Sine wave inverters deliver higher efficiency and superior performance by producing clean and stable AC output that closely mimics the utility grid, reducing harmonic distortion and minimizing interference with sensitive electronic devices. Square wave inverters operate with lower efficiency due to their abrupt waveform transitions, causing increased heat generation and potential damage to motors and audio equipment. The precise output of sine wave inverters ensures better energy utilization and longer equipment lifespan compared to the simpler and less efficient square wave inverters.
Power Quality and Output Waveform Analysis
Sine wave inverters produce a smooth, continuous waveform closely matching the utility grid, resulting in superior power quality and minimal harmonic distortion, which ensures efficient performance of sensitive electronic devices. Square wave inverters generate a stepped waveform with higher harmonic content, causing potential overheating, noise, and reduced efficiency in many appliances. Your choice impacts device longevity and performance, with sine wave inverters providing cleaner, more reliable power output suitable for a wide range of applications.
Compatibility with Household and Industrial Appliances
Sine wave inverters provide clean and smooth power output that closely mimics the utility grid, ensuring compatibility with sensitive household electronics such as TVs, computers, and medical equipment without causing damage or interference. Square wave inverters produce a rough, choppy power signal suitable only for simple appliances with motors or heating elements, but they can cause overheating, noise, or malfunction in complex industrial machinery and electronic devices. Choosing your power source based on inverter type safeguards appliance longevity and operational efficiency in both domestic and industrial environments.
Cost Implications: Investment and Maintenance
Square wave inverters generally have lower initial investment costs compared to sine wave inverters due to simpler design and fewer components. Maintenance expenses for square wave inverters may increase over time because their output can cause more wear on connected appliances and generate electrical noise. Sine wave inverters, while more expensive upfront, tend to have lower maintenance costs and better long-term reliability, making them more cost-effective for sensitive electronics and continuous use.
Pros and Cons of Sine Wave vs Square Wave Inverters
Sine wave inverters produce smooth, consistent power ideal for sensitive electronics, offering high efficiency and minimal interference but come at a higher cost and complexity. Square wave inverters are simpler, cheaper, and suitable for basic appliances, though they generate more harmonic distortion, potentially damaging modern devices and causing noise. Your choice depends on the quality of power required and the types of devices you plan to operate.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
Choosing the right inverter depends on the type of electronic devices you plan to power and efficiency requirements. Sine wave inverters produce smooth, clean power ideal for sensitive electronics, audio systems, and appliances, ensuring optimal performance and reduced electrical noise. Square wave inverters are typically less expensive and simpler but may cause overheating or inefficiency in complex devices, so assessing your power needs will help you determine the best option for your setup.
Sine wave inverter vs Square wave inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com