Polyfuses provide overcurrent protection by increasing resistance when heated, while resettable fuses automatically return to low resistance after cooling, offering reusable circuit protection without replacement. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best option for your electronic device; continue reading to explore their applications and benefits.
Table of Comparison
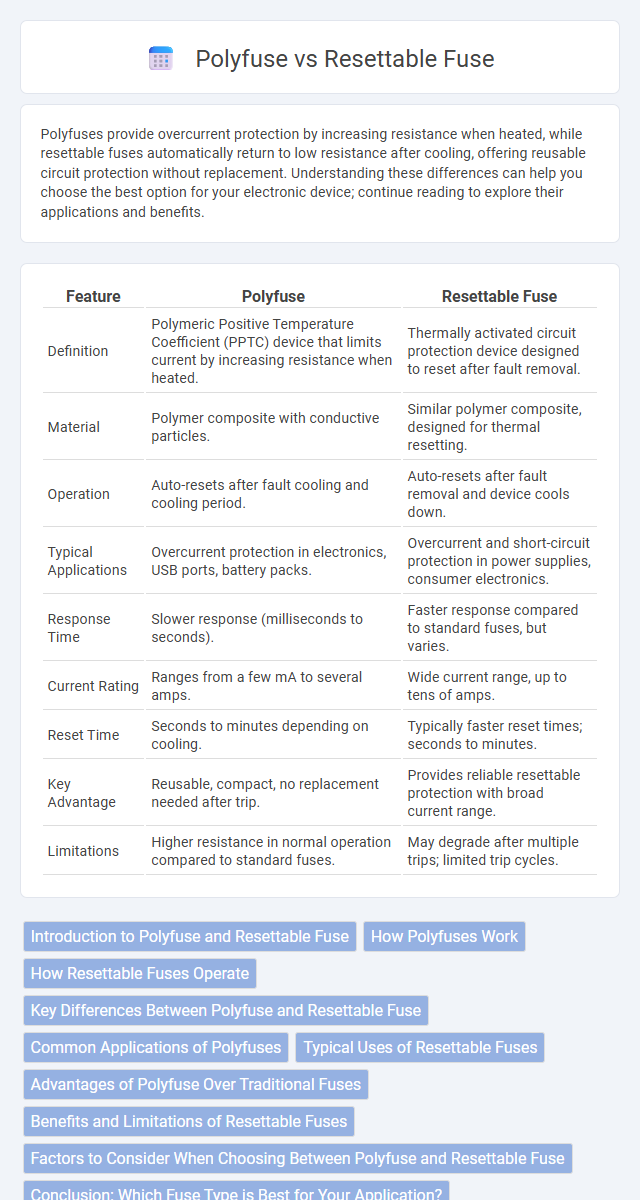
| Feature | Polyfuse | Resettable Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC) device that limits current by increasing resistance when heated. | Thermally activated circuit protection device designed to reset after fault removal. |
| Material | Polymer composite with conductive particles. | Similar polymer composite, designed for thermal resetting. |
| Operation | Auto-resets after fault cooling and cooling period. | Auto-resets after fault removal and device cools down. |
| Typical Applications | Overcurrent protection in electronics, USB ports, battery packs. | Overcurrent and short-circuit protection in power supplies, consumer electronics. |
| Response Time | Slower response (milliseconds to seconds). | Faster response compared to standard fuses, but varies. |
| Current Rating | Ranges from a few mA to several amps. | Wide current range, up to tens of amps. |
| Reset Time | Seconds to minutes depending on cooling. | Typically faster reset times; seconds to minutes. |
| Key Advantage | Reusable, compact, no replacement needed after trip. | Provides reliable resettable protection with broad current range. |
| Limitations | Higher resistance in normal operation compared to standard fuses. | May degrade after multiple trips; limited trip cycles. |
Introduction to Polyfuse and Resettable Fuse
Polyfuses, also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices, are self-resetting fuses that limit current by increasing resistance when overheated, protecting electronic circuits from overcurrent conditions. Resettable fuses operate similarly to traditional fuses but recover automatically after the fault condition clears, eliminating the need for replacement. Both Polyfuses and resettable fuses are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications to safeguard sensitive components.
How Polyfuses Work
Polyfuses, also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices, protect circuits by increasing their resistance sharply when excessive current flows, effectively limiting current without permanently damaging the component. When current returns to normal levels, the Polyfuse cools down and resets automatically, restoring full conductivity. Your device benefits from this self-healing property, ensuring reliable overcurrent protection without the need for fuse replacement.
How Resettable Fuses Operate
Resettable fuses, also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices or polyfuses, operate by increasing their resistance significantly when exposed to excessive current or heat, effectively limiting the current flow to protect circuits. Once the fault condition is removed and the device cools down, the resistance returns to its low, conductive state, allowing normal operation to resume without the need for replacement. This behavior contrasts with traditional fuses that blow permanently, making resettable fuses ideal for reusable circuit protection in electronic devices.
Key Differences Between Polyfuse and Resettable Fuse
Polyfuses are a type of resettable fuse that use a polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material to limit current by increasing resistance when overheated. The main difference lies in their response time and durability; polyfuses typically reset slowly after tripping and may degrade after multiple cycles, while some resettable fuses offer faster recovery and longer lifecycle stability. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate overcurrent protection for your electronic applications, balancing protection speed and component longevity.
Common Applications of Polyfuses
Polyfuses are widely used in consumer electronics, such as laptops and mobile devices, for overcurrent protection due to their ability to reset automatically after fault removal. They are common in USB ports, power adapters, and battery packs, safeguarding circuits without requiring replacement. These fuses provide reliable protection in power distribution networks and automotive electronics, ensuring device safety and longevity.
Typical Uses of Resettable Fuses
Resettable fuses are commonly used in electronic devices for overcurrent protection, safeguarding circuits in smartphones, laptops, and power supplies. They are ideal for applications requiring automatic recovery after fault conditions, such as USB ports, battery packs, and automotive electronics. These fuses provide reliable protection by preventing damage from short circuits and overloads without needing replacement.
Advantages of Polyfuse Over Traditional Fuses
Polyfuses offer significant advantages over traditional fuses due to their resettable nature, eliminating the need for replacement after a fault condition. They provide consistent overcurrent protection by automatically returning to a low-resistance state once cooled, which enhances reliability and reduces maintenance costs in electronic circuits. Furthermore, polyfuses are compact and integrate easily into compact devices, making them ideal for consumer electronics and industrial applications where space and durability are critical.
Benefits and Limitations of Resettable Fuses
Resettable fuses, also known as polyfuses, provide the significant benefit of automatically restoring circuit protection without needing replacement after an overcurrent event, enhancing device longevity and reducing maintenance. However, their higher resistance compared to traditional fuses can lead to power loss and heat generation, potentially affecting sensitive components in your system. While resettable fuses offer convenience and cost-effectiveness in repetitive fault scenarios, their slower response time and limited current rating must be carefully considered for high-precision applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Polyfuse and Resettable Fuse
When choosing between a Polyfuse and a Resettable Fuse, consider factors such as trip current, hold current, and maximum voltage rating to ensure device protection aligns with application requirements. Evaluate the time-to-trip characteristics and environmental conditions, as Polyfuses typically respond slower but provide reliable reset capabilities after overcurrent events. Cost-effectiveness and physical size also play critical roles, with Polyfuses offering compact solutions ideal for space-constrained designs, while resettable fuses might provide enhanced durability for repeated fault conditions.
Conclusion: Which Fuse Type is Best for Your Application?
Polyfuses offer compact, cost-effective overcurrent protection with automatic reset capabilities, ideal for low-current, consumer electronics where space and maintenance are critical. Resettable fuses excel in applications requiring repeated protection cycles and consistent performance under varying temperatures, such as industrial equipment and automotive systems. Choose polyfuses for compact, single-use designs and resettable fuses for durability and reliability in harsh or fluctuating environments.
Polyfuse vs Resettable fuse Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com