Body ECU controls vehicle body functions like lighting and climate control, ensuring comfort and safety. Gateway ECU manages communication between various electronic systems, acting as a network hub; explore this article to understand how these ECUs optimize your vehicle's performance.
Table of Comparison
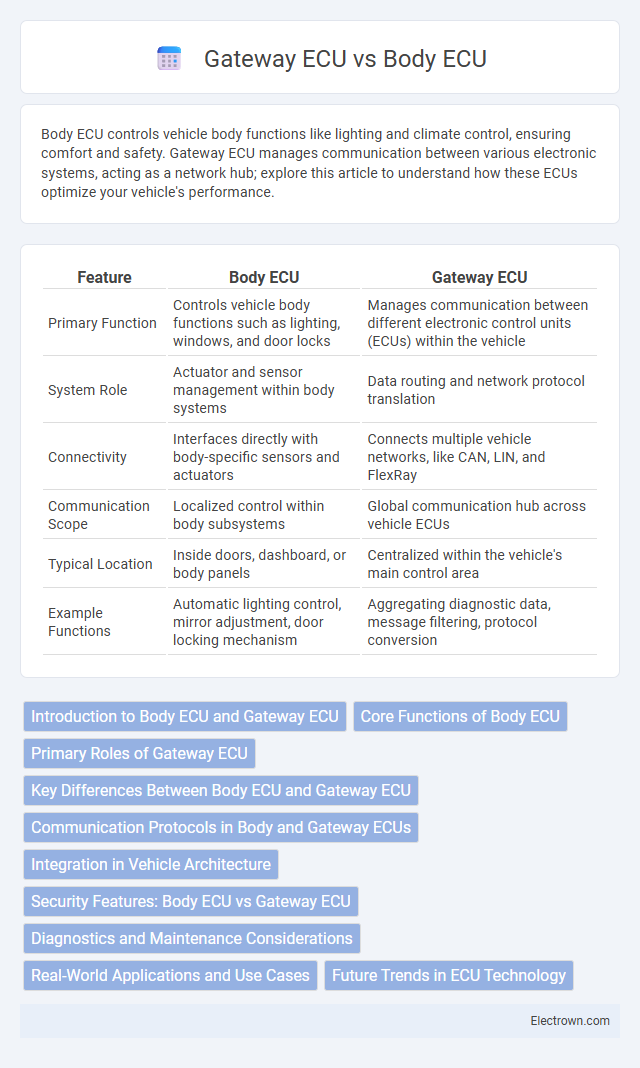
| Feature | Body ECU | Gateway ECU |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Controls vehicle body functions such as lighting, windows, and door locks | Manages communication between different electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle |
| System Role | Actuator and sensor management within body systems | Data routing and network protocol translation |
| Connectivity | Interfaces directly with body-specific sensors and actuators | Connects multiple vehicle networks, like CAN, LIN, and FlexRay |
| Communication Scope | Localized control within body subsystems | Global communication hub across vehicle ECUs |
| Typical Location | Inside doors, dashboard, or body panels | Centralized within the vehicle's main control area |
| Example Functions | Automatic lighting control, mirror adjustment, door locking mechanism | Aggregating diagnostic data, message filtering, protocol conversion |
Introduction to Body ECU and Gateway ECU
Body ECU manages vehicle functions such as lighting, climate control, and door operations, serving as a central control unit for comfort and convenience features. Gateway ECU acts as a communication bridge between different vehicle networks, ensuring seamless data exchange between powertrain, body, and infotainment ECUs. Both ECUs play critical roles in modern automotive electronic architecture, enhancing system integration and vehicle functionality.
Core Functions of Body ECU
The Body ECU primarily manages vehicle body-related functions such as lighting control, door lock mechanisms, and window operation, ensuring safety and convenience features operate seamlessly. It processes input from various sensors and user commands to control actuators related to the vehicle's comfort and security systems. Unlike the Gateway ECU, which handles communication between different vehicle networks, the Body ECU focuses on direct control and coordination of body electronics.
Primary Roles of Gateway ECU
Gateway ECUs primarily manage data communication between different in-vehicle networks such as CAN, LIN, and FlexRay, acting as central hubs for data routing and protocol translation. They ensure secure and efficient information exchange across various ECUs, including the Body ECU, which controls vehicle comfort and convenience functions like lighting, door locks, and climate control. By enabling interoperability and isolating faults within individual networks, Gateway ECUs enhance overall vehicle system reliability and cybersecurity.
Key Differences Between Body ECU and Gateway ECU
Body ECU controls specific vehicle functions such as lighting, door locks, and climate control, managing body-related electronic systems. Gateway ECU acts as the central communication hub between different vehicle networks, enabling data exchange among various control units including the Body ECU. The key difference lies in their roles: Body ECU manages localized body functions, while Gateway ECU facilitates network communication and integration across the entire vehicle.
Communication Protocols in Body and Gateway ECUs
Body ECUs typically utilize communication protocols such as CAN (Controller Area Network) and LIN (Local Interconnect Network) to manage various vehicle body functions like lighting, climate control, and door locks. Gateway ECUs act as bridges between different communication protocols, often integrating CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and Ethernet networks to facilitate seamless data exchange across multiple vehicle domains. The Gateway ECU ensures protocol translation and message routing to maintain efficient communication flow between heterogeneous vehicle networks.
Integration in Vehicle Architecture
The Body ECU manages specific vehicle functions such as lighting, climate control, and door operations, serving as a centralized unit for comfort and convenience systems. The Gateway ECU acts as a communication bridge, integrating the Body ECU with other critical ECUs like powertrain and safety systems to ensure seamless data exchange across the vehicle's network. Your vehicle's architecture relies on the Gateway ECU to synchronize signals and protocols, optimizing overall system performance and diagnostic efficiency.
Security Features: Body ECU vs Gateway ECU
Body ECUs and Gateway ECUs play critical roles in vehicle security, with distinct functions in data management and access control. Body ECUs primarily manage security features related to specific vehicle subsystems, such as door locks, alarm systems, and immobilizers, ensuring localized protection and authentication. Gateway ECUs act as central communication hubs, implementing advanced encryption and firewall protocols to safeguard data transmission between various ECUs, thereby preventing unauthorized access and cyber-attacks across the vehicle network.
Diagnostics and Maintenance Considerations
Body ECU handles diagnostics related to vehicle comfort and security systems, providing real-time data on components such as lighting, climate control, and door modules for targeted maintenance. Gateway ECU manages communication between different networks within the vehicle, centralizing diagnostic data flow and enabling efficient troubleshooting across multiple ECUs. Understanding the distinct roles of these units helps optimize your vehicle's maintenance strategy by ensuring accurate fault detection and streamlined repair processes.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Body ECUs manage vehicle functions such as lighting, door locks, and climate control, directly enhancing passenger comfort and safety in real-world applications. Gateway ECUs facilitate communication between different in-vehicle networks, enabling seamless data exchange across systems like powertrain, infotainment, and safety modules. In electric and autonomous vehicles, Gateway ECUs ensure integrated operation, while Body ECUs maintain essential cabin and security features.
Future Trends in ECU Technology
Body ECU and Gateway ECU technology is evolving with increasing integration of advanced sensor fusion, enhanced cybersecurity protocols, and over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities. Future trends emphasize the convergence of these ECUs into centralized domain controllers to optimize vehicle network communication and reduce latency. Enhanced AI-driven diagnostics and real-time data processing are set to improve system responsiveness and fault detection accuracy across automotive electronic control units.
Body ECU vs Gateway ECU Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com