Quartz crystals offer superior frequency stability and precision compared to ceramic resonators, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and low drift over time. Explore the rest of the article to discover which resonator best suits your specific needs and how each impacts your electronic circuit's performance.
Table of Comparison
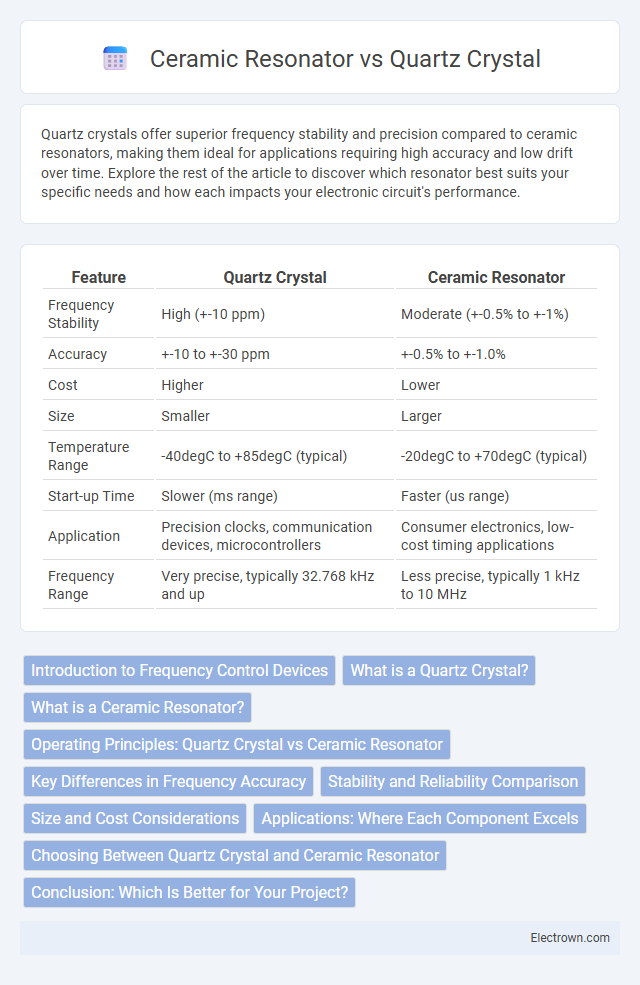
| Feature | Quartz Crystal | Ceramic Resonator |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Stability | High (+-10 ppm) | Moderate (+-0.5% to +-1%) |
| Accuracy | +-10 to +-30 ppm | +-0.5% to +-1.0% |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to +85degC (typical) | -20degC to +70degC (typical) |
| Start-up Time | Slower (ms range) | Faster (us range) |
| Application | Precision clocks, communication devices, microcontrollers | Consumer electronics, low-cost timing applications |
| Frequency Range | Very precise, typically 32.768 kHz and up | Less precise, typically 1 kHz to 10 MHz |
Introduction to Frequency Control Devices
Frequency control devices like quartz crystals and ceramic resonators play crucial roles in electronic circuits by providing stable oscillation frequencies. Quartz crystals offer high precision and low frequency drift due to their piezoelectric properties, making them essential for applications requiring exact timing such as communication systems and microcontrollers. Ceramic resonators, while less accurate, are cost-effective and suitable for less frequency-sensitive tasks, benefiting consumer electronics and simple timing functions.
What is a Quartz Crystal?
Quartz Crystal is a piezoelectric device made from synthetic quartz, known for its high frequency stability and precision in oscillators. It operates by converting mechanical vibrations into electrical signals, making it essential in timing applications such as watches, radios, and microcontrollers. Your electronic circuits benefit from Quartz Crystals due to their low drift and accurate frequency control compared to ceramic resonators.
What is a Ceramic Resonator?
A ceramic resonator is an electronic component used to generate precise timing signals by utilizing the mechanical vibrations of a piezoelectric ceramic material. It offers a cost-effective and compact alternative to quartz crystals, with slightly lower frequency stability and accuracy, making it suitable for applications like microcontrollers and consumer electronics. Your choice between ceramic resonators and quartz crystals depends on the required frequency precision and budget constraints.
Operating Principles: Quartz Crystal vs Ceramic Resonator
Quartz crystals operate based on the piezoelectric effect, where mechanical vibrations produce a precise frequency due to the crystal lattice structure. Ceramic resonators rely on electro-mechanical resonance in piezoelectric ceramic materials, offering less frequency stability and higher tolerance compared to quartz. Your choice depends on the need for accuracy and stability, with quartz crystals excelling in high-precision timing applications.
Key Differences in Frequency Accuracy
Quartz crystals offer superior frequency accuracy, typically within +-10 ppm, making them ideal for applications requiring precise timekeeping and stable oscillation frequencies. Ceramic resonators generally provide frequency accuracy around +-0.5% to +-0.1%, which is less precise but sufficient for many low-cost or less-critical timing applications. Your choice depends on the level of frequency accuracy and stability needed for your specific electronic circuit.
Stability and Reliability Comparison
Quartz crystals exhibit superior frequency stability and reliability due to their high Q-factor and low temperature coefficient, making them ideal for precision timing applications. Ceramic resonators offer less stability with wider frequency tolerance and greater susceptibility to temperature variations, which can impact performance consistency. Quartz crystals maintain stable oscillation frequencies over extended periods, whereas ceramic resonators may require frequent recalibration.
Size and Cost Considerations
Quartz crystals typically offer higher frequency stability and precision but tend to be larger and more expensive compared to ceramic resonators. Ceramic resonators are more compact and cost-effective, making them suitable for size-sensitive, budget-conscious applications. The choice depends on balancing the need for accuracy against size constraints and overall project cost.
Applications: Where Each Component Excels
Quartz crystals excel in applications requiring high frequency stability and precision, such as in communication devices, GPS systems, and high-end oscillators. Ceramic resonators are ideal for cost-sensitive consumer electronics, microcontrollers, and toys where moderate frequency accuracy is sufficient. Both components cater to different performance and budget needs across various electronic applications.
Choosing Between Quartz Crystal and Ceramic Resonator
Choosing between quartz crystal and ceramic resonator depends on the application's frequency stability and cost requirements. Quartz crystals offer superior frequency accuracy and stability, making them ideal for precision timing in communication devices and microcontrollers. Ceramic resonators provide a more cost-effective solution with moderate frequency stability, suitable for less critical timing applications where budget constraints are a priority.
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Your Project?
Quartz crystals offer superior frequency stability, precision, and temperature tolerance, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and reliability, such as telecommunications and instrumentation. Ceramic resonators provide a cost-effective solution with smaller size and adequate performance for less demanding applications like consumer electronics and microcontrollers. Choosing between the two depends on your project's accuracy requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions.
Quartz Crystal vs Ceramic Resonator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com