Thermocouples offer rapid temperature response and wide measurement ranges ideal for dynamic biomedical monitoring, while RTDs provide higher accuracy and stability crucial for precise body temperature assessments. Explore the full article to understand which sensor best suits your biomedical monitoring needs.
Table of Comparison
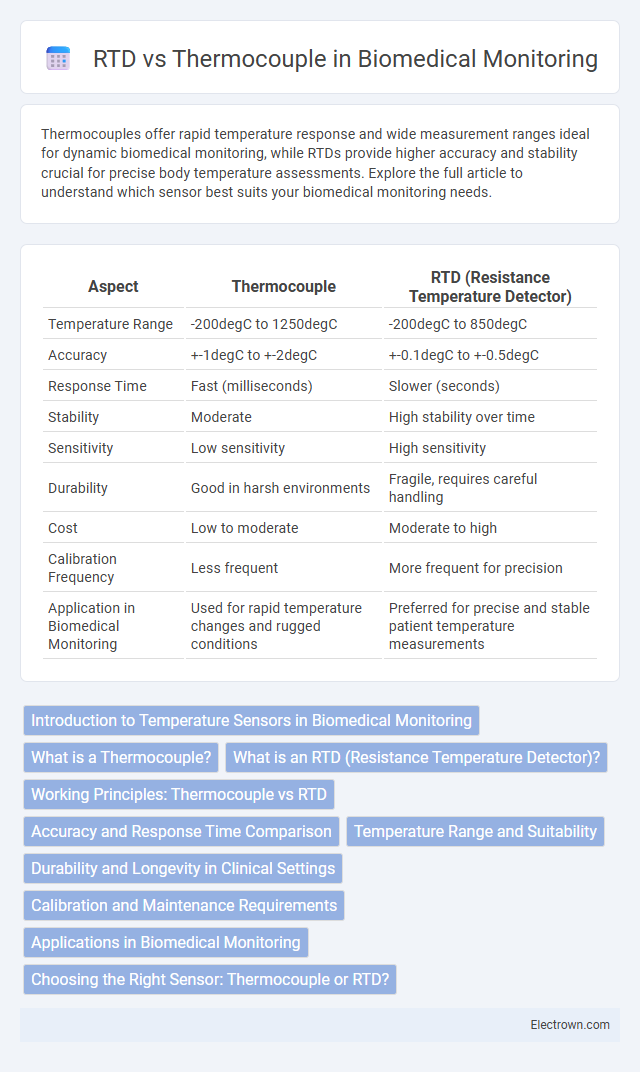
| Aspect | Thermocouple | RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 1250degC | -200degC to 850degC |
| Accuracy | +-1degC to +-2degC | +-0.1degC to +-0.5degC |
| Response Time | Fast (milliseconds) | Slower (seconds) |
| Stability | Moderate | High stability over time |
| Sensitivity | Low sensitivity | High sensitivity |
| Durability | Good in harsh environments | Fragile, requires careful handling |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Calibration Frequency | Less frequent | More frequent for precision |
| Application in Biomedical Monitoring | Used for rapid temperature changes and rugged conditions | Preferred for precise and stable patient temperature measurements |
Introduction to Temperature Sensors in Biomedical Monitoring
Temperature sensors like thermocouples and RTDs play a crucial role in biomedical monitoring by providing accurate body temperature measurements essential for patient diagnosis and treatment. Thermocouples offer fast response times and a wide temperature range, making them suitable for dynamic physiological monitoring, while RTDs deliver higher accuracy and stability, ideal for continuous and precise temperature tracking. Understanding the trade-offs between thermocouples' sensitivity and RTDs' precision ensures optimal selection for applications such as critical care, surgical procedures, and chronic disease management.
What is a Thermocouple?
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor consisting of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end, producing a voltage proportional to temperature difference. In biomedical monitoring, thermocouples offer rapid response times and wide temperature ranges, making them suitable for critical patient care environments. Your choice between thermocouple and RTD depends on factors like accuracy, durability, and specific application requirements.
What is an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector)?
An RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is a precision sensor used in biomedical monitoring to measure temperature by correlating the resistance of a metal element, typically platinum, with temperature changes. It offers high accuracy, stability, and repeatability, making it ideal for critical applications like patient monitoring and laboratory equipment. Your choice of RTD ensures reliable thermal readings essential for maintaining optimal conditions in healthcare environments.
Working Principles: Thermocouple vs RTD
Thermocouples operate based on the Seebeck effect, generating a voltage proportional to temperature differences between two dissimilar metal junctions, providing rapid response times ideal for dynamic biomedical monitoring. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) measure temperature by correlating the resistance change in pure metal, typically platinum, with temperature variations, offering high accuracy and stability for critical physiological measurements. The choice between thermocouples and RTDs in biomedical devices hinges on balancing response speed with precision and longevity in clinical environments.
Accuracy and Response Time Comparison
Thermocouples offer rapid response times, making them suitable for applications requiring quick temperature detection in biomedical monitoring, but their accuracy typically ranges between +-1 to +-2degC. RTDs provide higher accuracy, often within +-0.1 to +-0.5degC, essential for precise temperature measurements in critical biomedical environments, although their response time is generally slower than thermocouples. Your choice depends on prioritizing accuracy or response time: use thermocouples for speed and RTDs for precision.
Temperature Range and Suitability
Thermocouples offer a wide temperature range, typically from -200degC to 1800degC, making them suitable for rapid temperature changes in biomedical monitoring environments requiring fast response times. RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) operate effectively between -200degC and 600degC with higher accuracy and stability, ideal for precise and continuous body temperature measurements. Your choice depends on balancing the need for measurement speed with the requirement for accurate and consistent temperature readings.
Durability and Longevity in Clinical Settings
Thermocouples offer robust durability and fast response times, making them suitable for short-term biomedical monitoring, but their accuracy can degrade over time in clinical environments due to drift and corrosion. RTDs provide superior longevity and stable, precise temperature measurements essential for long-term patient monitoring, thanks to their construction with stable platinum elements resistant to wear. Your choice between thermocouple and RTD depends on the required lifespan and precision, with RTDs favored for reliable durability in demanding clinical settings.
Calibration and Maintenance Requirements
Thermocouples require frequent calibration due to their susceptibility to drift and aging effects, making routine maintenance essential in biomedical monitoring to ensure accuracy. RTDs offer greater stability and longer calibration intervals, reducing downtime and maintenance costs while providing precise temperature measurements critical for patient safety. Your choice between the two sensors should consider these calibration and maintenance demands to maintain reliable monitoring performance.
Applications in Biomedical Monitoring
Thermocouples and RTDs serve critical roles in biomedical monitoring due to their temperature sensing capabilities. Thermocouples are often used in applications requiring fast response times and wide temperature ranges, such as monitoring patient core temperature during surgeries. RTDs provide high accuracy and stability, making them ideal for precise body temperature measurement and long-term patient monitoring scenarios where consistent data are essential for Your health assessments.
Choosing the Right Sensor: Thermocouple or RTD?
Choosing the right sensor for biomedical monitoring depends on factors such as accuracy, temperature range, and response time. RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) offer high accuracy and stability for precise body temperature measurements, while thermocouples provide faster response times and wider temperature ranges suitable for rapid thermal changes or high-temperature monitoring. Selecting an RTD or thermocouple should align with specific biomedical application requirements, emphasizing accuracy for critical patient monitoring or speed for dynamic physiological studies.
Thermocouple vs RTD in Biomedical Monitoring Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com