Dry electrodes offer ease of use and long-term monitoring without the need for conductive gels, making them ideal for mobile or wearable devices. Understanding the advantages and limitations of dry versus wet electrodes can help you choose the right solution for accurate and comfortable biopotential measurement--explore the full article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
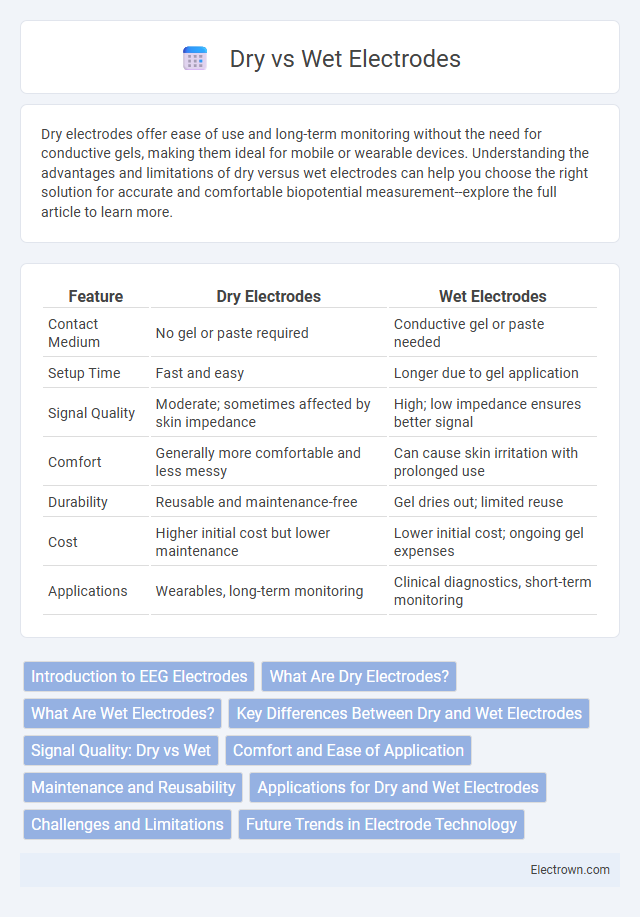
| Feature | Dry Electrodes | Wet Electrodes |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Medium | No gel or paste required | Conductive gel or paste needed |
| Setup Time | Fast and easy | Longer due to gel application |
| Signal Quality | Moderate; sometimes affected by skin impedance | High; low impedance ensures better signal |
| Comfort | Generally more comfortable and less messy | Can cause skin irritation with prolonged use |
| Durability | Reusable and maintenance-free | Gel dries out; limited reuse |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but lower maintenance | Lower initial cost; ongoing gel expenses |
| Applications | Wearables, long-term monitoring | Clinical diagnostics, short-term monitoring |
Introduction to EEG Electrodes
EEG electrodes capture electrical brain activity by detecting voltage fluctuations on the scalp. Dry electrodes offer convenience and faster setup by eliminating the need for conductive gels, but may face contact impedance challenges. Wet electrodes require conductive gel for improved signal quality and lower impedance, making them preferable for clinical and research-grade EEG recordings.
What Are Dry Electrodes?
Dry electrodes are sensors used to capture electrical signals from the skin without the need for conductive gels or liquids. These electrodes utilize materials such as conductive polymers, metals, or carbon-based substances to ensure reliable contact and signal transmission. Your monitoring devices benefit from dry electrodes by providing a comfortable, quick setup and reduced maintenance compared to traditional wet electrodes.
What Are Wet Electrodes?
Wet electrodes consist of conductive materials coated with a gel or paste that facilitates electrical signal transmission by improving skin contact and reducing impedance. Commonly used in electrocardiography (ECG) and electroencephalography (EEG), these electrodes provide reliable and stable recordings due to the conductive electrolyte gel. The gel ensures enhanced conductivity, minimizes motion artifacts, and improves signal quality compared to dry electrodes.
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Electrodes
Dry electrodes use conductive materials like metal or carbon without any gel, offering ease of use and longer-term monitoring with minimal skin irritation. Wet electrodes rely on a conductive gel or adhesive to enhance signal quality but may cause skin discomfort and require frequent maintenance. Your choice depends on specific needs for signal reliability, comfort, and duration of use.
Signal Quality: Dry vs Wet
Wet electrodes typically provide superior signal quality due to better skin conductivity from the gel or adhesive, resulting in clearer and more stable bioelectric readings. Dry electrodes, while more convenient and comfortable for extended use, may suffer from higher impedance and increased noise, affecting the accuracy of your physiological measurements. Selecting the right electrode depends on your priority for signal fidelity versus ease of use in specific applications.
Comfort and Ease of Application
Dry electrodes offer enhanced comfort by eliminating the need for gels, reducing skin irritation and allowing longer wear time with minimal maintenance. Wet electrodes provide superior signal quality but require conductive gels that can cause discomfort, skin irritation, and require careful application and removal. Your choice depends on balancing convenience and comfort with signal accuracy for your specific application.
Maintenance and Reusability
Dry electrodes require minimal maintenance since they do not need gel application, making them easy to clean and store after each use. Wet electrodes demand diligent maintenance, including careful cleaning to remove conductive gel residue and timely replacement to prevent skin irritation and signal degradation. Your choice between dry and wet electrodes will impact long-term usability and cost based on ease of upkeep and electrode lifespan.
Applications for Dry and Wet Electrodes
Dry electrodes are predominantly used in wearable health monitors, brain-computer interfaces, and long-term electrophysiological recordings due to their convenience and reduced skin irritation. Wet electrodes find their applications mainly in clinical settings such as electroencephalography (EEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and electromyography (EMG) where high signal fidelity and lower impedance are critical. Both types serve essential roles in biomedical engineering, neurotechnology, and rehabilitation devices, adapting to specific user needs and environmental conditions.
Challenges and Limitations
Dry electrodes often face challenges such as higher impedance and reduced signal quality due to poor skin contact and lack of conductive gel. Wet electrodes provide better conductivity and signal consistency but are limited by skin irritation, drying out over time, and the need for frequent replacement or reapplication. Both types present trade-offs in comfort, reliability, and maintenance requirements, impacting their suitability for long-term or wearable biosignal monitoring.
Future Trends in Electrode Technology
Future trends in electrode technology emphasize the development of advanced dry electrodes with improved conductivity and skin compatibility, reducing the dependency on conductive gels used in wet electrodes. Innovations in materials like flexible graphene and nanomaterials aim to enhance signal quality and user comfort, supporting long-term monitoring applications. Integration with wearable devices and wireless systems will drive more efficient, real-time electrophysiological data acquisition in clinical and consumer health markets.
Dry vs Wet Electrodes Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com