Single-lead ECG devices provide a simplified, portable option for monitoring heart rhythm, ideal for basic cardiac assessments and home use. To understand which ECG type best suits Your needs and offers comprehensive cardiac insights, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
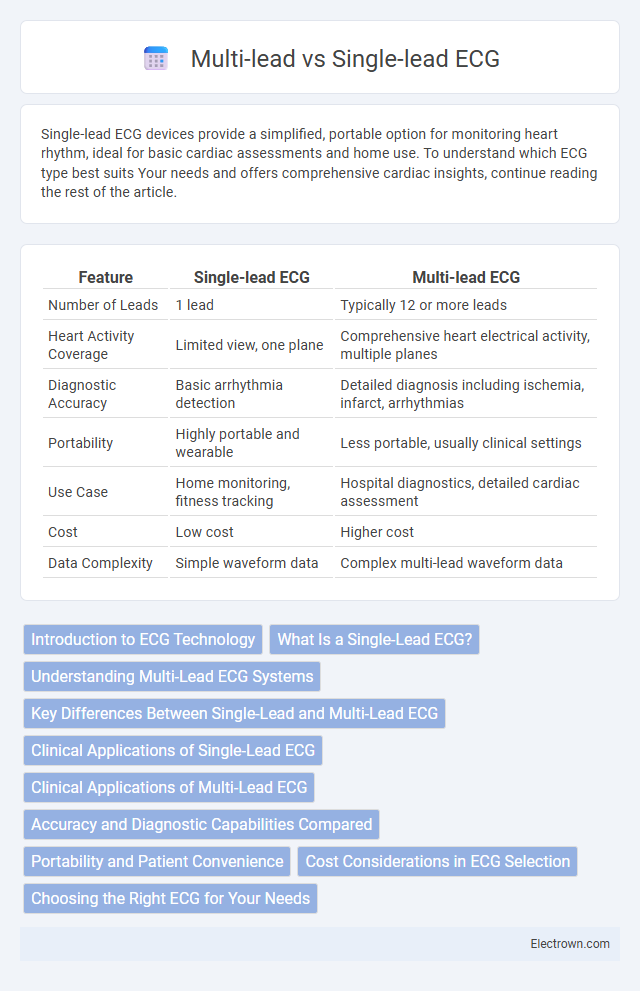
| Feature | Single-lead ECG | Multi-lead ECG |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Leads | 1 lead | Typically 12 or more leads |
| Heart Activity Coverage | Limited view, one plane | Comprehensive heart electrical activity, multiple planes |
| Diagnostic Accuracy | Basic arrhythmia detection | Detailed diagnosis including ischemia, infarct, arrhythmias |
| Portability | Highly portable and wearable | Less portable, usually clinical settings |
| Use Case | Home monitoring, fitness tracking | Hospital diagnostics, detailed cardiac assessment |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost |
| Data Complexity | Simple waveform data | Complex multi-lead waveform data |
Introduction to ECG Technology
Single-lead ECG uses one electrode pair to monitor heart rhythm, offering basic cardiac activity data suitable for wearable devices and remote monitoring. Multi-lead ECG employs multiple electrodes placed on the body to capture detailed electrical activity across various heart regions, providing comprehensive diagnostics essential for detecting arrhythmias and ischemic heart disease. Advances in ECG technology integrate signal processing and AI algorithms to enhance accuracy and enable real-time analysis in both single-lead and multi-lead systems.
What Is a Single-Lead ECG?
A single-lead ECG records the heart's electrical activity using one pair of electrodes, capturing a simplified view of cardiac rhythms and useful for basic arrhythmia detection. This type of ECG is often used in wearable devices and portable monitors for continuous heart rate tracking, offering convenience and ease of use. Your healthcare provider may recommend a single-lead ECG for quick screening or ongoing monitoring with minimal equipment.
Understanding Multi-Lead ECG Systems
Multi-lead ECG systems utilize multiple electrodes placed strategically on the body to capture comprehensive electrical activity of the heart from various angles, enhancing diagnostic accuracy for conditions such as arrhythmias and myocardial infarctions. Unlike single-lead ECGs, which provide a limited view often used for basic rhythm monitoring, multi-lead systems typically include 12 leads, offering detailed spatial information crucial for identifying ischemia, conduction abnormalities, and chamber enlargement. The integration of data from multiple leads allows clinicians to construct a three-dimensional perspective of cardiac electrical patterns, improving precision in clinical assessments and treatment planning.
Key Differences Between Single-Lead and Multi-Lead ECG
Single-lead ECG records heart activity using one electrode, offering simplicity and portability ideal for continuous monitoring or basic rhythm detection. Multi-lead ECG employs multiple electrodes, typically 12, providing a comprehensive view of the heart's electrical activity crucial for diagnosing complex cardiac conditions like arrhythmias or myocardial infarction. Your choice between single-lead and multi-lead ECG should depend on the required diagnostic depth and clinical context.
Clinical Applications of Single-Lead ECG
Single-lead ECG devices are widely used in clinical settings for continuous cardiac monitoring, early detection of arrhythmias, and remote patient management due to their portability and ease of use. They are particularly effective in outpatient care and emergency situations for identifying atrial fibrillation and monitoring heart rate trends over time. Although single-lead ECGs provide limited waveform data compared to multi-lead systems, their accessibility supports timely intervention and reduces the burden on healthcare facilities.
Clinical Applications of Multi-Lead ECG
Multi-lead ECG provides comprehensive cardiac monitoring by capturing electrical activity from multiple angles, essential for diagnosing complex arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and ischemia. Your healthcare provider relies on multi-lead ECGs to detect subtle abnormalities, enabling precise treatment planning and improved patient outcomes. This advanced monitoring surpasses single-lead ECG's limited perspective, making it critical for thorough cardiovascular assessment.
Accuracy and Diagnostic Capabilities Compared
Multi-lead ECGs provide superior accuracy and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities by capturing electrical activity from multiple angles of the heart, enabling detection of localized abnormalities and complex arrhythmias. Single-lead ECGs, while more convenient and portable, offer limited spatial information, reducing their effectiveness in identifying certain cardiac conditions. Your choice between these depends on the clinical context, where multi-lead systems are preferred for detailed cardiac assessments and single-lead devices suit basic rhythm monitoring.
Portability and Patient Convenience
Single-lead ECG devices are highly portable and easy to use, making them ideal for quick, on-the-go heart monitoring and providing significant convenience for patients who require frequent assessments. Multi-lead ECG systems, while less portable due to their size and multiple electrode leads, offer comprehensive cardiac data essential for detailed diagnostics and inpatient care. Your choice between single-lead and multi-lead ECG should balance the need for portability with the desired depth of cardiac information.
Cost Considerations in ECG Selection
Single-lead ECG devices generally incur lower upfront and maintenance costs, making them a cost-effective option for basic cardiac monitoring and home use. Multi-lead ECG systems, while more expensive due to sophisticated hardware and advanced diagnostic capabilities, provide comprehensive cardiac data essential for accurate arrhythmia detection and detailed heart health assessments. Your selection should balance budget constraints with the clinical need for diagnostic accuracy and the complexity of cardiac conditions being monitored.
Choosing the Right ECG for Your Needs
Choosing the right ECG depends on the specific diagnostic requirements and patient monitoring needs. Single-lead ECGs offer portability and ease of use for basic heart rhythm monitoring, ideal for ambulatory or home settings. Multi-lead ECGs provide comprehensive cardiac analysis with multiple electrical view angles, essential for diagnosing complex arrhythmias, ischemia, and myocardial infarction in clinical environments.
Single-lead vs Multi-lead ECG Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com