Piezoresistive pressure sensors measure pressure by detecting changes in electrical resistance due to applied stress, offering high accuracy and stability in various industrial applications. Understanding the differences between piezoresistive and piezoelectric pressure sensors can help You choose the best option for your specific measurement needs; read on to explore their unique advantages and ideal uses.
Table of Comparison
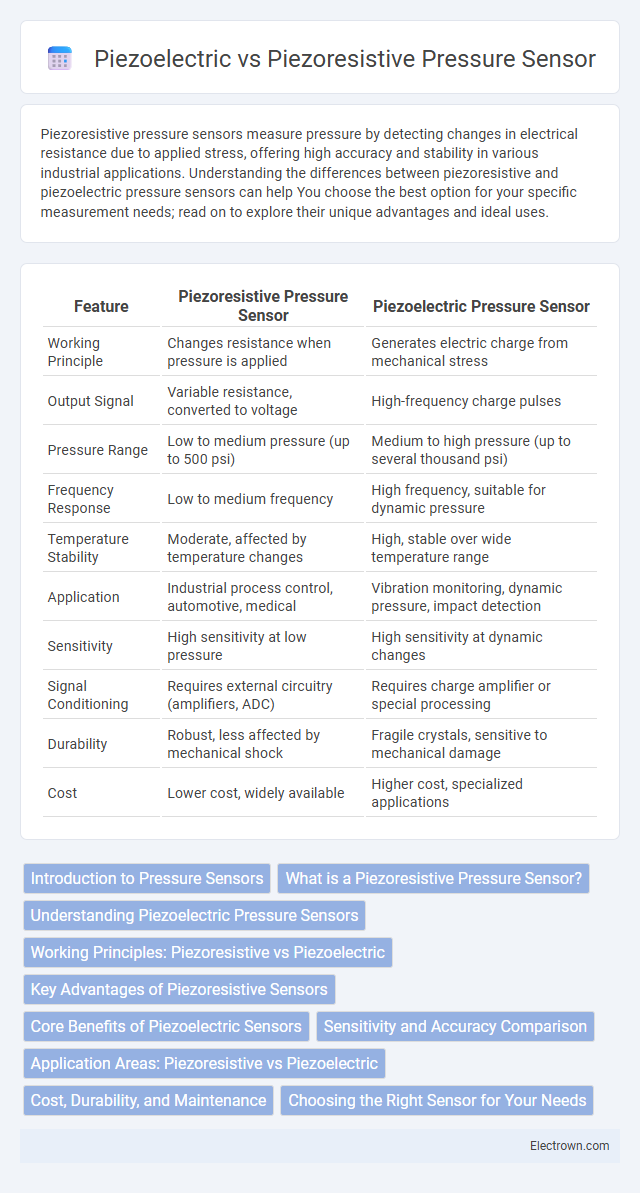
| Feature | Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor | Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Changes resistance when pressure is applied | Generates electric charge from mechanical stress |
| Output Signal | Variable resistance, converted to voltage | High-frequency charge pulses |
| Pressure Range | Low to medium pressure (up to 500 psi) | Medium to high pressure (up to several thousand psi) |
| Frequency Response | Low to medium frequency | High frequency, suitable for dynamic pressure |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate, affected by temperature changes | High, stable over wide temperature range |
| Application | Industrial process control, automotive, medical | Vibration monitoring, dynamic pressure, impact detection |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity at low pressure | High sensitivity at dynamic changes |
| Signal Conditioning | Requires external circuitry (amplifiers, ADC) | Requires charge amplifier or special processing |
| Durability | Robust, less affected by mechanical shock | Fragile crystals, sensitive to mechanical damage |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized applications |
Introduction to Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors measure force exerted by liquids, gases, or solids and convert it into an electrical signal. Piezoresistive sensors utilize changes in electrical resistance caused by mechanical stress, offering high sensitivity and stability for measuring static and dynamic pressure. Piezoelectric sensors generate electric charge in response to applied pressure, excelling in dynamic pressure detection with rapid response times but limited to dynamic or fast-changing pressure measurements.
What is a Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor?
A Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor measures pressure by detecting changes in electrical resistance caused by mechanical strain applied to a semiconductor material. This sensor type converts pressure variations into a measurable electrical signal, making it ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and sensitivity, such as medical devices and industrial equipment. Understanding how your system responds to pressure changes can be enhanced by using piezoresistive technology, which provides reliable and precise pressure data.
Understanding Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
Piezoelectric pressure sensors utilize the piezoelectric effect, where certain crystalline materials generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress, enabling precise dynamic pressure measurement. These sensors excel in detecting rapid pressure changes and high-frequency vibrations, making them ideal for applications in engine monitoring, industrial process control, and medical devices. Unlike piezoresistive sensors, piezoelectric sensors do not require external power for charge generation but typically need specialized electronics to convert the charge into a usable voltage signal.
Working Principles: Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric
Piezoresistive pressure sensors operate based on the change in electrical resistance of a material when mechanical strain is applied, converting pressure-induced deformation into a measurable electrical signal. Piezoelectric pressure sensors function by generating an electric charge in certain crystalline materials, such as quartz, when subjected to mechanical stress, enabling dynamic pressure measurement. The piezoresistive effect is typically utilized for static and low-frequency pressure detection, whereas piezoelectric sensors excel in high-frequency, dynamic pressure sensing applications.
Key Advantages of Piezoresistive Sensors
Piezoresistive pressure sensors offer high sensitivity and excellent linearity, making them ideal for precise pressure measurement in various applications such as automotive and medical devices. Their compatibility with semiconductor manufacturing processes allows for miniaturization and integration into complex electronic systems. You benefit from their low power consumption and robustness under harsh environmental conditions, enhancing reliability and performance in your pressure sensing solutions.
Core Benefits of Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric sensors offer high sensitivity and rapid response to dynamic pressure changes, making them ideal for applications requiring precise vibration or impact measurements. Their ability to operate without an external power source enhances reliability and reduces maintenance in harsh environments. You can rely on piezoelectric sensors for accurate and durable performance where fast transient pressure detection is critical.
Sensitivity and Accuracy Comparison
Piezoresistive pressure sensors offer high sensitivity and excellent linearity, making them ideal for precise pressure measurements in harsh environments. Piezoelectric sensors excel in dynamic pressure detection with rapid response times but may exhibit lower accuracy under static conditions. Your choice should align with whether you prioritize steady-state accuracy (piezoresistive) or dynamic sensitivity (piezoelectric).
Application Areas: Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric
Piezoresistive pressure sensors are widely used in automotive systems, medical devices, and industrial process control due to their high sensitivity to low pressure ranges and compatibility with microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Piezoelectric pressure sensors excel in dynamic pressure measurements in aerospace, engine diagnostics, and vibration monitoring, benefiting from their ability to generate electrical signals under rapidly changing pressure conditions. Application areas for piezoresistive sensors favor static and low-frequency pressure detection, while piezoelectric sensors are preferred for high-frequency, dynamic environments.
Cost, Durability, and Maintenance
Piezoresistive pressure sensors typically have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance requirements compared to piezoelectric sensors, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Piezoelectric sensors offer superior durability and reliability in high-frequency and dynamic pressure measurements due to their robust piezoelectric materials. Maintenance demands are lower for piezoresistive sensors in static pressure environments, while piezoelectric sensors excel in long-term operation with minimal degradation under harsh industrial conditions.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Needs
Selecting the right pressure sensor depends on application requirements such as sensitivity, temperature range, and durability; piezoresistive sensors offer excellent linearity and are ideal for static and low-frequency measurements, while piezoelectric sensors excel in dynamic, high-frequency pressure changes and harsh environments. Piezoresistive sensors typically provide stable output for continuous monitoring, making them suitable for medical and industrial process control, whereas piezoelectric sensors generate charge only during rapid pressure fluctuations, favored in vibration and impact sensing. Understanding these distinctions ensures optimal sensor performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness aligned with specific industrial, automotive, or research needs.
Piezoresistive vs Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com