ECG (electrocardiogram) measures the electrical activity of the heart, providing detailed insights into heart rhythm and detecting arrhythmias, while PPG (photoplethysmography) uses light to measure blood volume changes, offering a non-invasive way to monitor heart rate and blood oxygen levels. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right method for health monitoring; explore the rest of this article to learn more about ECG and PPG technologies.
Table of Comparison
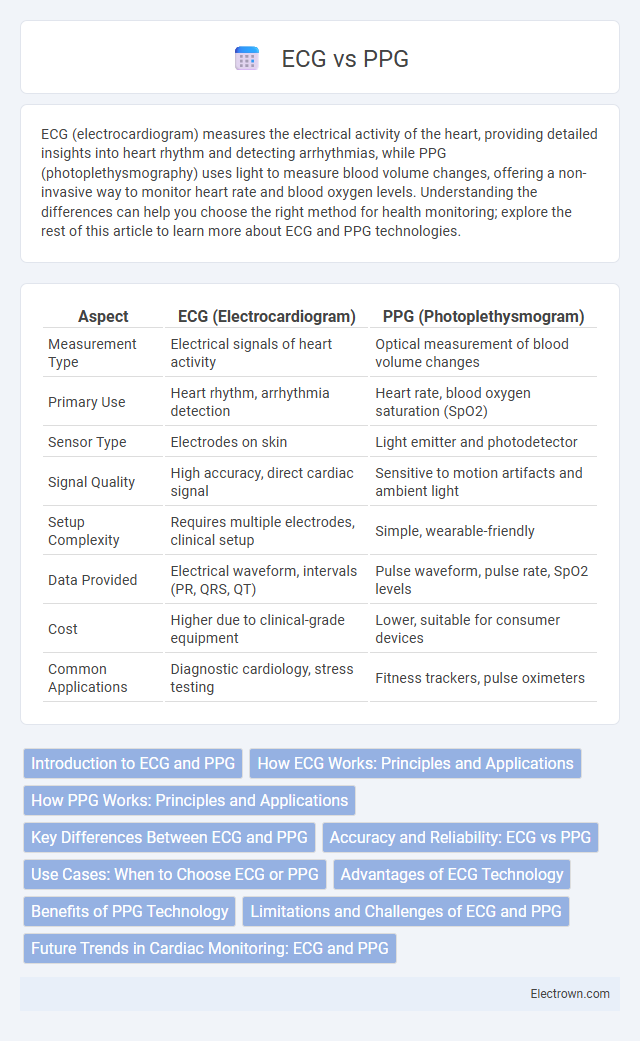
| Aspect | ECG (Electrocardiogram) | PPG (Photoplethysmogram) |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Electrical signals of heart activity | Optical measurement of blood volume changes |
| Primary Use | Heart rhythm, arrhythmia detection | Heart rate, blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) |
| Sensor Type | Electrodes on skin | Light emitter and photodetector |
| Signal Quality | High accuracy, direct cardiac signal | Sensitive to motion artifacts and ambient light |
| Setup Complexity | Requires multiple electrodes, clinical setup | Simple, wearable-friendly |
| Data Provided | Electrical waveform, intervals (PR, QRS, QT) | Pulse waveform, pulse rate, SpO2 levels |
| Cost | Higher due to clinical-grade equipment | Lower, suitable for consumer devices |
| Common Applications | Diagnostic cardiology, stress testing | Fitness trackers, pulse oximeters |
Introduction to ECG and PPG
Electrocardiography (ECG) measures the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes placed on the skin, providing detailed information about cardiac rhythm and heartbeat irregularities. Photoplethysmography (PPG) uses optical sensors to detect blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, often employed for heart rate monitoring and peripheral circulation assessment. Both technologies serve critical roles in cardiovascular health monitoring but utilize fundamentally different mechanisms--electrical signal detection for ECG and light absorption for PPG.
How ECG Works: Principles and Applications
Electrocardiography (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin, detecting the heart's rhythm and electrical impulses to provide real-time cardiac monitoring. Its principles involve measuring voltage changes during the cardiac cycle, enabling detection of arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and other heart conditions. You can rely on ECG for accurate diagnosis and continuous cardiac function assessment, making it essential in clinical settings.
How PPG Works: Principles and Applications
Photoplethysmography (PPG) operates by emitting light into the skin and measuring the variations in light absorption caused by blood volume changes within the microvascular bed. This optical technique captures pulse waveforms through sensors typically placed on the fingertip or earlobe, enabling non-invasive monitoring of heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, and vascular health. PPG's principles facilitate applications in wearable fitness devices, remote patient monitoring, and early detection of cardiovascular abnormalities by providing continuous, real-time data on circulatory dynamics.
Key Differences Between ECG and PPG
ECG (electrocardiogram) measures the electrical activity of the heart via electrodes, providing precise data on heart rhythm and cardiac health, while PPG (photoplethysmography) uses optical sensors to detect blood volume changes in microvascular tissue, primarily indicating heart rate and blood flow. ECG is highly accurate for diagnosing arrhythmias and cardiac conditions, whereas PPG is commonly used in wearable devices for real-time pulse monitoring and fitness tracking. Your choice depends on the need for detailed cardiac diagnostics (ECG) versus convenient, continuous heart rate monitoring (PPG).
Accuracy and Reliability: ECG vs PPG
ECG (Electrocardiogram) provides higher accuracy and reliability in measuring heart activity by directly detecting electrical signals of the heart, making it the gold standard for arrhythmia detection and cardiac diagnosis. PPG (Photoplethysmography) uses light to measure blood volume changes and is less accurate due to susceptibility to motion artifacts, skin tone variations, and environmental factors. For critical health monitoring, especially in clinical settings, ECG remains the preferred choice, whereas PPG suits wearable devices aimed at general heart rate tracking for your fitness and wellness needs.
Use Cases: When to Choose ECG or PPG
ECG (Electrocardiogram) is ideal for detailed cardiac monitoring, arrhythmia detection, and clinical diagnosis due to its direct measurement of electrical heart activity. PPG (Photoplethysmography) suits wearable fitness devices and continuous monitoring of heart rate and blood oxygen levels, offering non-invasive and convenient data collection. Choose ECG for high-precision cardiovascular assessment and PPG for easily accessible, real-time wellness tracking.
Advantages of ECG Technology
ECG technology provides precise measurement of the heart's electrical activity, enabling accurate detection of arrhythmias and ischemic changes that PPG may miss. Its high temporal resolution ensures reliable real-time monitoring of heart rate variability and complex cardiac conditions. Unlike PPG, ECG is less affected by motion artifacts and ambient light interference, making it superior for clinical diagnostics and critical patient monitoring.
Benefits of PPG Technology
PPG technology offers a non-invasive, cost-effective alternative to ECG by using light-based sensors to monitor blood volume changes in the microvascular tissue. This method enables continuous, comfortable heart rate and oxygen saturation monitoring without the need for bulky electrodes, making it ideal for wearable devices and remote health tracking. Its simplicity and portability enhance patient compliance and facilitate real-time data collection outside clinical settings.
Limitations and Challenges of ECG and PPG
ECG faces limitations such as signal noise from muscle artifacts and electrode placement variations, complicating accurate heart rate monitoring in dynamic settings. PPG struggles with motion artifacts and sensitivity to skin tone and ambient light, reducing its reliability for continuous cardiovascular assessment. Both technologies require advanced filtering and calibration techniques to overcome these challenges for precise heart rate and oxygen saturation measurements.
Future Trends in Cardiac Monitoring: ECG and PPG
Future trends in cardiac monitoring emphasize the integration of ECG and PPG technologies to enhance accuracy and usability. ECG provides detailed electrical activity of the heart, while PPG offers continuous, non-invasive monitoring through optical sensors, making wearable devices more versatile. Your cardiac health management will benefit from advancements in AI-driven analysis and real-time data fusion between ECG and PPG signals.
ECG vs PPG Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com