Acoustic stethoscopes rely on sound waves transmitted through hollow tubes to your ears, providing clear, direct auscultation without electronic amplification, while electric stethoscopes amplify and filter body sounds to enhance diagnostic precision, especially in noisy environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover which stethoscope best suits your clinical needs and preferences.
Table of Comparison
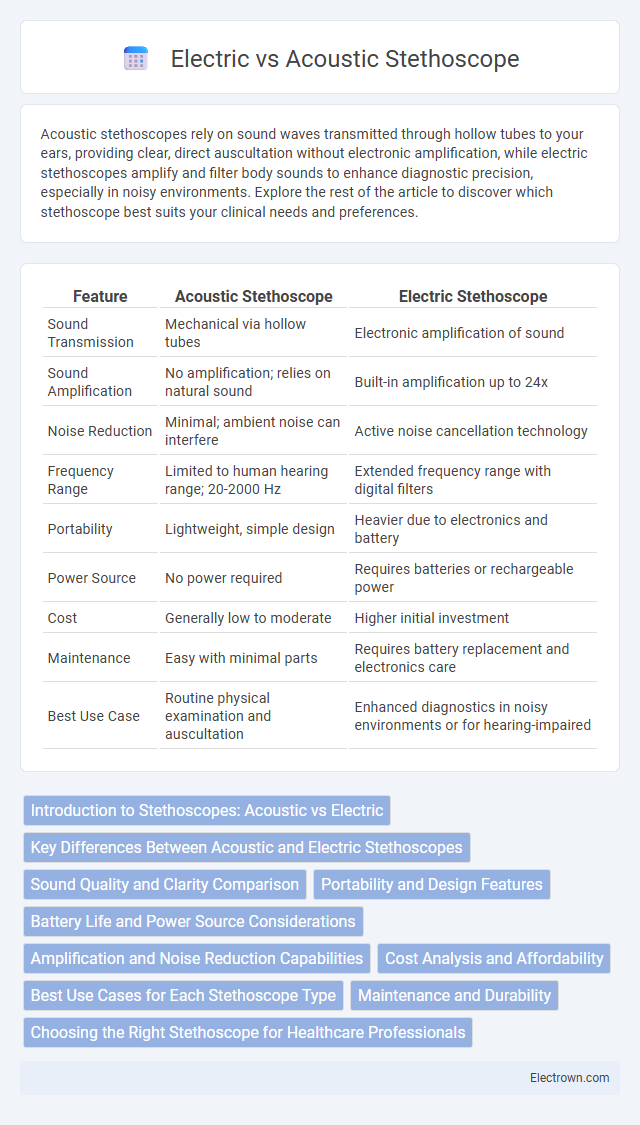
| Feature | Acoustic Stethoscope | Electric Stethoscope |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Transmission | Mechanical via hollow tubes | Electronic amplification of sound |
| Sound Amplification | No amplification; relies on natural sound | Built-in amplification up to 24x |
| Noise Reduction | Minimal; ambient noise can interfere | Active noise cancellation technology |
| Frequency Range | Limited to human hearing range; 20-2000 Hz | Extended frequency range with digital filters |
| Portability | Lightweight, simple design | Heavier due to electronics and battery |
| Power Source | No power required | Requires batteries or rechargeable power |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Easy with minimal parts | Requires battery replacement and electronics care |
| Best Use Case | Routine physical examination and auscultation | Enhanced diagnostics in noisy environments or for hearing-impaired |
Introduction to Stethoscopes: Acoustic vs Electric
Acoustic stethoscopes rely on sound waves transmitted through hollow tubes to amplify heart and lung sounds, offering simplicity and durability favored in traditional clinical settings. Electric stethoscopes use electronic amplification and filtering to enhance sound quality, often including features like noise cancellation and digital recording for more precise diagnostics. Choosing between acoustic and electric stethoscopes depends on clinical needs, environmental noise levels, and the importance of advanced features for auscultation accuracy.
Key Differences Between Acoustic and Electric Stethoscopes
Acoustic stethoscopes rely on sound waves transmitted through hollow tubes to deliver body sounds directly to your ears, offering simplicity and reliability without needing batteries. Electric stethoscopes amplify sound electronically, enhancing faint noises and reducing ambient noise for improved diagnostic accuracy in noisy environments. The primary differences lie in sound amplification, noise reduction capabilities, and power requirements, affecting their suitability depending on clinical needs.
Sound Quality and Clarity Comparison
Acoustic stethoscopes deliver natural, unamplified sounds directly through hollow tubes, providing clear, high-fidelity audio essential for detecting subtle heartbeats and lung anomalies. Electric stethoscopes amplify body sounds electronically, enhancing volume and allowing filtration of ambient noise, which improves clarity in noisy environments. The choice between acoustic and electric models depends on the clinical setting, with electric stethoscopes offering superior audibility for low-frequency sounds and acoustic stethoscopes excelling in delivering authentic sound quality.
Portability and Design Features
Acoustic stethoscopes are lightweight, cordless, and highly portable, making them ideal for quick assessments and routine checkups across various settings. Electric stethoscopes often feature bulkier designs with integrated amplification technology and noise-canceling capabilities, which may reduce portability but enhance sound clarity in noisy environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize easy transport and simplicity or advanced audio features and design innovation.
Battery Life and Power Source Considerations
Acoustic stethoscopes require no batteries, providing unlimited use without power concerns, while electric stethoscopes depend on rechargeable or replaceable batteries that typically last between 20 to 40 hours per charge. Battery life directly impacts the device's reliability in clinical settings, making electric models less ideal for extended use without access to charging. Selecting a stethoscope involves weighing the convenience of acoustic models against the enhanced amplification features of electric versions that necessitate regular battery maintenance.
Amplification and Noise Reduction Capabilities
Electric stethoscopes provide superior amplification compared to acoustic models, enabling healthcare professionals to hear faint heart and lung sounds clearly. Advanced noise reduction technology in electronic stethoscopes minimizes ambient noise, improving diagnostic accuracy in noisy environments. Acoustic stethoscopes rely solely on natural sound transmission, offering limited amplification and minimal noise filtering capabilities.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Acoustic stethoscopes generally offer a lower upfront cost, making them more affordable for students and professionals on a budget. Electric stethoscopes, with advanced amplification and noise reduction features, often come at a higher price point but provide enhanced diagnostic capabilities. When considering cost analysis, acoustic models require minimal maintenance expenses, whereas electric stethoscopes may incur additional costs for batteries and repairs.
Best Use Cases for Each Stethoscope Type
Acoustic stethoscopes excel in routine physical exams, offering clear auscultation of heart, lung, and bowel sounds without electronic interference, making them ideal for general practitioners and medical students. Electric stethoscopes enhance sound amplification and filtration, which is particularly useful in noisy environments, cardiology, and for users with hearing impairments by providing clearer detection of subtle heart murmurs or lung anomalies. Selecting between acoustic and electric stethoscopes depends on the clinical setting, patient needs, and specific diagnostic requirements.
Maintenance and Durability
Acoustic stethoscopes require minimal maintenance, with regular cleaning and occasional diaphragm replacement ensuring durability over years of use. Electric stethoscopes need more frequent care, including battery management and electronic component checks, to maintain optimal performance. Your choice impacts long-term reliability, as acoustic models tend to withstand physical wear better, while electric versions demand careful handling to preserve functionality.
Choosing the Right Stethoscope for Healthcare Professionals
Selecting the right stethoscope is crucial for healthcare professionals seeking accurate diagnoses and patient comfort. Acoustic stethoscopes offer traditional, reliable sound transmission ideal for general assessments, while electric stethoscopes amplify heart and lung sounds, enhancing detection of subtle abnormalities. Consider your clinical needs, such as sound clarity, ambient noise reduction, and patient interaction, to ensure your choice supports optimal medical evaluations.
Acoustic vs Electric Stethoscope Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com