Fiber-optic catheters offer superior image resolution and real-time visualization compared to electrical catheters, enhancing precision in diagnostic and interventional procedures. Discover how choosing the right catheter can impact your outcomes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
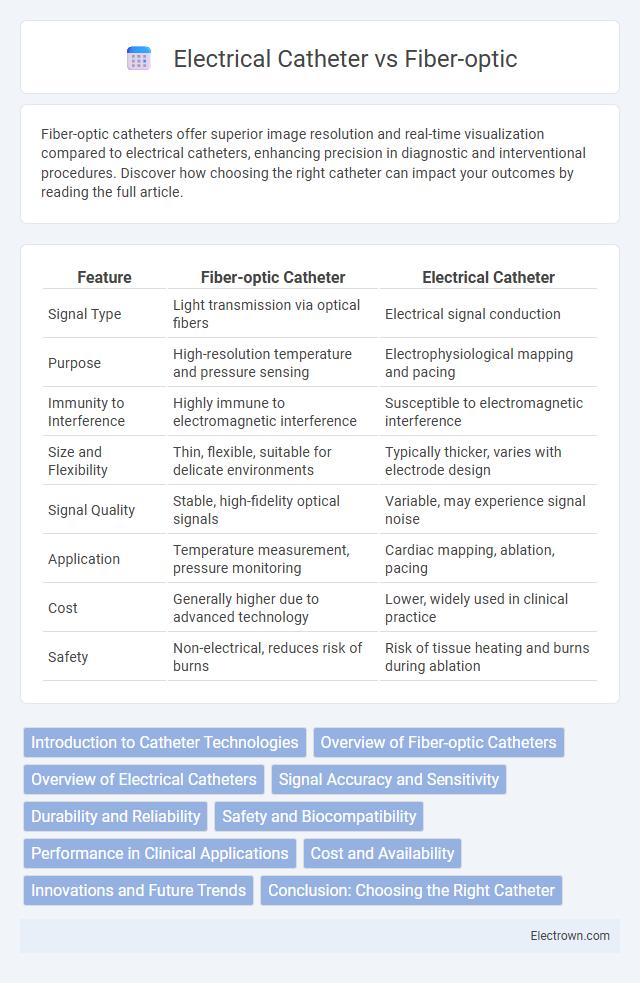
| Feature | Fiber-optic Catheter | Electrical Catheter |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Light transmission via optical fibers | Electrical signal conduction |
| Purpose | High-resolution temperature and pressure sensing | Electrophysiological mapping and pacing |
| Immunity to Interference | Highly immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference |
| Size and Flexibility | Thin, flexible, suitable for delicate environments | Typically thicker, varies with electrode design |
| Signal Quality | Stable, high-fidelity optical signals | Variable, may experience signal noise |
| Application | Temperature measurement, pressure monitoring | Cardiac mapping, ablation, pacing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology | Lower, widely used in clinical practice |
| Safety | Non-electrical, reduces risk of burns | Risk of tissue heating and burns during ablation |
Introduction to Catheter Technologies
Fiber-optic catheters utilize light transmission for precise imaging and temperature sensing, leveraging optical fibers that offer high sensitivity and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Electrical catheters rely on conductive materials to transmit electrical signals for pacing and defibrillation, featuring robust designs optimized for electrical conductivity and biocompatibility. Your choice between these technologies depends on the specific clinical application, with fiber-optic catheters excelling in diagnostic precision and electrical catheters in therapeutic interventions.
Overview of Fiber-optic Catheters
Fiber-optic catheters utilize thin optical fibers to transmit light signals for precise imaging and measurement within the body, offering high-resolution and real-time data. These catheters are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference compared to electrical catheters, enhancing signal accuracy in complex medical environments. Commonly employed in cardiovascular and neurological procedures, fiber-optic technology improves diagnostic capabilities by providing detailed visualization of internal structures.
Overview of Electrical Catheters
Electrical catheters are specialized medical devices used in cardiac electrophysiology to map and ablate abnormal electrical pathways within the heart. These catheters typically consist of multiple electrodes that record intracardiac signals and deliver radiofrequency energy to disrupt arrhythmic tissue. Compared to fiber-optic catheters, electrical catheters provide direct electrical measurements but have limitations in signal resolution and artifact susceptibility.
Signal Accuracy and Sensitivity
Fiber-optic catheters offer superior signal accuracy and sensitivity compared to electrical catheters due to their immunity to electromagnetic interference and ability to detect minute physiological changes. Electrical catheters may experience signal degradation or noise, affecting the precision of measurements in complex environments. Your selection of a fiber-optic catheter can ensure enhanced diagnostic reliability and sensitivity, particularly in high-precision clinical applications.
Durability and Reliability
Fiber-optic catheters offer superior durability and reliability compared to electrical catheters due to their resistance to electromagnetic interference and lower susceptibility to signal degradation over time. Their robust glass or plastic fibers maintain consistent performance in harsh environments, making them ideal for long-term medical monitoring or telecommunications applications. Your choice of catheter can significantly impact the accuracy and longevity of critical diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Safety and Biocompatibility
Fiber-optic catheters offer superior safety and biocompatibility compared to electrical catheters due to their non-conductive nature, reducing risks of electrical interference and tissue damage. These catheters minimize inflammatory responses and demonstrate greater compatibility with bodily tissues, enhancing patient comfort during prolonged use. Your choice of a fiber-optic catheter can significantly improve procedural safety and reduce complications associated with electrical catheter insertion.
Performance in Clinical Applications
Fiber-optic catheters provide superior signal fidelity and immunity to electromagnetic interference, enabling precise real-time monitoring in complex clinical environments. Electrical catheters, while widely used for pacing and ablation, may encounter signal distortion and limited spatial resolution compared to fiber-optic alternatives. Enhanced sensitivity and minimal noise of fiber-optic systems improve diagnostic accuracy in cardiac electrophysiology and neurophysiology applications.
Cost and Availability
Fiber-optic catheters tend to have higher upfront costs due to advanced materials and technology, limiting their availability in some healthcare settings. Electrical catheters are generally more affordable and widely accessible, making them a preferred choice for many hospitals and clinics. Your decision should consider the balance between cost constraints and the specific diagnostic or therapeutic benefits each catheter offers.
Innovations and Future Trends
Fiber-optic catheters incorporate advanced light-based sensing technologies that enable enhanced real-time imaging and precise tissue characterization, surpassing the resolution limits of traditional electrical catheters. Innovations such as integrated multi-modal fiber optics and miniaturized photonic sensors are driving improvements in diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic interventions. Future trends point towards increased integration with AI-driven analytics and wireless data transmission, enabling more efficient, minimally invasive procedures and personalized treatment protocols.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Catheter
Choosing the right catheter depends on the specific clinical application, with fiber-optic catheters offering superior signal clarity and immunity to electromagnetic interference, ideal for precise cardiac monitoring. Electrical catheters remain advantageous for cost-effectiveness and widespread availability in standard electrophysiology procedures. Clinicians must weigh factors such as procedural complexity, accuracy requirements, and budget constraints to optimize patient outcomes.
Fiber-optic vs Electrical Catheter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com