Heart sounds are the audible noises produced by the closing of heart valves during the cardiac cycle, providing crucial information about valve function and blood flow. Understanding the differences between these acoustic signals and the electrical signals recorded by an electrocardiogram can enhance your knowledge of cardiac health; continue reading to explore their roles and diagnostic significance.
Table of Comparison
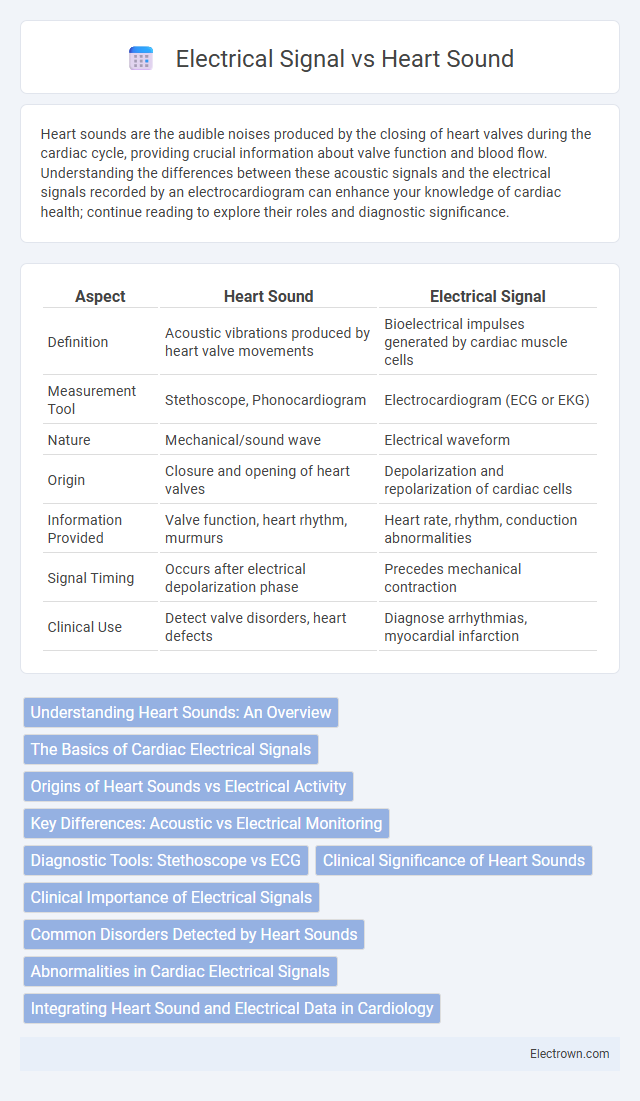
| Aspect | Heart Sound | Electrical Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acoustic vibrations produced by heart valve movements | Bioelectrical impulses generated by cardiac muscle cells |
| Measurement Tool | Stethoscope, Phonocardiogram | Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) |
| Nature | Mechanical/sound wave | Electrical waveform |
| Origin | Closure and opening of heart valves | Depolarization and repolarization of cardiac cells |
| Information Provided | Valve function, heart rhythm, murmurs | Heart rate, rhythm, conduction abnormalities |
| Signal Timing | Occurs after electrical depolarization phase | Precedes mechanical contraction |
| Clinical Use | Detect valve disorders, heart defects | Diagnose arrhythmias, myocardial infarction |
Understanding Heart Sounds: An Overview
Heart sounds are mechanical vibrations produced by the closing of heart valves and blood flow turbulence, which differ from the electrical signals generated by the heart's conduction system that regulate heartbeat rhythm. Understanding heart sounds involves recognizing key components like the "lub-dub" sounds corresponding to systole and diastole, while electrical signals are measured via electrocardiograms (ECGs) to monitor cardiac electrical activity. You can use auscultation alongside ECG readings to gain a comprehensive view of heart function and detect abnormalities effectively.
The Basics of Cardiac Electrical Signals
Cardiac electrical signals originate from the sinoatrial node, generating impulses that propagate through the atria to the atrioventricular node and His-Purkinje system, coordinating heart contractions. These electrical activities produce the heart's rhythm, which can be recorded as an electrocardiogram (ECG) for diagnostic purposes. Unlike heart sounds caused by valve closures, electrical signals reflect the heart's bioelectrical functions vital for maintaining synchronized cardiac cycles.
Origins of Heart Sounds vs Electrical Activity
Heart sounds originate from the mechanical actions of the heart, specifically the closing of valves and the turbulence of blood flow within the chambers. Electrical activity, on the other hand, stems from the generation and propagation of action potentials across the cardiac conduction system, including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, Bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. These electrical signals trigger myocardial contraction, which subsequently produces the audible heart sounds detected during auscultation.
Key Differences: Acoustic vs Electrical Monitoring
Heart sound monitoring captures acoustic signals generated by valve movements and blood flow, providing real-time information about cardiac function through auscultation. Electrical signal monitoring, such as electrocardiography (ECG), records the heart's electrical impulses, enabling detailed analysis of rhythm, rate, and conduction abnormalities. Your choice between acoustic and electrical monitoring depends on whether you need mechanical activity insights or precise electrical cardiac data.
Diagnostic Tools: Stethoscope vs ECG
A stethoscope detects heart sounds by amplifying acoustic vibrations generated by valve closures, providing real-time, non-invasive insights into heart murmurs and rhythm abnormalities. An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart's electrical signals through electrodes on the skin, offering detailed data on cardiac rhythm, conduction pathways, and ischemic events. Your choice between these diagnostic tools depends on whether acoustic evaluation or electrical activity assessment is required for accurate cardiovascular diagnosis.
Clinical Significance of Heart Sounds
Heart sounds provide critical clinical information about valve function and cardiac cycle events, enabling early detection of abnormalities such as murmurs, stenosis, and regurgitation. Unlike electrical signals recorded by ECG that represent myocardial depolarization and repolarization, heart sounds directly reflect mechanical activity and blood flow dynamics within the heart. Accurate auscultation and phonocardiography are essential for diagnosing valvular diseases and monitoring hemodynamic status in cardiovascular care.
Clinical Importance of Electrical Signals
Electrical signals, such as those recorded in an electrocardiogram (ECG), provide crucial clinical insights into the heart's rhythm and electrical conduction system. These signals help diagnose arrhythmias, ischemia, and other cardiac abnormalities that may not be detected through heart sounds alone. Your physician relies on electrical signals to guide precise treatment and monitor heart health effectively.
Common Disorders Detected by Heart Sounds
Heart sounds reveal abnormalities such as murmurs, clicks, and gallops that indicate disorders like valvular stenosis, regurgitation, and heart failure. Unlike electrical signals from an ECG that detect arrhythmias and conduction problems, heart sounds provide critical information about mechanical function and blood flow disturbances. Your healthcare provider uses auscultation to diagnose conditions like mitral valve prolapse, aortic stenosis, and congestive heart failure efficiently.
Abnormalities in Cardiac Electrical Signals
Abnormalities in cardiac electrical signals, such as arrhythmias, are detected through electrocardiograms (ECGs) that record the heart's electrical activity, unlike heart sound analysis which monitors mechanical function. Electrical signal disruptions can indicate issues like atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or heart block, which may not always produce obvious changes in heart sounds. Accurate detection of these electrical irregularities is crucial for diagnosing and managing cardiac conditions and preventing complications like stroke or sudden cardiac arrest.
Integrating Heart Sound and Electrical Data in Cardiology
Integrating heart sound and electrical signal data enhances diagnostic accuracy in cardiology by combining phonocardiogram (PCG) analysis with electrocardiogram (ECG) readings. This multimodal approach enables detailed assessment of cardiac function, identifying abnormalities such as arrhythmias and valvular defects more reliably than isolated methods. Machine learning algorithms applied to synchronized heart sound and electrical signals improve early detection and monitoring of cardiovascular diseases.
Heart Sound vs Electrical Signal Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com