Non-invasive glucose meters measure blood sugar levels without piercing the skin, using technologies such as infrared light or electromagnetic sensors, offering pain-free and convenient monitoring. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice between non-invasive and invasive options impacts accuracy, cost, and daily diabetes management.
Table of Comparison
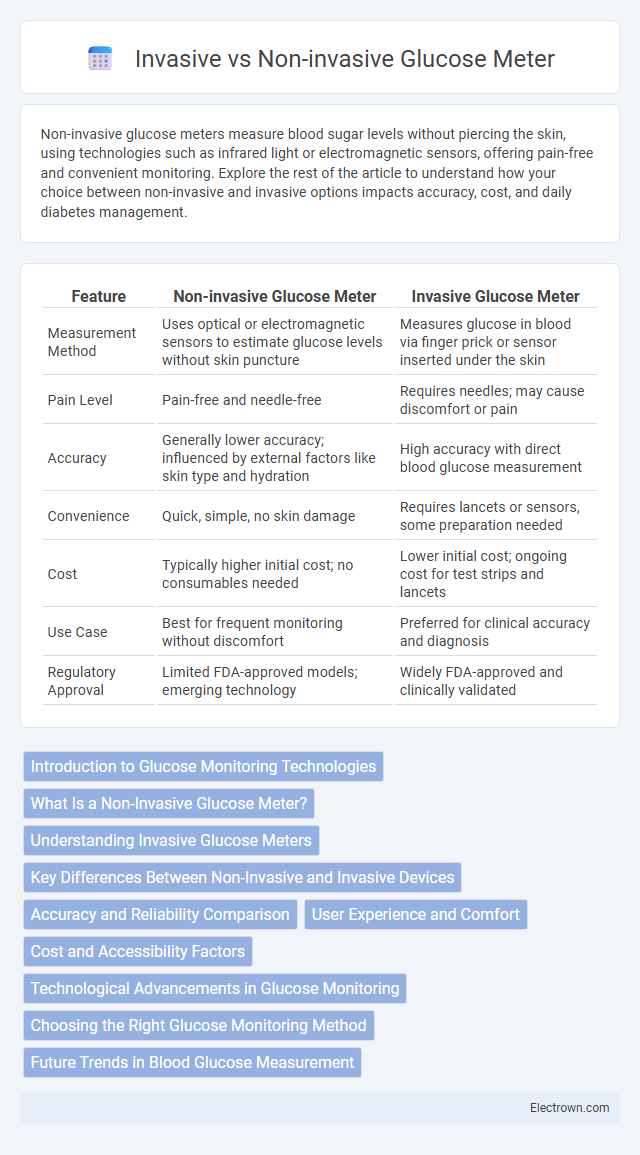
| Feature | Non-invasive Glucose Meter | Invasive Glucose Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Uses optical or electromagnetic sensors to estimate glucose levels without skin puncture | Measures glucose in blood via finger prick or sensor inserted under the skin |
| Pain Level | Pain-free and needle-free | Requires needles; may cause discomfort or pain |
| Accuracy | Generally lower accuracy; influenced by external factors like skin type and hydration | High accuracy with direct blood glucose measurement |
| Convenience | Quick, simple, no skin damage | Requires lancets or sensors, some preparation needed |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost; no consumables needed | Lower initial cost; ongoing cost for test strips and lancets |
| Use Case | Best for frequent monitoring without discomfort | Preferred for clinical accuracy and diagnosis |
| Regulatory Approval | Limited FDA-approved models; emerging technology | Widely FDA-approved and clinically validated |
Introduction to Glucose Monitoring Technologies
Glucose monitoring technologies encompass both non-invasive and invasive methods designed to measure blood sugar levels accurately. Non-invasive glucose meters use sensors to detect glucose through the skin or interstitial fluid, eliminating the need for finger pricks. Invasive glucose meters require blood samples, typically obtained via a fingerstick, providing direct and precise glucose readings essential for managing diabetes effectively.
What Is a Non-Invasive Glucose Meter?
A non-invasive glucose meter measures blood sugar levels without requiring needles or blood samples, using techniques like optical sensors or electromagnetic waves. This technology reduces discomfort, risk of infection, and inconvenience compared to invasive meters that involve finger-pricking. Your choice of a non-invasive glucose meter can improve daily diabetes management by offering pain-free and continuous monitoring options.
Understanding Invasive Glucose Meters
Invasive glucose meters measure blood sugar levels by analyzing a small blood sample obtained through a finger prick, providing highly accurate and real-time data essential for diabetes management. These devices rely on enzymatic reactions with glucose oxidase or glucose dehydrogenase to convert blood glucose into an electrical signal, ensuring precise quantification. Despite the discomfort and risk of infection from repeated skin penetration, invasive meters remain the clinical gold standard due to their reliability and rapid response times.
Key Differences Between Non-Invasive and Invasive Devices
Non-invasive glucose meters measure blood sugar levels through the skin using optical or electromagnetic sensors, eliminating the need for finger pricks, while invasive devices require blood samples via lancets for accurate glucose readings. Non-invasive devices offer pain-free testing and convenience but may have slightly lower accuracy compared to invasive meters, which remain the gold standard for precise monitoring. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the optimal glucose meter tailored to your lifestyle and glucose management needs.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Invasive glucose meters, which rely on blood samples, provide higher accuracy and reliability with precise glucose level readings essential for diabetes management. Non-invasive glucose meters, using methods like infrared spectroscopy or electromagnetic sensors, offer convenience but often face challenges in consistent accuracy due to factors like skin variability and hydration levels. Recent advancements in sensor technology aim to improve non-invasive meter reliability, yet invasive devices remain the gold standard for clinically dependable glucose monitoring.
User Experience and Comfort
Non-invasive glucose meters enhance user experience by eliminating pain and reducing skin irritation associated with frequent finger pricks, offering a comfortable and convenient monitoring method. Invasive glucose meters, while highly accurate, often cause discomfort and can lead to calluses or infections due to repeated needle use. Your choice between these devices can significantly impact daily comfort and ease of glucose tracking.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Non-invasive glucose meters often have a higher upfront cost due to advanced technology but offer greater accessibility by eliminating the need for frequent consumables like test strips. Invasive glucose meters typically cost less initially but incur ongoing expenses for lancets and strips, which can add up over time, impacting affordability. Your choice between the two depends on balancing budget constraints with the convenience and ease of regular blood sugar monitoring.
Technological Advancements in Glucose Monitoring
Technological advancements in glucose monitoring have led to the development of both non-invasive and invasive glucose meters, each with distinct benefits. Non-invasive glucose meters utilize optical sensors, electromagnetic technology, or spectroscopy to measure blood glucose levels without skin penetration, offering pain-free, continuous monitoring and enhanced patient compliance. In contrast, invasive glucose meters rely on electrochemical sensors with blood samples obtained via finger pricking, providing highly accurate and real-time data crucial for critical care and diabetes management.
Choosing the Right Glucose Monitoring Method
Choosing the right glucose monitoring method depends on your lifestyle, accuracy needs, and comfort preferences. Non-invasive glucose meters offer pain-free, continuous monitoring without blood samples, ideal for users seeking convenience and minimal discomfort. Invasive glucose meters provide highly accurate and reliable blood glucose readings through finger pricks, making them suitable for precise diabetes management and critical medical situations.
Future Trends in Blood Glucose Measurement
Non-invasive glucose meters employ optical sensors and spectroscopy to measure blood sugar levels without skin penetration, offering painless and continuous monitoring that enhances user comfort and adherence. Invasive meters, despite their accuracy, face limitations due to finger-pricking discomfort and infection risks, driving innovation toward minimally invasive sensors using microneedles or implantable devices. Future trends emphasize integration of wearable technology, AI-driven predictive analytics, and real-time data sharing with healthcare providers to optimize diabetes management and personalize treatment protocols.
Non-invasive vs Invasive Glucose Meter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com