EMG measures electrical activity of muscles, while ENG records electrical signals from nerves to evaluate nerve function and detect abnormalities. Understanding the differences between EMG and ENG can help you make informed decisions about diagnosing neuromuscular conditions; read on to explore their distinct purposes, procedures, and clinical applications.
Table of Comparison
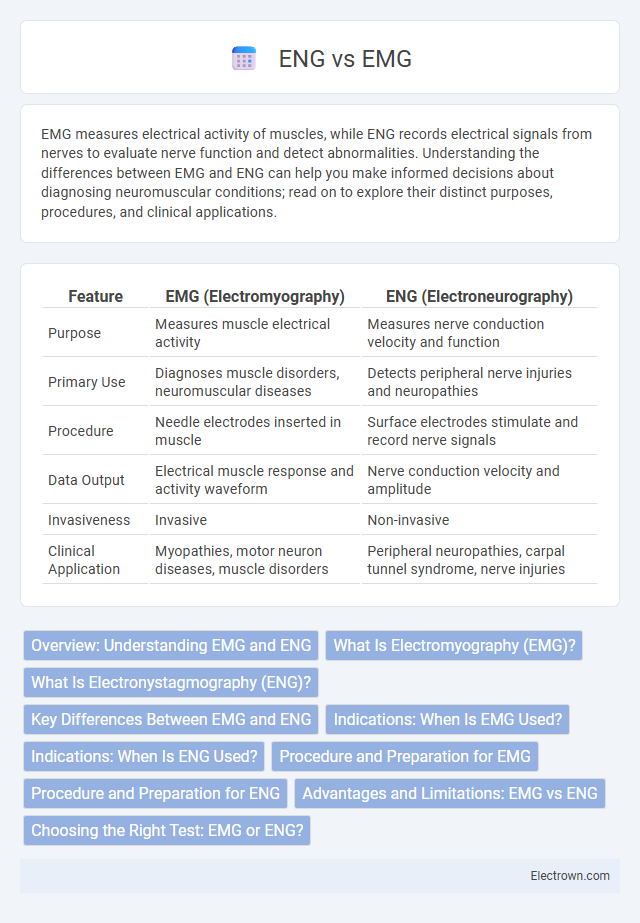
| Feature | EMG (Electromyography) | ENG (Electroneurography) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures muscle electrical activity | Measures nerve conduction velocity and function |
| Primary Use | Diagnoses muscle disorders, neuromuscular diseases | Detects peripheral nerve injuries and neuropathies |
| Procedure | Needle electrodes inserted in muscle | Surface electrodes stimulate and record nerve signals |
| Data Output | Electrical muscle response and activity waveform | Nerve conduction velocity and amplitude |
| Invasiveness | Invasive | Non-invasive |
| Clinical Application | Myopathies, motor neuron diseases, muscle disorders | Peripheral neuropathies, carpal tunnel syndrome, nerve injuries |
Overview: Understanding EMG and ENG
Electromyography (EMG) measures electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles to assess muscle function and diagnose neuromuscular disorders. Electronegoneurography (ENG) evaluates nerve conduction velocity and amplitude by recording electrical signals along peripheral nerves, aiding in the diagnosis of neuropathies. Both EMG and ENG provide complementary insights into the integrity of the neuromuscular system through distinct but related electrophysiological assessments.
What Is Electromyography (EMG)?
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure that measures the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles to assess their health and function. It involves inserting fine needle electrodes into muscle tissue to detect electrical potentials generated during muscle contraction and at rest. This technique helps diagnose neuromuscular disorders such as muscular dystrophy, neuropathies, and myopathies by analyzing muscle response to nerve stimulation.
What Is Electronystagmography (ENG)?
Electronystagmography (ENG) is a diagnostic test that measures involuntary eye movements called nystagmus to assess the function of the vestibular system and diagnose balance disorders. ENG records eye muscle activity using electrodes placed around the eyes, providing insights into inner ear and central nervous system issues. Understanding ENG can help your healthcare provider evaluate dizziness, vertigo, or imbalance symptoms accurately.
Key Differences Between EMG and ENG
EMG (Electromyography) measures electrical activity in skeletal muscles to evaluate muscle health and nerve function, while ENG (Electroneurography) assesses the conduction velocity of peripheral nerves to diagnose neuropathies. EMG records muscle response to nerve stimulation, detecting abnormalities like muscle dystrophies or nerve dysfunction, whereas ENG quantifies nerve impulse speed and amplitude to identify demyelinating or axonal neuropathies. Both tests complement each other in neuromuscular diagnosis, but EMG focuses on muscle electrical activity, and ENG emphasizes peripheral nerve conduction properties.
Indications: When Is EMG Used?
EMG is primarily used to diagnose disorders affecting muscle tissue and the nerves controlling them, such as muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and peripheral neuropathies. Your physician may request an EMG when you experience unexplained muscle weakness, twitching, or numbness to evaluate the electrical activity of muscles during contraction and rest. This test helps distinguish between muscle disorders and nerve dysfunction, guiding accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Indications: When Is ENG Used?
Electroneurography (ENG) is primarily indicated for assessing peripheral nerve function by measuring nerve conduction velocity and amplitude, often used in cases of suspected nerve injuries, neuropathies, or entrapment syndromes like carpal tunnel syndrome. ENG is preferred when there's a need to localize nerve lesions and differentiate between demyelinating and axonal neuropathies. Compared to electromyography (EMG), which evaluates muscle electrical activity, ENG specifically diagnoses nerve conduction deficits, making it essential for precise neuromuscular disorder identification.
Procedure and Preparation for EMG
EMG (electromyography) involves inserting fine needles into specific muscles to measure electrical activity, requiring minimal preparation such as avoiding lotions and informing your doctor about medications or infections. ENG (electroneurography) tests nerve conduction by stimulating nerves with small electrical pulses while surface electrodes record responses, typically needing little to no preparation. Both procedures are performed in a medical setting under professional supervision to ensure accurate diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders.
Procedure and Preparation for ENG
Electroneurography (ENG) involves stimulating peripheral nerves with small electrical pulses and recording the resulting compound muscle action potentials to assess nerve conduction velocity and latency. Preparation for ENG typically requires avoiding caffeine and medications that affect nerve function, ensuring the skin is clean and free of lotions where electrodes will be placed. During the procedure, surface electrodes are strategically positioned along the nerve pathway, and minimal discomfort is experienced while the nerve responses are recorded and analyzed.
Advantages and Limitations: EMG vs ENG
Electromyography (EMG) offers precise measurement of muscle electrical activity, making it ideal for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders, while electroneurography (ENG) excels in assessing peripheral nerve conduction velocity and latency. EMG's advantage lies in detecting muscle dysfunction directly, but it is limited by discomfort and inability to evaluate sensory nerve function, whereas ENG is non-invasive and provides clear data on nerve integrity but cannot measure muscle response. Your choice between EMG and ENG depends on whether the diagnostic goal is to evaluate muscle activity or nerve conduction, balancing invasiveness with the specific clinical information required.
Choosing the Right Test: EMG or ENG?
EMG (Electromyography) measures electrical activity in muscles to diagnose neuromuscular disorders, while ENG (Electroneurography) evaluates nerve conduction velocity to detect peripheral nerve damage. Choosing the right test depends on symptoms: EMG is preferred for assessing muscle abnormalities and motor neuron diseases, whereas ENG is ideal for identifying nerve compression or demyelinating neuropathies. Clinical presentation and suspected pathology guide physicians in selecting EMG or ENG for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
EMG vs ENG Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com