A LISN (Line Impedance Stabilization Network) is designed to provide a consistent impedance and isolate measurement equipment from noise on power lines, while an isolation transformer primarily isolates electrical devices to prevent ground loops and interference. Understanding the differences between these devices is crucial for optimizing your EMC testing setup--read on to explore their distinct roles and applications.
Table of Comparison
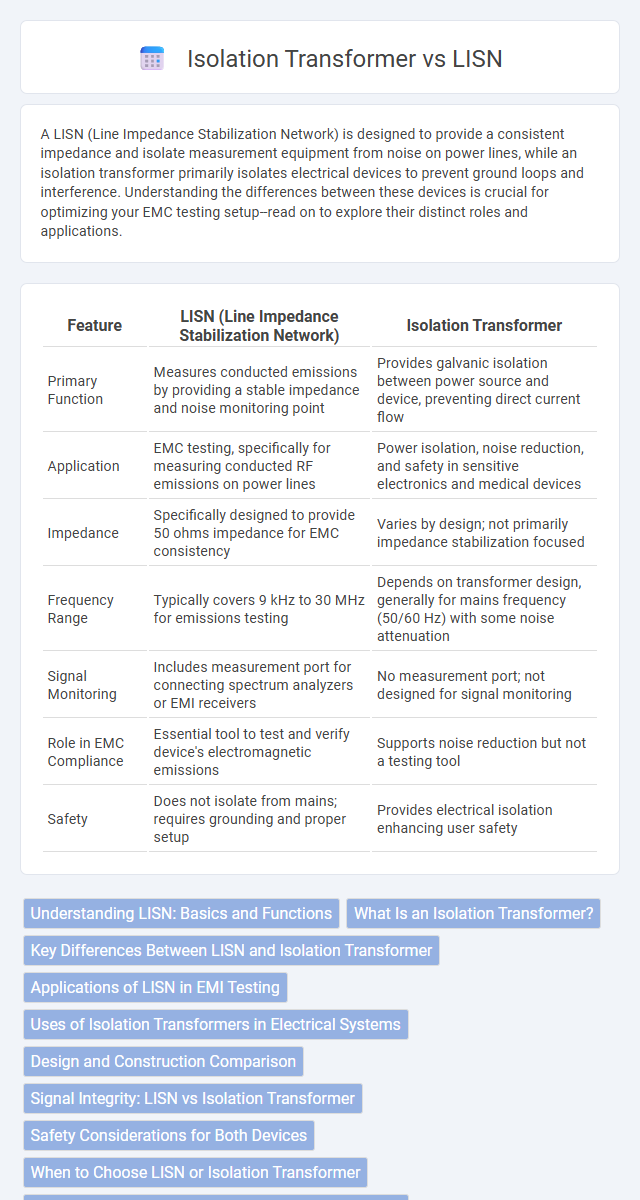
| Feature | LISN (Line Impedance Stabilization Network) | Isolation Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures conducted emissions by providing a stable impedance and noise monitoring point | Provides galvanic isolation between power source and device, preventing direct current flow |
| Application | EMC testing, specifically for measuring conducted RF emissions on power lines | Power isolation, noise reduction, and safety in sensitive electronics and medical devices |
| Impedance | Specifically designed to provide 50 ohms impedance for EMC consistency | Varies by design; not primarily impedance stabilization focused |
| Frequency Range | Typically covers 9 kHz to 30 MHz for emissions testing | Depends on transformer design, generally for mains frequency (50/60 Hz) with some noise attenuation |
| Signal Monitoring | Includes measurement port for connecting spectrum analyzers or EMI receivers | No measurement port; not designed for signal monitoring |
| Role in EMC Compliance | Essential tool to test and verify device's electromagnetic emissions | Supports noise reduction but not a testing tool |
| Safety | Does not isolate from mains; requires grounding and proper setup | Provides electrical isolation enhancing user safety |
Understanding LISN: Basics and Functions
A Line Impedance Stabilization Network (LISN) provides a consistent impedance for power line emissions testing, ensuring accurate and repeatable measurements of conducted electromagnetic interference (EMI) in compliance with regulatory standards like CISPR and FCC. It isolates the device under test (DUT) from power line fluctuations and external noise by offering a stable 50-ohm impedance while allowing measurement instruments to capture high-frequency noise signals. Unlike isolation transformers that primarily prevent ground loops and voltage spikes, LISNs serve a critical role in EMI testing environments by both stabilizing line impedance and facilitating noise measurement for proper electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) analysis.
What Is an Isolation Transformer?
An isolation transformer is an electrical device designed to transfer power from a source to a load while isolating the powered device from the power source for safety and noise reduction. It consists of two magnetically coupled windings that provide galvanic isolation, minimizing the risk of electric shock and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Isolation transformers are crucial in sensitive electronic testing environments and are often compared with Line Impedance Stabilization Networks (LISNs) for their roles in managing electrical noise and ensuring equipment protection.
Key Differences Between LISN and Isolation Transformer
LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) and isolation transformers serve distinct purposes in electrical testing and power systems. LISNs are designed to provide a consistent impedance for EMI measurement and to separate noise signals for accurate radio frequency interference (RFI) detection, while isolation transformers primarily focus on isolating the device under test from the power source to prevent ground loops and enhance safety. The key differences lie in their functions: LISNs enable precise EMI measurement by stabilizing line impedance and filtering noise, whereas isolation transformers ensure electrical isolation and noise reduction without impedance stabilization.
Applications of LISN in EMI Testing
LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) are essential in EMI testing to measure conducted emissions from electronic devices by providing a stable impedance and isolating the device from external power source noise. They are widely used in compliance testing for regulatory standards such as CISPR, FCC, and MIL-STD to ensure that your product meets electromagnetic interference limits. Unlike isolation transformers that primarily serve to isolate equipment for safety and noise reduction, LISNs specifically facilitate accurate and repeatable EMI measurements.
Uses of Isolation Transformers in Electrical Systems
Isolation transformers are essential in electrical systems for providing galvanic isolation, which enhances safety by preventing direct current flow between circuits while allowing AC signals to pass. They are commonly used for noise reduction, protecting sensitive equipment from voltage spikes, and breaking ground loops in audio and communication setups. Your electrical installations benefit from improved signal integrity and reduced risk of electric shock when isolation transformers are properly employed.
Design and Construction Comparison
LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) feature precise impedance elements and filtering capacitors designed to measure conducted emissions in compliance with EMC standards, ensuring consistent impedance across a wide frequency range. Isolation transformers consist of wound coils with magnetic cores that provide galvanic isolation and voltage transformation while minimizing high-frequency noise through careful shielding and core material selection. The LISN's focus on impedance stabilization contrasts with the isolation transformer's emphasis on electrical isolation and noise attenuation, resulting in distinct design priorities and construction techniques.
Signal Integrity: LISN vs Isolation Transformer
LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) provide a stable and defined impedance for accurate measurement of conducted emissions, ensuring signal integrity during EMC testing by isolating noise from the power source. Isolation transformers improve signal integrity by electrically separating equipment from the power source, reducing common-mode noise and preventing ground loops, but they do not offer impedance stabilization like LISNs. For precise conducted emission testing, LISNs are essential due to their standardized impedance characteristics, whereas isolation transformers primarily enhance overall noise reduction and equipment protection.
Safety Considerations for Both Devices
LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) are designed with built-in isolation transformers to protect test equipment from high-voltage spikes and ensure accurate EMI measurements, enhancing operator safety by minimizing electrical shock risks. Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation between input and output, preventing dangerous ground currents and reducing the risk of electrical hazards during maintenance or testing. To ensure your safety, always verify that the isolation transformer or LISN complies with relevant safety standards such as IEC 61010 or UL certifications before use.
When to Choose LISN or Isolation Transformer
Choose a LISN (Line Impedance Stabilization Network) when measuring conducted emissions and performing EMC testing to ensure consistent and repeatable impedance on the power line. Opt for an Isolation Transformer when the primary goal is to isolate the device under test (DUT) from the main power source to prevent electrical noise, enhance safety, and protect the test setup from ground loops during testing procedures. Selecting between LISN and Isolation Transformer depends on whether emission measurement precision or electrical isolation and noise suppression is the priority.
Summary: Selecting the Right Device for Your Needs
Choosing between a LISN (Line Impedance Stabilization Network) and an isolation transformer depends on your specific electromagnetic compatibility testing requirements and power isolation needs. A LISN is specialized for measuring conducted emissions by providing a defined impedance and isolating the power source noise, while an isolation transformer primarily offers electrical isolation to prevent ground loops and ensure safety. Understanding your device's testing objectives and electrical environment helps you select the right equipment to ensure accurate measurements and protect your systems effectively.
LISN vs Isolation Transformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com