Needle biopsy involves extracting tissue samples using a thin needle, providing precise histological analysis for diagnosing various conditions, while optical biopsy uses advanced imaging techniques to assess tissue in real time without physical removal, offering a less invasive alternative. Explore the rest of this article to understand which method best suits your diagnostic needs and the latest advancements in biopsy technology.
Table of Comparison
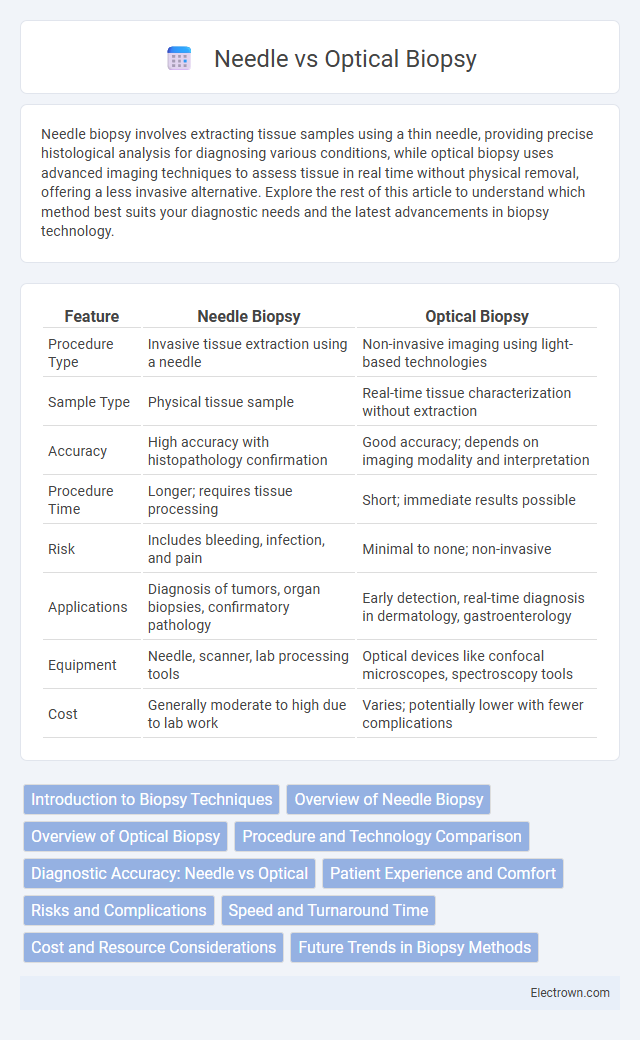
| Feature | Needle Biopsy | Optical Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Invasive tissue extraction using a needle | Non-invasive imaging using light-based technologies |
| Sample Type | Physical tissue sample | Real-time tissue characterization without extraction |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with histopathology confirmation | Good accuracy; depends on imaging modality and interpretation |
| Procedure Time | Longer; requires tissue processing | Short; immediate results possible |
| Risk | Includes bleeding, infection, and pain | Minimal to none; non-invasive |
| Applications | Diagnosis of tumors, organ biopsies, confirmatory pathology | Early detection, real-time diagnosis in dermatology, gastroenterology |
| Equipment | Needle, scanner, lab processing tools | Optical devices like confocal microscopes, spectroscopy tools |
| Cost | Generally moderate to high due to lab work | Varies; potentially lower with fewer complications |
Introduction to Biopsy Techniques
Needle biopsy and optical biopsy are two advanced techniques used to obtain tissue samples for diagnostic purposes, each offering distinct methods and benefits. Needle biopsy involves extracting tissue using a fine or core needle, providing precise samples with minimal invasiveness, while optical biopsy uses imaging technologies such as endoscopy or spectroscopy to assess tissue characteristics in real-time without physical removal. Understanding these methods helps you select the appropriate technique based on the clinical context and diagnostic requirements.
Overview of Needle Biopsy
Needle biopsy involves extracting a small tissue sample using a fine or core needle, offering a minimally invasive approach to diagnose abnormalities such as tumors or lesions. This procedure is guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scans to ensure accurate targeting of the suspicious area. Your healthcare provider may recommend a needle biopsy for quick, precise results with minimal discomfort and reduced recovery time compared to surgical options.
Overview of Optical Biopsy
Optical biopsy uses advanced imaging technologies such as confocal laser endomicroscopy and optical coherence tomography to provide real-time, high-resolution tissue analysis without physical sample removal. This method enhances diagnostic accuracy by enabling immediate visualization of cellular and subcellular structures, reducing the need for invasive needle biopsy procedures. Optical biopsy is particularly valuable in identifying malignancies in epithelial tissues, improving patient outcomes through quicker diagnosis and treatment planning.
Procedure and Technology Comparison
Needle biopsy involves extracting tissue samples using a fine or core needle guided by imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT, or MRI, enabling minimally invasive access to suspicious lesions. Optical biopsy employs advanced imaging technologies like confocal laser endomicroscopy or optical coherence tomography to visualize cellular structures in vivo without removing tissue, offering real-time microscopic analysis. The key procedural distinction lies in needle biopsy's physical tissue extraction versus optical biopsy's non-invasive, image-based diagnosis, with optical biopsy providing immediate results but currently limited by penetration depth and tissue specificity.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Needle vs Optical
Needle biopsy provides a high diagnostic accuracy by extracting tissue samples for histopathological analysis, making it reliable for identifying malignancies with sensitivity rates often exceeding 85%. Optical biopsy employs advanced imaging techniques such as confocal laser endomicroscopy and optical coherence tomography to assess cellular structures in real-time, achieving diagnostic accuracies comparable to traditional biopsies, often above 80% in specific clinical settings. The choice between needle and optical biopsy depends on the lesion location, required diagnostic precision, and the need for immediate results, with optical methods offering non-invasive evaluation and needle biopsies providing definitive tissue diagnosis.
Patient Experience and Comfort
Needle biopsies often cause mild discomfort and localized pain due to the extraction of tissue through a small incision, with patients typically experiencing brief recovery times. Optical biopsies are non-invasive, using advanced imaging technology to assess tissue in real-time, resulting in minimal or no pain and immediate results, enhancing patient comfort. Studies indicate higher patient satisfaction rates with optical biopsies because they reduce anxiety associated with invasive procedures and limit post-procedure complications.
Risks and Complications
Needle biopsy risks include bleeding, infection, and potential damage to surrounding tissues due to its invasive nature. Optical biopsy, being a non-invasive technique, significantly reduces complications such as pain, infection, and recovery time. Your choice between these methods should consider the balance between diagnostic accuracy and the level of procedural risk you can tolerate.
Speed and Turnaround Time
Needle biopsies offer rapid sample collection, often providing preliminary results within 24 to 48 hours, making them ideal for quick diagnostic decisions. Optical biopsies utilize advanced imaging technologies like confocal microscopy or Raman spectroscopy to deliver near-real-time tissue analysis without physical extraction, significantly reducing turnaround times. Both methods enhance clinical workflow efficiency, but optical biopsies excel in speed by eliminating the need for laboratory processing and histopathological examination.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Needle biopsies generally incur lower costs and require fewer resources compared to optical biopsies, making them a more accessible option in many healthcare settings. Optical biopsies involve advanced imaging technology that demands significant investment in equipment and specialized training. Cost-effectiveness analyses often favor needle biopsy for initial diagnostics, especially in resource-limited environments.
Future Trends in Biopsy Methods
Emerging trends in biopsy methods emphasize minimally invasive techniques like needle biopsies enhanced with real-time imaging, enabling precise tissue sampling with reduced patient discomfort and faster recovery. Optical biopsies, utilizing technologies such as confocal laser endomicroscopy and Raman spectroscopy, offer non-destructive, in vivo cellular analysis, potentially eliminating the need for traditional tissue extraction. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in both needle and optical biopsy platforms is advancing diagnostic accuracy and enabling personalized treatment planning.
Needle vs Optical Biopsy Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com