AC and DC defibrillators differ primarily in the type of current they deliver to restore normal heart rhythm, with DC defibrillators using a short, controlled pulse of direct current to reduce heart muscle damage and improve patient outcomes. Understanding these differences can help You make informed choices about defibrillation technology--read on to learn more about how each type impacts treatment effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
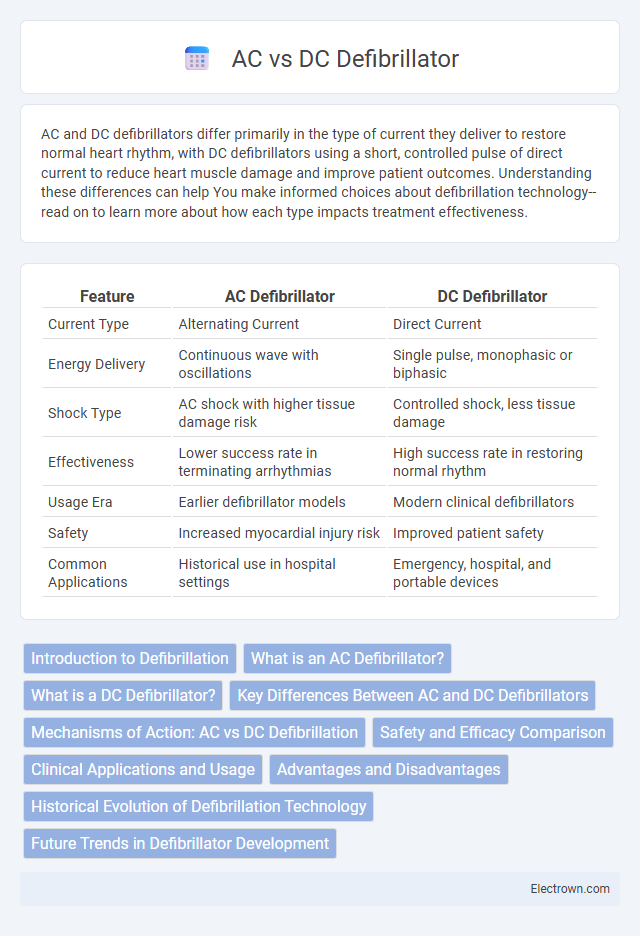
| Feature | AC Defibrillator | DC Defibrillator |
|---|---|---|
| Current Type | Alternating Current | Direct Current |
| Energy Delivery | Continuous wave with oscillations | Single pulse, monophasic or biphasic |
| Shock Type | AC shock with higher tissue damage risk | Controlled shock, less tissue damage |
| Effectiveness | Lower success rate in terminating arrhythmias | High success rate in restoring normal rhythm |
| Usage Era | Earlier defibrillator models | Modern clinical defibrillators |
| Safety | Increased myocardial injury risk | Improved patient safety |
| Common Applications | Historical use in hospital settings | Emergency, hospital, and portable devices |
Introduction to Defibrillation
Defibrillation is a critical medical procedure used to restore normal heart rhythm by delivering an electrical shock to the heart during life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. AC defibrillators deliver alternating current shocks, which were largely replaced by DC defibrillators due to the latter's ability to provide safer, more effective monophasic or biphasic waveforms that minimize myocardial damage. Modern DC defibrillators use precise energy levels measured in joules to ensure optimal electrical delivery for successful resuscitation without causing excessive cardiac tissue injury.
What is an AC Defibrillator?
An AC defibrillator delivers alternating current to restore normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest, typically using higher voltage and longer pulse durations compared to modern devices. These defibrillators operate by passing a sinusoidal current through the chest, which can cause more tissue damage and discomfort. Due to these drawbacks, AC defibrillators have largely been replaced by DC defibrillators that provide safer, more controlled monophasic or biphasic shocks.
What is a DC Defibrillator?
A DC defibrillator delivers a controlled direct current shock to restore normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest. Unlike AC defibrillators, which use alternating current, DC defibrillators provide a single, high-energy pulse that effectively depolarizes the heart muscle. Your medical team relies on DC defibrillators for their precision, safety, and improved outcomes in emergency cardiac care.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Defibrillators
AC defibrillators deliver alternating current, causing continuous energy oscillation, which can increase the risk of myocardial damage and arrhythmias. DC defibrillators use a direct current pulse, providing a controlled, high-energy shock that efficiently restores normal heart rhythm with reduced cardiac injury. Your choice between AC and DC defibrillators impacts treatment effectiveness, patient safety, and overall clinical outcomes.
Mechanisms of Action: AC vs DC Defibrillation
AC defibrillation uses alternating current to deliver continuous electrical energy, causing prolonged depolarization and potential myocardial damage due to sustained electrical exposure. DC defibrillation delivers a brief, high-energy electrical shock that depolarizes a critical mass of cardiac cells simultaneously, allowing the natural pacemaker to restore normal heart rhythm efficiently. DC defibrillators are preferred due to their precise control over shock duration and energy, reducing myocardial injury compared to the continuous current of AC devices.
Safety and Efficacy Comparison
DC defibrillators deliver controlled, high-energy shocks that effectively restore normal heart rhythm with lower risk of myocardial damage, making them safer and more efficacious than AC defibrillators. AC defibrillators use alternating current, which can cause continuous muscle contractions and increase the likelihood of cardiac injury. Your choice of a DC defibrillator ensures better patient outcomes due to its precise energy delivery and reduced complication rates.
Clinical Applications and Usage
DC defibrillators are predominantly used in clinical settings due to their ability to deliver controlled, high-energy shocks that effectively terminate life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. AC defibrillators, once common, are now largely obsolete because their continuous alternating current can cause myocardial damage and are less precise in energy delivery. Modern emergency response protocols and advanced cardiac life support guidelines recommend DC defibrillation for improved patient outcomes during cardiac arrest situations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
AC defibrillators provide a consistent electric current capable of depolarizing the heart muscle but carry a higher risk of causing myocardial damage or arrhythmias due to prolonged energy delivery. DC defibrillators deliver a brief, high-energy shock that effectively restores normal heart rhythm with less tissue damage, making them the preferred choice in modern cardiac care. However, DC devices can be more expensive and require precise energy calibration compared to simpler AC models.
Historical Evolution of Defibrillation Technology
The historical evolution of defibrillation technology began with the introduction of alternating current (AC) defibrillators in the 1930s, which utilized high-voltage AC shocks to restore normal heart rhythm but carried risks of myocardial damage. The development of direct current (DC) defibrillators in the 1960s marked a significant advancement, providing more controlled and safer biphasic or monophasic shocks that increased survival rates from cardiac arrest. Modern DC defibrillators incorporate sophisticated waveform technology, minimizing energy delivery while maximizing defibrillation efficacy and patient safety.
Future Trends in Defibrillator Development
Emerging trends in defibrillator technology emphasize enhanced energy efficiency and precise waveform modulation to improve patient outcomes in both AC and DC devices. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms enables real-time rhythm analysis and personalized shock delivery, increasing the success rate of cardiac resuscitation. Wireless connectivity and miniaturization facilitate remote monitoring and portability, transforming defibrillator accessibility in emergency settings and at-home care.
AC vs DC Defibrillator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com