Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance in a smaller size with better stability, while ceramic capacitors provide excellent high-frequency performance and lower cost. Discover which capacitor type best fits Your specific electronic applications in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
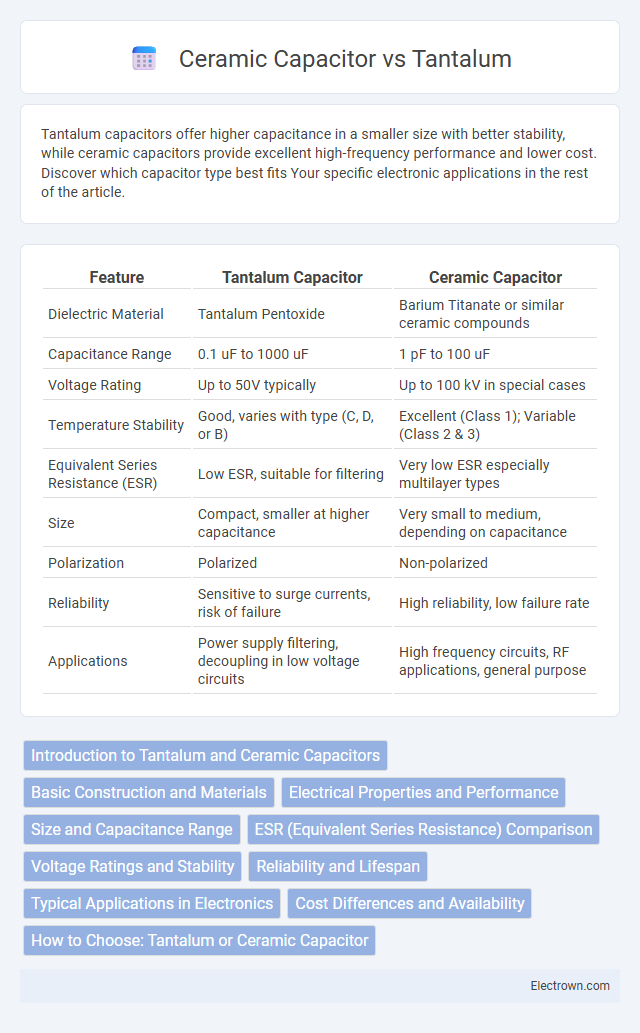
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Tantalum Pentoxide | Barium Titanate or similar ceramic compounds |
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 1000 uF | 1 pF to 100 uF |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 50V typically | Up to 100 kV in special cases |
| Temperature Stability | Good, varies with type (C, D, or B) | Excellent (Class 1); Variable (Class 2 & 3) |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Low ESR, suitable for filtering | Very low ESR especially multilayer types |
| Size | Compact, smaller at higher capacitance | Very small to medium, depending on capacitance |
| Polarization | Polarized | Non-polarized |
| Reliability | Sensitive to surge currents, risk of failure | High reliability, low failure rate |
| Applications | Power supply filtering, decoupling in low voltage circuits | High frequency circuits, RF applications, general purpose |
Introduction to Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and excellent frequency response, making them suitable for compact, high-performance electronic circuits. Ceramic capacitors provide low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and high stability over a wide temperature range, ideal for filtering and decoupling applications. Both types serve critical roles in modern electronics, with material composition and electrical characteristics defining their specific use cases.
Basic Construction and Materials
Tantalum capacitors consist of a tantalum metal anode coated with an oxide layer that acts as the dielectric, housed within a conductive cathode and encased in epoxy resin, offering high capacitance in a compact form. Ceramic capacitors use a ceramic material as the dielectric sandwiched between metal electrodes, resulting in a multilayer structure that provides stability and low losses at high frequencies. Understanding these fundamental construction differences helps you select the right capacitor for your application's electrical and environmental requirements.
Electrical Properties and Performance
Tantalum capacitors exhibit high capacitance per volume and stable electrical performance, making them ideal for applications requiring low ESR and reliable long-term operation. Ceramic capacitors offer low inductance and excellent high-frequency performance, with superior temperature and voltage stability across a broad range of dielectric classes such as X7R and C0G. While tantalum capacitors provide better energy density and stable capacitance under DC bias, ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency filtering and decoupling due to their low dielectric losses and minimal aging effects.
Size and Capacitance Range
Tantalum capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values in a smaller package compared to ceramic capacitors, making them ideal for compact electronic devices requiring stable capacitance. Ceramic capacitors generally provide lower capacitance ranges but excel in high-frequency applications due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR). The size advantage of tantalum capacitors supports designs with limited space, while ceramic capacitors cover a broader voltage range with smaller capacitance values.
ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) Comparison
Tantalum capacitors typically exhibit lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to ceramic capacitors, making them suitable for applications requiring stable performance at higher frequencies. Ceramic capacitors, especially Class 2 and 3 dielectrics, tend to have higher ESR values but offer advantages in size and voltage ratings. The low ESR characteristic of tantalum capacitors enhances efficiency in power supply filtering and decoupling circuits where minimized energy loss is critical.
Voltage Ratings and Stability
Tantalum capacitors typically offer higher voltage ratings ranging from 6.3V up to 50V, supporting stable performance in demanding power applications. Ceramic capacitors provide a broader range, from as low as 6.3V to over 100V, with superior stability across temperature variations due to their Class 1 dielectrics. Your choice should consider the required voltage rating and stability needed for the specific electronic circuit.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors offer high reliability with stable capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them suitable for long-term applications but can be prone to catastrophic failures if subjected to voltage spikes. Ceramic capacitors exhibit excellent durability and a longer lifespan due to their robust construction, tolerance to high voltage peaks, and resistance to environmental factors like temperature and humidity. Both capacitor types vary in reliability based on application conditions, with ceramic capacitors generally favored for high-frequency, high-reliability requirements and tantalum capacitors preferred for stable performance in low-voltage circuits.
Typical Applications in Electronics
Tantalum capacitors are commonly used in applications requiring stable capacitance and reliable performance at low voltages, such as in filter circuits, power supply decoupling, and audio equipment. Ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency applications, including RF circuits, tuning circuits, and signal processing due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and high dielectric strength. Your choice between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on factors like voltage requirements, frequency range, and desired stability in your electronic designs.
Cost Differences and Availability
Tantalum capacitors generally have a higher cost compared to ceramic capacitors due to their complex manufacturing process and superior capacitance stability. Ceramic capacitors are widely available in various sizes and voltage ratings, offering cost-effective solutions for mass production and consumer electronics. The availability of ceramic capacitors in standard values and bulk quantities often makes them a preferred choice for designs with tight budget constraints.
How to Choose: Tantalum or Ceramic Capacitor
Choosing between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on your application's voltage, capacitance, and stability requirements. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and stable performance in low-voltage, space-constrained circuits but have a higher risk of failure under voltage spikes. Ceramic capacitors provide excellent high-frequency characteristics, low ESR, and better reliability for general-purpose use, making them suitable for filtering and decoupling in your electronic designs.
Tantalum vs Ceramic Capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com