Multilayer PCBs offer increased circuit density, enhanced performance, and improved electromagnetic interference control compared to single layer PCBs, which are simpler and more cost-effective for basic applications. Discover which PCB type best suits Your project's requirements by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
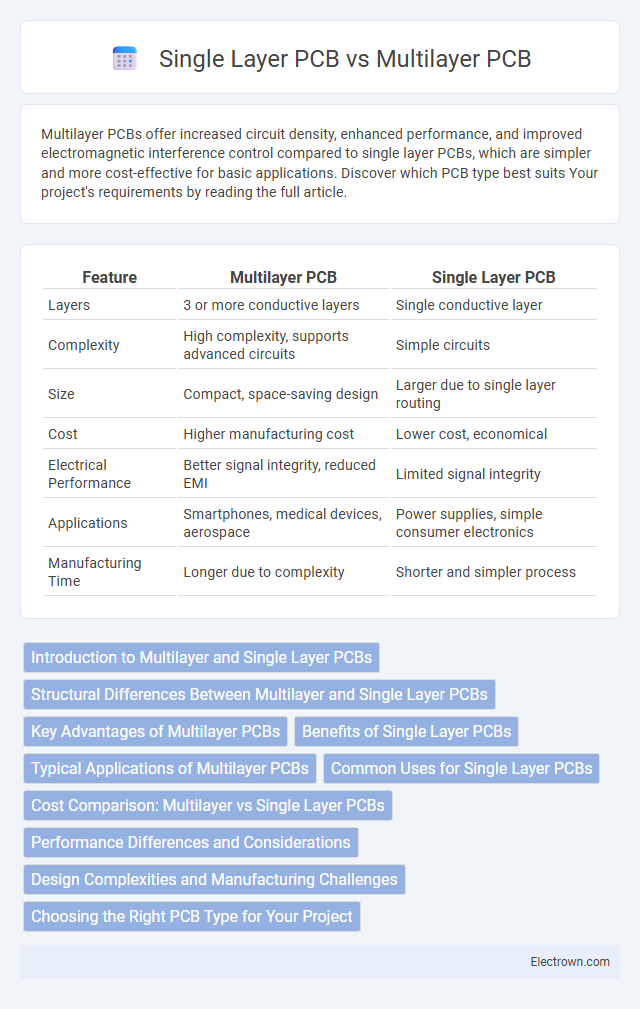
| Feature | Multilayer PCB | Single Layer PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Layers | 3 or more conductive layers | Single conductive layer |
| Complexity | High complexity, supports advanced circuits | Simple circuits |
| Size | Compact, space-saving design | Larger due to single layer routing |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, economical |
| Electrical Performance | Better signal integrity, reduced EMI | Limited signal integrity |
| Applications | Smartphones, medical devices, aerospace | Power supplies, simple consumer electronics |
| Manufacturing Time | Longer due to complexity | Shorter and simpler process |
Introduction to Multilayer and Single Layer PCBs
Single Layer PCBs consist of a single conductive layer and are ideal for simple electronic devices with limited circuit complexity. Multilayer PCBs feature multiple stacked layers of conductive material separated by insulating layers, enabling higher circuit density and enhanced performance. Your choice between these options depends on the complexity, size, and functionality requirements of your electronic project.
Structural Differences Between Multilayer and Single Layer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs consist of three or more insulating layers sandwiched between conductive copper layers, enabling complex circuit designs and higher component density. Single layer PCBs have a single conductive copper layer on one side of an insulating substrate, suitable for simple, low-density circuits. The structural composition of multilayer PCBs provides improved signal integrity and electromagnetic interference shielding compared to the basic, single-layer construction.
Key Advantages of Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs offer significant benefits over single layer PCBs, including higher circuit density and improved electrical performance due to multiple conductive layers stacked together. They enable compact and complex designs essential for modern electronics, providing better signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI). Choosing multilayer PCBs for your project enhances durability and supports advanced functionalities in devices requiring miniaturization and high-speed operation.
Benefits of Single Layer PCBs
Single layer PCBs offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for low-complexity, high-volume electronics. Their straightforward design reduces manufacturing time and lowers production costs, which benefits consumer electronics and automotive applications requiring basic circuits. Additionally, single layer PCBs provide easier troubleshooting and repairs due to accessible component placement and minimal layering.
Typical Applications of Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs are commonly used in complex, high-performance electronics such as smartphones, aerospace systems, medical devices, and advanced computing equipment due to their ability to support higher circuit density and enhanced electrical performance. These PCBs enable better signal integrity and electromagnetic interference reduction, making them ideal for applications requiring compact size and reliability. Your projects that demand multi-signal layers and compact design will benefit the most from multilayer PCB technology.
Common Uses for Single Layer PCBs
Single layer PCBs are widely used in simple electronic devices such as calculators, power supplies, and LED lighting systems due to their straightforward design and cost-effectiveness. They are ideal for applications requiring low-density circuits and minimal complexity, including toys, home appliances, and basic industrial equipment. Their single copper layer structure enables easy manufacturing and maintenance in devices with limited circuit requirements.
Cost Comparison: Multilayer vs Single Layer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs typically incur higher manufacturing costs compared to single layer PCBs due to the complexity of their design, additional materials, and advanced fabrication processes. Single layer PCBs are cost-effective for simple circuit designs, making them ideal for low-budget and high-volume production. The choice between multilayer and single layer PCBs depends on balancing performance requirements against budget constraints and production scale.
Performance Differences and Considerations
Multilayer PCBs offer superior performance compared to single layer PCBs due to their ability to support complex circuitry with enhanced signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference. The multiple layers enable efficient power distribution and better thermal management, crucial for high-speed and high-density electronic applications. Single layer PCBs, while cost-effective and simpler to manufacture, are limited in circuit complexity and are less suitable for advanced performance requirements.
Design Complexities and Manufacturing Challenges
Multilayer PCBs involve intricate design complexities due to multiple signal layers requiring precise alignment and advanced software tools, making routing denser and more challenging compared to Single Layer PCBs. Manufacturing challenges for multilayer boards include controlled lamination processes, strict quality inspections for inter-layer connectivity, and higher costs due to material and process demands. Your choice between multilayer and single layer PCBs should consider these factors to ensure optimal performance and manufacturability based on application requirements.
Choosing the Right PCB Type for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate PCB type hinges on project complexity, space constraints, and electrical performance requirements. Single layer PCBs are ideal for simple, low-cost designs with minimal components, while multilayer PCBs support advanced circuits with high component density and enhanced signal integrity. Evaluating factors such as thermal management, electromagnetic interference, and manufacturing budget ensures optimal function and reliability in your electronic device.
Multilayer PCB vs Single Layer PCB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com