Choosing between split rail and single rail power supplies depends on your device's power management needs, with split rail offering separate voltages for improved stability and safety, while single rail provides a simpler, high-current output. Explore the rest of the article to determine which power supply best suits your system's requirements.
Table of Comparison
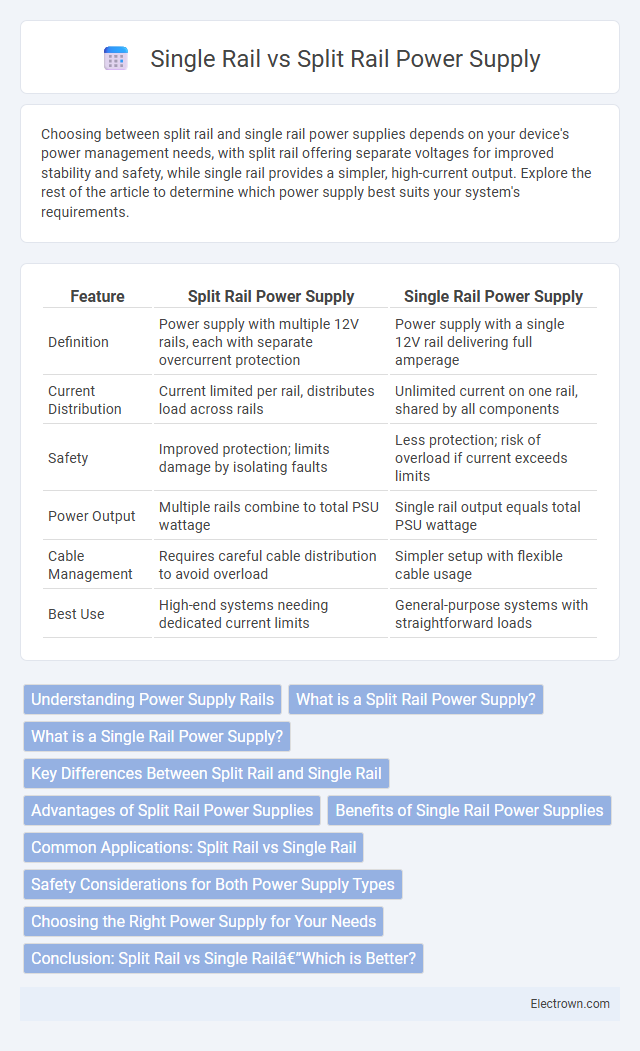
| Feature | Split Rail Power Supply | Single Rail Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power supply with multiple 12V rails, each with separate overcurrent protection | Power supply with a single 12V rail delivering full amperage |
| Current Distribution | Current limited per rail, distributes load across rails | Unlimited current on one rail, shared by all components |
| Safety | Improved protection; limits damage by isolating faults | Less protection; risk of overload if current exceeds limits |
| Power Output | Multiple rails combine to total PSU wattage | Single rail output equals total PSU wattage |
| Cable Management | Requires careful cable distribution to avoid overload | Simpler setup with flexible cable usage |
| Best Use | High-end systems needing dedicated current limits | General-purpose systems with straightforward loads |
Understanding Power Supply Rails
Power supply rails represent distinct voltage lines within a power supply that deliver specific voltages to computer components or circuits. A split rail power supply divides the output into multiple rails, each with dedicated overcurrent protection, enhancing safety and reducing risk of overload. Your choice between split rail and single rail directly impacts system stability, efficiency, and component protection based on how power distribution and load management are handled.
What is a Split Rail Power Supply?
A split rail power supply provides two equal but opposite voltage outputs relative to a common ground, commonly used in audio and operational amplifier circuits to allow symmetrical power distribution. Unlike a single rail power supply that offers only one positive voltage reference, split rail supplies enable both positive and negative voltages, improving signal handling and reducing distortion. This design is essential for balanced analog circuits requiring dual polarity voltages for optimal performance.
What is a Single Rail Power Supply?
A Single Rail Power Supply delivers all its available current through one voltage rail, typically +12V, simplifying power distribution and making it easier to manage load requirements. This type offers a consistent and unified power source, reducing the complexity of monitoring multiple rails and minimizing the risk of uneven power distribution. Single rail designs are popular in high-performance PCs and gaming systems where delivering maximum power to components without division is critical.
Key Differences Between Split Rail and Single Rail
Split rail power supplies provide multiple output voltages, typically positive, negative, and ground, allowing for better voltage distribution in circuits requiring dual polarity. Single rail power supplies deliver one consistent voltage output, simplifying design but limiting versatility in applications needing balanced power. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right power supply for your device's voltage and current requirements.
Advantages of Split Rail Power Supplies
Split rail power supplies offer distinct advantages by providing dual voltage outputs, such as +15V and -15V, which are essential for powering analog circuits and operational amplifiers requiring symmetric power rails. This configuration enhances signal integrity and reduces noise by maintaining a stable reference point, improving overall circuit performance. Your designs benefit from increased flexibility and compatibility with a broader range of components compared to single rail power supplies.
Benefits of Single Rail Power Supplies
Single rail power supplies provide consistent and stable power delivery by offering a single, high-amperage +12V rail, reducing the risk of uneven power distribution and simplifying system design. This design enhances compatibility with high-performance components, particularly GPUs and CPUs, by ensuring they receive adequate power without fluctuations. Additionally, single rail configurations improve safety by eliminating the need to balance loads across multiple rails, minimizing complexity and potential points of failure.
Common Applications: Split Rail vs Single Rail
Split rail power supplies are commonly used in audio equipment and operational amplifiers where symmetrical voltage rails, such as +-12V or +-15V, are essential for proper signal processing and noise reduction. Single rail power supplies dominate applications requiring a single positive voltage source, notably in most consumer electronics, LED lighting, and computer power supplies due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Industrial control systems often favor split rail designs for balanced output and stability, while single rail configurations are standard in portable devices benefiting from compact and efficient power delivery.
Safety Considerations for Both Power Supply Types
Split rail and single rail power supplies each present unique safety considerations critical for protecting your electronic components and ensuring user safety. Split rail power supplies offer balanced voltages, reducing the risk of voltage spikes and making them ideal for audio and analog circuits where noise reduction is paramount. Single rail power supplies, while simpler, require careful current management to avoid overloads and potential short circuits, necessitating proper fusing and circuit protection to maintain safe operation.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
Choosing the right power supply involves understanding the differences between split rail and single rail systems to match your device's power demands effectively. Split rail power supplies provide multiple voltage outputs separately, ensuring better stability and safety for sensitive components, while single rail units deliver all power through one line, offering simplicity and higher peak current capacity. Evaluate your components' current requirements, protection features, and overall system configuration to select a power supply that optimizes performance and safeguards your equipment.
Conclusion: Split Rail vs Single Rail—Which is Better?
Split rail power supplies provide multiple voltage outputs, offering improved stability and better handling of complex loads in high-performance systems. Single rail power supplies deliver all power through one rail, making them simpler but potentially riskier under high current demands. Your choice depends on system requirements; split rails offer enhanced safety and load distribution, while single rails are often sufficient for standard setups.
Split Rail vs Single Rail Power Supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com