Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a stable reference voltage in low-power applications, while TVS diodes protect sensitive electronics from high-voltage transients and electrostatic discharges. Discover how understanding the differences between Zener and TVS diodes can enhance your circuit design by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
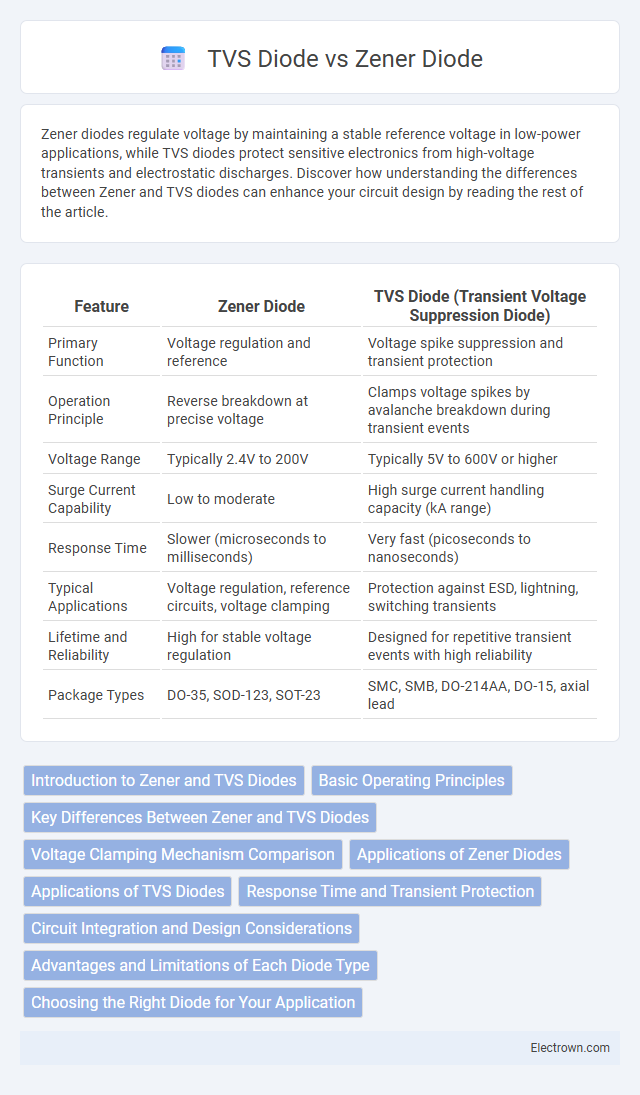
| Feature | Zener Diode | TVS Diode (Transient Voltage Suppression Diode) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Voltage regulation and reference | Voltage spike suppression and transient protection |
| Operation Principle | Reverse breakdown at precise voltage | Clamps voltage spikes by avalanche breakdown during transient events |
| Voltage Range | Typically 2.4V to 200V | Typically 5V to 600V or higher |
| Surge Current Capability | Low to moderate | High surge current handling capacity (kA range) |
| Response Time | Slower (microseconds to milliseconds) | Very fast (picoseconds to nanoseconds) |
| Typical Applications | Voltage regulation, reference circuits, voltage clamping | Protection against ESD, lightning, switching transients |
| Lifetime and Reliability | High for stable voltage regulation | Designed for repetitive transient events with high reliability |
| Package Types | DO-35, SOD-123, SOT-23 | SMC, SMB, DO-214AA, DO-15, axial lead |
Introduction to Zener and TVS Diodes
Zener diodes are designed to maintain a stable reference voltage by operating in the reverse breakdown region, primarily used for voltage regulation and overvoltage protection in low-power circuits. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diodes specialize in protecting sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes and transient events by clamping high voltage surges rapidly. Both devices function as voltage protection components, but Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation, while TVS diodes are optimized for transient surge suppression.
Basic Operating Principles
A Zener diode regulates voltage by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, providing precise voltage reference and stabilization. A TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diode protects circuits by clamping sudden voltage spikes, reacting almost instantaneously to transient overvoltages to safeguard sensitive components. Your choice between a Zener diode and a TVS diode depends on whether you require steady voltage regulation or transient voltage protection.
Key Differences Between Zener and TVS Diodes
Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage in electronic circuits, while TVS diodes protect sensitive components from transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge or lightning. The voltage rating of a Zener diode is typically precise and lower compared to the higher breakdown voltage and faster response time of TVS diodes designed for surge suppression. Zener diodes have a well-defined breakdown voltage used for steady-state voltage control, whereas TVS diodes are optimized for transient event clamping with high peak pulse power handling capability.
Voltage Clamping Mechanism Comparison
Zener diodes regulate voltage by entering avalanche breakdown at a precise reverse voltage, thereby clamping voltage to a stable level suitable for low-power applications. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes clamp voltage rapidly by transitioning into a low-impedance state during transient spikes, effectively protecting circuits from high-energy surges. The voltage clamping of TVS diodes operates faster and can handle higher peak currents compared to Zener diodes, making them ideal for transient voltage suppression in automotive and telecommunications environments.
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are primarily used in voltage regulation applications, providing a stable reference voltage in power supplies and protecting circuits from overvoltage by clamping voltage spikes. They serve as precise voltage references in measurement equipment and act as protection devices in low-voltage circuits. Your electronic designs benefit from Zener diodes when consistent voltage levels and circuit protection under normal operating conditions are critical.
Applications of TVS Diodes
TVS diodes are primarily used for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from voltage spikes and transient surges caused by lightning strikes, electrostatic discharge (ESD), and inductive load switching. They are widely applied in telecommunications, automotive electronics, and power supply systems to safeguard components and ensure device reliability. Your circuits benefit from TVS diodes by maintaining stable operation during unexpected voltage events, unlike Zener diodes which are typically used for voltage regulation.
Response Time and Transient Protection
Zener diodes offer slower response times in comparison to TVS diodes, which are engineered for ultra-fast transient voltage suppression to protect sensitive electronic circuits. TVS diodes react within picoseconds to nanoseconds, clamping voltage spikes effectively during transient events, whereas Zener diodes primarily regulate voltage levels and are less efficient for transient suppression. The superior transient protection performance and rapid response of TVS diodes make them ideal for safeguarding against electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and other high-energy transients in critical electronic applications.
Circuit Integration and Design Considerations
Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation in circuits, making them suitable for low-current applications where stable reference voltages are required. TVS diodes are designed to protect sensitive electronics from transient voltage spikes by clamping surge voltages rapidly, necessitating careful placement near input/output lines for effective protection. Your circuit design should account for the differing response times, energy absorption capabilities, and voltage ratings when integrating Zener or TVS diodes to ensure optimal performance and device reliability.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Diode Type
Zener diodes offer precise voltage regulation with low cost and simplicity, ideal for stable reference voltage applications but have limited surge protection capacity and slower response to transient voltage spikes. TVS diodes excel in fast transient voltage suppression and robust surge immunity, protecting sensitive electronics from ESD and lightning-induced transients, yet they typically have higher leakage current and cost compared to Zener diodes. Choosing between Zener and TVS diodes depends on application requirements for voltage regulation accuracy versus transient surge protection efficiency.
Choosing the Right Diode for Your Application
Selecting the right diode depends on the specific protection requirements of your application: Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by clamping voltage at a fixed level, ideal for low-power circuits needing voltage reference or stabilization. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes offer fast, high-energy transient voltage spike suppression, making them suitable for protecting sensitive electronic devices from ESD, lightning, and switching transients. Consider factors like response time, clamping voltage, power rating, and transient energy absorption to ensure optimal circuit protection and performance.
Zener diode vs TVS diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com