Trellis coding enhances error correction by combining convolutional encoding with modulation, providing higher data reliability in noisy channels, while block coding involves encoding fixed-length data blocks to detect and correct errors. Explore the detailed comparison to understand how each method impacts your communication system's performance.
Table of Comparison
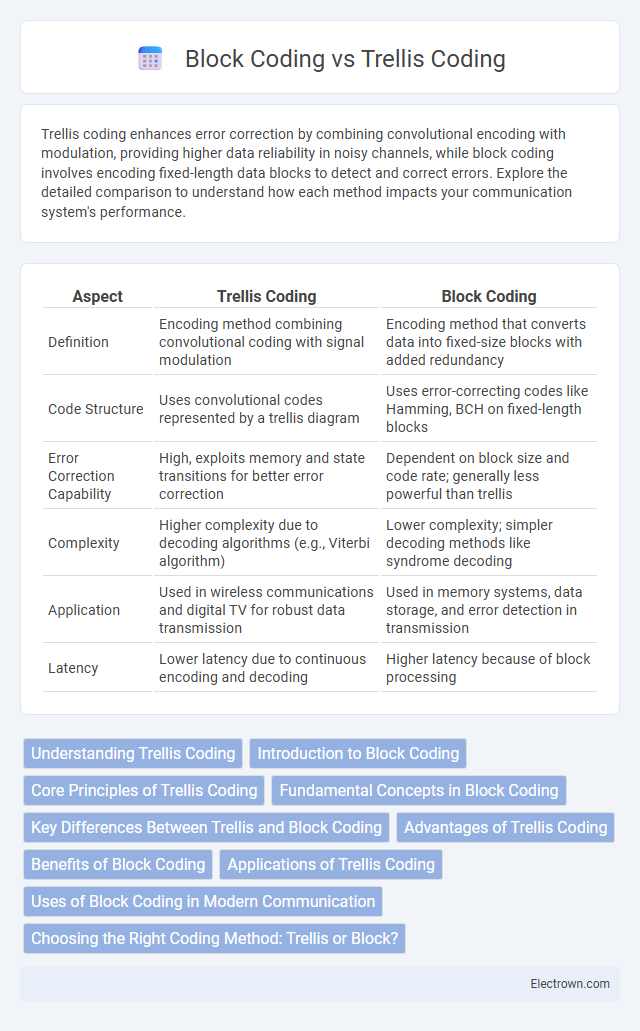
| Aspect | Trellis Coding | Block Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encoding method combining convolutional coding with signal modulation | Encoding method that converts data into fixed-size blocks with added redundancy |
| Code Structure | Uses convolutional codes represented by a trellis diagram | Uses error-correcting codes like Hamming, BCH on fixed-length blocks |
| Error Correction Capability | High, exploits memory and state transitions for better error correction | Dependent on block size and code rate; generally less powerful than trellis |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to decoding algorithms (e.g., Viterbi algorithm) | Lower complexity; simpler decoding methods like syndrome decoding |
| Application | Used in wireless communications and digital TV for robust data transmission | Used in memory systems, data storage, and error detection in transmission |
| Latency | Lower latency due to continuous encoding and decoding | Higher latency because of block processing |
Understanding Trellis Coding
Trellis coding combines convolutional coding with modulation to improve error performance without enlarging bandwidth, offering a powerful alternative to traditional block coding methods. It encodes data by using a state machine that maps input bits to output symbols, enhancing error correction through sequence-based decisions rather than isolated blocks. Your communication system benefits from Trellis coding by achieving higher data integrity and resistance to noise compared to standard block coding techniques.
Introduction to Block Coding
Block coding encodes fixed-size blocks of input data into larger blocks of coded output to improve error detection and correction in digital communication systems. Common block codes include Hamming codes, Reed-Solomon codes, and BCH codes, which add redundancy through parity bits to ensure reliable data transmission. These codes optimize data integrity by enabling the identification and correction of errors within each fixed-length block.
Core Principles of Trellis Coding
Trellis coding integrates convolutional encoding with modulation to enhance error correction and bandwidth efficiency, using a state transition diagram called a trellis to represent possible symbol sequences. This technique exploits both time and coding redundancy, improving performance over noisy channels compared to traditional block coding that treats codewords independently. Your communication system benefits from trellis coding's ability to provide soft-decision decoding and continuous error correction, optimizing reliability in data transmission.
Fundamental Concepts in Block Coding
Block coding is a method of error control in digital communication where data bits are grouped into fixed-size blocks and encoded using predefined codewords to detect and correct errors. Each block is independently processed, ensuring that error correction can be performed based on the redundancy introduced within that block. Your communication system can benefit from block coding due to its structured approach in simplifying error detection and correction while maintaining manageable complexity.
Key Differences Between Trellis and Block Coding
Trellis coding combines convolutional encoding with modulation, providing error correction by exploiting time dependencies, while block coding processes fixed-size blocks of data independently for error detection and correction. Trellis coding is typically used in communication systems requiring high performance and spectral efficiency, utilizing a trellis diagram for decoding via the Viterbi algorithm. Block coding offers simpler implementation with fixed-length codewords, making it suitable for applications with less stringent error correction requirements.
Advantages of Trellis Coding
Trellis coding offers significant advantages over block coding by providing enhanced error correction capabilities through convolutional encoding combined with modulation, leading to improved signal reliability in noisy channels. Its use of state machines enables more efficient decoding with the Viterbi algorithm, resulting in better performance at lower signal-to-noise ratios. You benefit from higher data rates and robustness in communication systems, making trellis coding ideal for wireless and digital transmission applications.
Benefits of Block Coding
Block coding offers robust error detection and correction by dividing data into fixed-size blocks, allowing for efficient identification and correction of errors within each block. This method enhances data integrity and reliability, especially in noisy communication channels. Your systems benefit from simplified encoding and decoding processes, leading to faster and more efficient data transmission.
Applications of Trellis Coding
Trellis coding is widely utilized in digital communication systems such as wireless networks, satellite communication, and mobile telephony due to its ability to provide error correction with minimal bandwidth expansion. Its convolutional structure enables efficient encoding and decoding processes, making it suitable for real-time applications like voice and video transmission where low latency is critical. Compared to block coding, trellis coding offers better performance in channels with memory, significantly enhancing data reliability and throughput in fading or noisy environments.
Uses of Block Coding in Modern Communication
Block coding is widely employed in modern communication systems for error detection and correction, ensuring data integrity across noisy channels. It serves crucial roles in digital data transmission, including satellite communication, wireless networks, and storage devices, by encoding fixed-size blocks of data into longer codes to identify and correct errors. Technologies like Reed-Solomon and Hamming codes exemplify block coding applications that enhance reliability in data transfer and storage solutions.
Choosing the Right Coding Method: Trellis or Block?
Choosing between trellis coding and block coding depends on the specific error correction needs and system complexity of your communication channel. Trellis coding offers superior performance in scenarios with continuous data transmission and noisy environments due to its use of convolutional codes combined with modulation, enhancing error correction without bandwidth expansion. Block coding, while simpler and easier to implement, is more suitable for applications requiring fixed-length data blocks and lower computational resources, making your choice critical based on system constraints and error resilience requirements.
Trellis Coding vs Block Coding Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com