A T/R switch efficiently alternates between transmitting and receiving signals in a radar or communication system, ensuring minimal loss and preventing signal interference, while a duplexer allows simultaneous transmission and reception on the same antenna by isolating the transmit and receive paths. Understanding the differences between these components can optimize Your system's performance; continue reading to learn more about their applications and advantages.
Table of Comparison
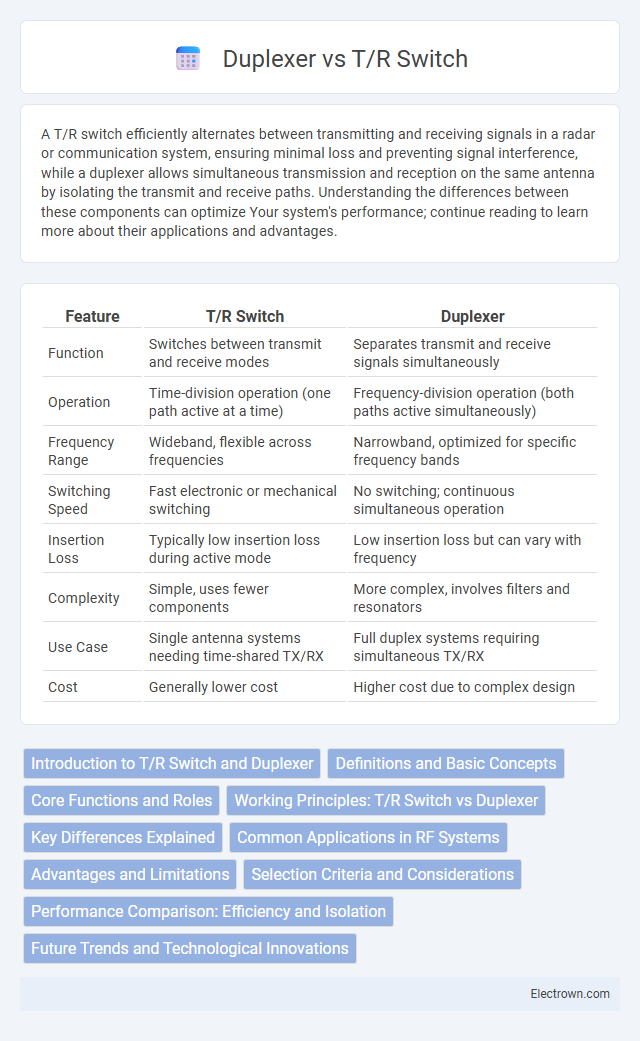
| Feature | T/R Switch | Duplexer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Switches between transmit and receive modes | Separates transmit and receive signals simultaneously |
| Operation | Time-division operation (one path active at a time) | Frequency-division operation (both paths active simultaneously) |
| Frequency Range | Wideband, flexible across frequencies | Narrowband, optimized for specific frequency bands |
| Switching Speed | Fast electronic or mechanical switching | No switching; continuous simultaneous operation |
| Insertion Loss | Typically low insertion loss during active mode | Low insertion loss but can vary with frequency |
| Complexity | Simple, uses fewer components | More complex, involves filters and resonators |
| Use Case | Single antenna systems needing time-shared TX/RX | Full duplex systems requiring simultaneous TX/RX |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex design |
Introduction to T/R Switch and Duplexer
A T/R switch controls signal paths by toggling between transmit and receive modes in wireless communication systems, crucial for preventing signal interference. Duplexers enable simultaneous transmission and reception on a single antenna by isolating frequencies, enhancing system efficiency and reducing hardware complexity. Understanding the differences helps you optimize your wireless setup for performance and cost-effectiveness.
Definitions and Basic Concepts
A T/R switch, or transmit/receive switch, is a device that alternates a radio transceiver's antenna connection between transmitting and receiving modes, preventing signal interference by isolating these functions in time. A duplexer, on the other hand, is a passive device that allows simultaneous transmission and reception on the same antenna by separating signals based on frequency, enabling full-duplex communication. Understanding these basic concepts helps you choose the appropriate component for efficient antenna system design, depending on whether time or frequency division is required.
Core Functions and Roles
A T/R switch primarily manages the transmission and reception pathways in a radio system by rapidly toggling between the transmitter and receiver to prevent signal interference. A duplexer, on the other hand, allows simultaneous transmission and reception over a single antenna by separating the outgoing and incoming frequencies using filters. Understanding the core functions of these components helps optimize Your communication system's efficiency and signal integrity.
Working Principles: T/R Switch vs Duplexer
A T/R switch rapidly alternates a single antenna's connection between the transmitter and receiver to prevent signal interference during transmission and reception, ensuring efficient use of one antenna. In contrast, a duplexer uses frequency-selective filters to simultaneously separate transmitted and received signals on the same antenna without switching, enabling continuous two-way communication. Understanding these working principles helps optimize your communication system design for either time-shared or simultaneous signal handling.
Key Differences Explained
A T/R switch (Transmit/Receive switch) rapidly toggles between transmission and reception modes on a single antenna, ensuring signal isolation to prevent damage to receiver components during transmission. A duplexer enables simultaneous transmission and reception on separate frequencies through a single antenna by filtering and separating frequency bands, supporting full-duplex communication. The key difference lies in operational mode: T/R switches alternate between transmit and receive to avoid interference, while duplexers allow concurrent operation by frequency discrimination.
Common Applications in RF Systems
T/R switches are commonly used in radar systems and handheld radios to alternate between transmit and receive modes quickly, ensuring minimal signal loss and high isolation. Duplexers are essential in base stations and repeaters for cellular and communication systems, allowing simultaneous transmission and reception on a single antenna by separating frequencies. Both components optimize RF system efficiency, but T/R switches excel in time-division operations, whereas duplexers are preferred in frequency-division multiplexing scenarios.
Advantages and Limitations
T/R switches offer rapid switching between transmit and receive modes with minimal insertion loss, making them ideal for time-division duplex (TDD) systems, but they can suffer from limited power handling and isolation compared to duplexers. Duplexers provide simultaneous transmission and reception on separate frequency bands with high isolation and lower insertion loss, enhancing full-duplex performance in frequency-division duplex (FDD) systems, though they tend to be bulkier and more complex. Both components balance trade-offs between size, isolation, switching speed, and power handling depending on application requirements.
Selection Criteria and Considerations
T/R switches are preferable in low-power, low-cost applications due to their simple design and fast switching speed, while duplexers are suited for higher power systems requiring simultaneous transmit and receive paths with high isolation and minimal insertion loss. Selection criteria include frequency range, power handling capability, insertion loss, isolation, size, and cost constraints, with duplexers offering better performance in complex RF environments. Considerations also involve system architecture, such as half-duplex versus full-duplex operation, and the trade-offs between switching speed and signal integrity.
Performance Comparison: Efficiency and Isolation
T/R switches offer high efficiency with low insertion loss, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid switching between transmit and receive modes. Duplexers provide superior isolation between transmit and receive paths, minimizing interference and ensuring signal integrity in simultaneous operation systems. The choice between T/R switch and duplexer depends on the specific requirements for switching speed, isolation levels, and overall system efficiency.
Future Trends and Technological Innovations
Future trends in T/R switch and duplexer technology emphasize miniaturization and enhanced linearity, driven by the demand for higher frequency bands in 5G and beyond. Innovations include RF MEMS and GaN-based components, which offer faster switching speeds and improved power handling crucial for advanced communication systems. Your choice between these components will depend on specific application needs, balancing size, efficiency, and integration complexity.
T/R switch vs Duplexer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com