Baud rate measures the number of signal changes or symbols transmitted per second, while bit rate indicates the amount of data (bits) transferred per second; understanding their difference is crucial for optimizing your communication system's efficiency and performance. Explore the rest of the article to delve deeper into how these rates impact data transmission and what factors influence their relationship.
Table of Comparison
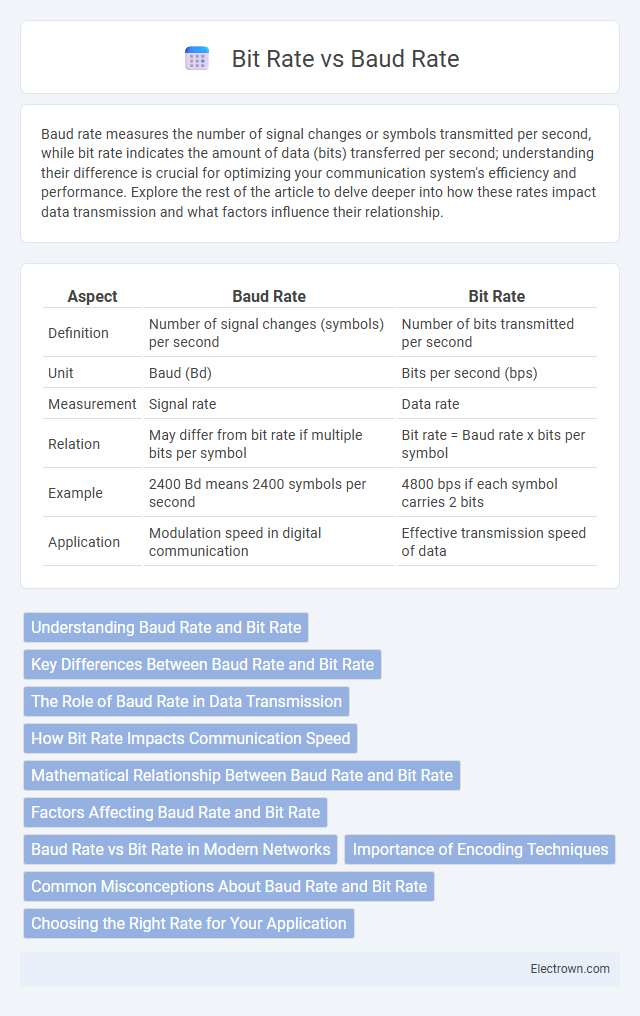
| Aspect | Baud Rate | Bit Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of signal changes (symbols) per second | Number of bits transmitted per second |
| Unit | Baud (Bd) | Bits per second (bps) |
| Measurement | Signal rate | Data rate |
| Relation | May differ from bit rate if multiple bits per symbol | Bit rate = Baud rate x bits per symbol |
| Example | 2400 Bd means 2400 symbols per second | 4800 bps if each symbol carries 2 bits |
| Application | Modulation speed in digital communication | Effective transmission speed of data |
Understanding Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Baud rate measures the number of signal changes or symbols transmitted per second, while bit rate represents the total number of bits communicated per second. In digital communication, understanding the distinction is crucial because multiple bits can be encoded in a single symbol, making bit rate potentially higher than baud rate. Your network's efficiency depends on optimizing both rates to achieve faster and more reliable data transmission.
Key Differences Between Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Baud rate measures the number of signal changes or symbols transmitted per second, while bit rate indicates the total number of bits transmitted per second. Each symbol in baud rate can represent multiple bits depending on the modulation scheme, making bit rate potentially higher than baud rate. Understanding the key differences between baud rate and bit rate helps optimize your network's data transmission efficiency.
The Role of Baud Rate in Data Transmission
Baud rate measures the number of signal changes or symbols transmitted per second in a communication channel, directly impacting data transmission speed. Unlike bit rate, which represents the total bits transmitted per second, baud rate reflects the modulation method and the number of bits encoded per symbol, playing a crucial role in optimizing bandwidth efficiency. Understanding baud rate helps you design systems that maximize data transmission quality and minimize errors over various communication mediums.
How Bit Rate Impacts Communication Speed
Bit rate directly influences communication speed by determining how many bits are transmitted per second, thereby affecting the overall data transfer rate. Higher bit rates enable faster information exchange, crucial for applications demanding quick responsiveness or large data volumes. Your network's efficiency and performance depend largely on optimizing bit rate to match channel capacity and minimize errors.
Mathematical Relationship Between Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Baud rate represents the number of signal units transmitted per second, while bit rate quantifies the number of bits transmitted per second. The mathematical relationship between baud rate and bit rate is given by the formula: Bit Rate = Baud Rate x log2(M), where M is the number of distinct signal levels or symbols. For example, with 16-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), where each symbol encodes 4 bits (log2(16) = 4), a baud rate of 1000 baud results in a bit rate of 4000 bits per second.
Factors Affecting Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Baud rate and bit rate are influenced by signal modulation techniques, bandwidth, and channel noise levels. Higher order modulation schemes increase bit rate by transmitting multiple bits per symbol, affecting baud rate differently. Your communication system's efficiency depends on balancing these factors to optimize data transmission speed and reliability.
Baud Rate vs Bit Rate in Modern Networks
Baud rate measures the number of signal changes or symbols transmitted per second, while bit rate quantifies the actual data bits transmitted per second. In modern networks, advanced modulation techniques like QAM and PSK allow multiple bits per symbol, causing the bit rate to often exceed the baud rate significantly. Your network's performance is optimized by understanding this distinction, as higher bit rates improve data throughput without increasing the baud rate.
Importance of Encoding Techniques
Encoding techniques directly influence the relationship between baud rate and bit rate by determining how bits are represented as signal changes or symbols. Efficient encoding schemes, such as Manchester or 4B/5B encoding, maximize bit rate within a given baud rate, enhancing data transmission speed and reliability. Your choice of encoding method can significantly optimize channel bandwidth usage and reduce errors in digital communication systems.
Common Misconceptions About Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Baud rate and bit rate are often mistakenly considered identical, but baud rate measures the number of signal changes per second, while bit rate quantifies the actual data transmitted per second. Many assume a one-to-one correlation, neglecting that modern modulation schemes can transmit multiple bits per baud, increasing bit rate without changing baud rate. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately evaluating communication system performance and optimizing Your data transmission efficiency.
Choosing the Right Rate for Your Application
Choosing the right baud rate versus bit rate depends on your application's requirements for speed and signal complexity. Baud rate measures symbol changes per second, while bit rate indicates the number of bits transmitted per second, often higher when multiple bits are encoded per symbol. Selecting a rate that balances efficient data throughput with the limitations of your communication channel ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Baud Rate vs Bit Rate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com