NLOS (Non-Line of Sight) refers to signal transmission where obstacles block the direct path between the transmitter and receiver, causing signal reflection and diffraction, while LOS (Line of Sight) ensures a clear, unobstructed path for optimal signal strength and quality. Understanding the differences between NLOS and LOS can improve your wireless communication setup; read on to explore the advantages and challenges of each.
Table of Comparison
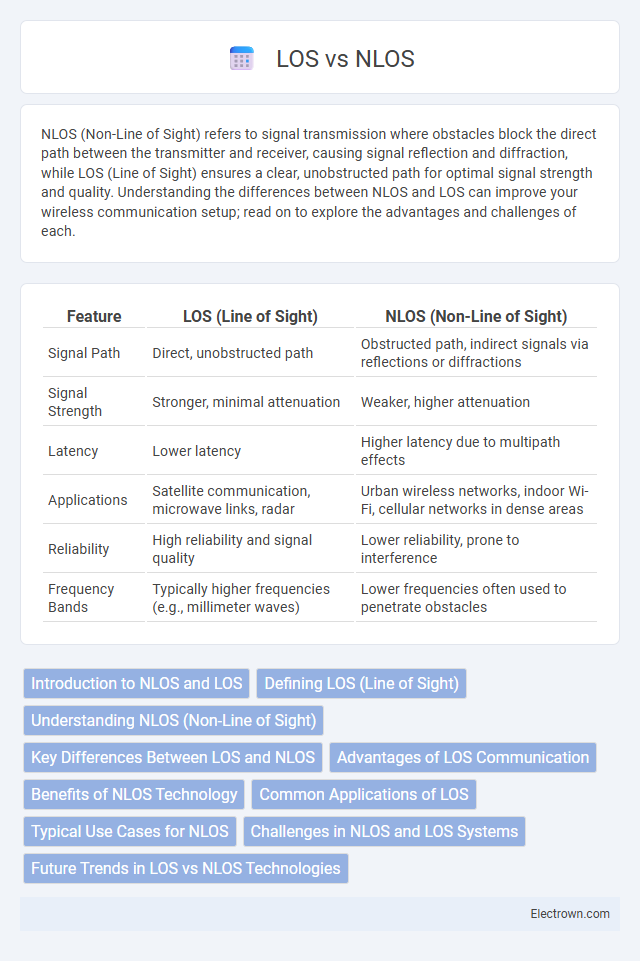
| Feature | LOS (Line of Sight) | NLOS (Non-Line of Sight) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Path | Direct, unobstructed path | Obstructed path, indirect signals via reflections or diffractions |
| Signal Strength | Stronger, minimal attenuation | Weaker, higher attenuation |
| Latency | Lower latency | Higher latency due to multipath effects |
| Applications | Satellite communication, microwave links, radar | Urban wireless networks, indoor Wi-Fi, cellular networks in dense areas |
| Reliability | High reliability and signal quality | Lower reliability, prone to interference |
| Frequency Bands | Typically higher frequencies (e.g., millimeter waves) | Lower frequencies often used to penetrate obstacles |
Introduction to NLOS and LOS
Line-of-sight (LOS) communication requires a direct, unobstructed path between the transmitter and receiver for optimal signal transmission, commonly used in technologies such as microwave and infrared systems. Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) communication occurs when obstacles like buildings, trees, or terrain block the direct path, causing signals to reach the receiver through reflection, diffraction, or scattering, which is typical in urban cellular and Wi-Fi networks. Understanding the distinctions between NLOS and LOS is crucial for designing effective wireless communication systems that maximize coverage and reliability.
Defining LOS (Line of Sight)
Line of Sight (LOS) refers to a direct, unobstructed path between a transmitter and receiver, allowing clear signal transmission. LOS is critical in wireless communications, satellite links, and radar systems to ensure minimal signal attenuation and delay. Your network performance significantly improves with LOS, as obstacles causing Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) conditions lead to interference and weaker signals.
Understanding NLOS (Non-Line of Sight)
Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) communication occurs when the transmitter and receiver are obstructed by physical objects, causing signal reflection, diffraction, or scattering, which affects signal quality and reliability. NLOS environments often result in increased signal attenuation and multipath interference, challenging wireless systems such as 5G, Wi-Fi, and radar. Effective NLOS understanding is crucial for optimizing network performance, enabling technologies like beamforming and adaptive modulation to mitigate signal degradation.
Key Differences Between LOS and NLOS
Line of Sight (LOS) communication requires a clear, unobstructed path between the transmitter and receiver, ensuring minimal signal degradation and higher data transmission rates. Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) communication involves signal transmission where obstacles like buildings or terrain block direct paths, often causing multipath reflection, scattering, and signal attenuation, leading to reduced signal quality. The key difference lies in the presence of a direct path for LOS, enabling more reliable and faster communication, whereas NLOS relies on indirect paths, increasing latency and reducing overall communication performance.
Advantages of LOS Communication
Line-of-sight (LOS) communication offers significant advantages including higher signal strength, reduced interference, and greater data transmission speeds compared to non-line-of-sight (NLOS) communication. The direct path between transmitter and receiver minimizes multipath fading and signal attenuation, ensuring more reliable connectivity. Your network performance improves with LOS by enabling clearer signals, essential for applications requiring low latency and high bandwidth.
Benefits of NLOS Technology
NLOS (Non-Line-of-Sight) technology enables wireless communication without direct visual paths, offering enhanced connectivity in urban environments, inside buildings, and around obstacles. Its ability to penetrate walls and circumvent barriers improves network reliability and coverage in challenging terrains where LOS (Line-of-Sight) signals fail. This technology is crucial for applications such as emergency response, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructure, ensuring consistent data transmission despite physical obstructions.
Common Applications of LOS
Line-of-sight (LOS) communication is commonly used in applications such as microwave transmission, satellite communication, and radar systems, where a clear, unobstructed path between transmitting and receiving antennas is essential for signal integrity. LOS is critical in wireless systems like point-to-point links, free-space optical communication, and certain types of 5G networks that rely on direct beamforming to maximize bandwidth and minimize latency. Its prevalence in aviation, maritime navigation, and outdoor wireless broadband ensures high data rates and low interference compared to non-line-of-sight (NLOS) setups.
Typical Use Cases for NLOS
Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) communication is essential in urban environments where buildings, walls, and other obstacles block direct Line-of-Sight (LOS) signals, making it ideal for dense cityscapes. NLOS technology is commonly employed in indoor wireless networks, underground facilities, and autonomous vehicle navigation systems where signal paths often encounter obstructions. It enhances connectivity for applications like drone communication, disaster recovery, and military operations by leveraging reflection, diffraction, and scattering to maintain reliable communication links.
Challenges in NLOS and LOS Systems
NLOS (Non-Line-of-Sight) systems face significant challenges including signal attenuation, multipath fading, and increased latency due to obstacles obstructing direct paths between transmitter and receiver. LOS (Line-of-Sight) systems offer clearer communication channels but demand precise alignment and suffer performance degradation in dynamic environments with frequent blockages or mobility. Both systems must address interference management and maintain signal integrity to optimize wireless network reliability and throughput.
Future Trends in LOS vs NLOS Technologies
Emerging advancements in LOS (Line-of-Sight) technologies emphasize higher frequency bands like millimeter-wave and terahertz spectrum for ultra-high-speed connectivity with minimal latency. NLOS (Non-Line-of-Sight) solutions increasingly leverage AI-driven signal processing and massive MIMO to overcome obstacles, enhancing urban and indoor coverage reliability. Hybrid systems combining LOS precision and NLOS flexibility are poised to dominate next-generation wireless networks, optimizing spectrum efficiency and user experience.
NLOS vs LOS Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com