Modem and codec serve distinct roles in digital communication; a modem modulates and demodulates signals for internet connectivity, while a codec compresses and decompresses audio or video data to enhance media quality and transmission efficiency. Explore the article to understand how these technologies impact your digital experiences and which might be best suited for your needs.
Table of Comparison
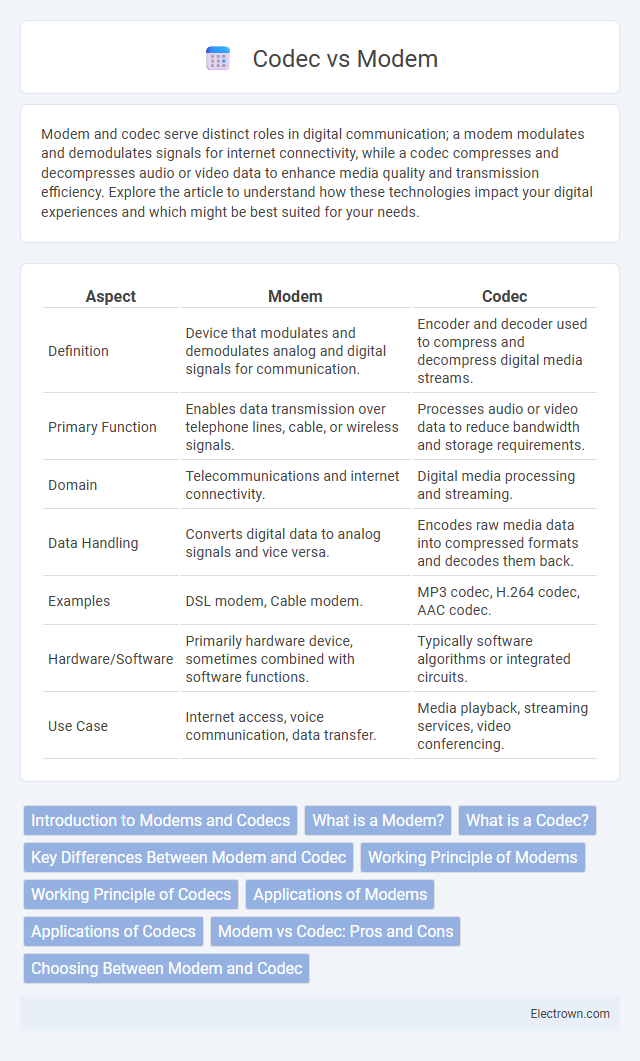
| Aspect | Modem | Codec |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Device that modulates and demodulates analog and digital signals for communication. | Encoder and decoder used to compress and decompress digital media streams. |
| Primary Function | Enables data transmission over telephone lines, cable, or wireless signals. | Processes audio or video data to reduce bandwidth and storage requirements. |
| Domain | Telecommunications and internet connectivity. | Digital media processing and streaming. |
| Data Handling | Converts digital data to analog signals and vice versa. | Encodes raw media data into compressed formats and decodes them back. |
| Examples | DSL modem, Cable modem. | MP3 codec, H.264 codec, AAC codec. |
| Hardware/Software | Primarily hardware device, sometimes combined with software functions. | Typically software algorithms or integrated circuits. |
| Use Case | Internet access, voice communication, data transfer. | Media playback, streaming services, video conferencing. |
Introduction to Modems and Codecs
Modems convert digital data into analog signals and vice versa, enabling communication over telephone lines and other analog mediums by modulating and demodulating signals. Codecs compress and decompress audio or video data, optimizing the quality and reducing bandwidth usage for efficient storage and transmission. Your choice between a modem and a codec depends on whether you need to transmit data across networks or process multimedia content effectively.
What is a Modem?
A modem is a hardware device that modulates and demodulates digital signals for communication over telephone lines, cable systems, or satellite connections. It converts digital data from a computer into analog signals for transmission and then reconverts received analog signals back into digital data. This essential function enables internet connectivity and data exchange across various networks.
What is a Codec?
A codec is a device or software that compresses and decompresses digital audio or video signals to enable efficient transmission and storage. Unlike a modem, which modulates and demodulates analog signals over communication channels, a codec focuses specifically on encoding and decoding multimedia data formats such as MP3, AAC, or H.264. Codecs improve media quality and reduce bandwidth usage by using compression algorithms tailored for audio or video content.
Key Differences Between Modem and Codec
Modems and codecs serve distinct roles in digital communication, with modems primarily converting digital data to analog signals for transmission over telephone lines, while codecs encode and decode audio or video signals to enable efficient compression and playback. Your modem ensures connectivity by modulating and demodulating signals between devices and networks, whereas codecs optimize media quality by reducing file sizes without significant loss of fidelity. Key differences include their operational domain--modems handle data transmission, codecs manage multimedia processing--and the types of signals they work with, analog versus digital media streams.
Working Principle of Modems
Modems work by converting digital data from a computer into analog signals suitable for transmission over telephone lines or cable systems, then demodulating incoming analog signals back into digital data. This modulation and demodulation process enables devices to communicate over long distances using existing infrastructure. Advanced modems use techniques such as phase-shift keying (PSK) and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) to maximize data transfer rates while minimizing signal degradation.
Working Principle of Codecs
Codecs operate by encoding and decoding digital data streams to compress audio or video signals for efficient transmission and storage. They utilize algorithms that reduce file size while preserving quality through lossy or lossless compression techniques. Unlike modems that modulate and demodulate signals for network communication, codecs focus explicitly on signal conversion within multimedia processing.
Applications of Modems
Modems play a crucial role in enabling data communication across telephone lines, cable systems, and cellular networks by converting digital signals into analog and vice versa. Widely used in internet access, remote work setups, and IoT devices, modems support both broadband and narrowband transmissions to ensure seamless connectivity. Understanding your modem's capabilities can optimize performance for streaming, video conferencing, and other data-intensive applications.
Applications of Codecs
Codecs are essential in multimedia applications, enabling efficient compression and decompression of audio and video files for streaming, video conferencing, and digital broadcasting. Unlike modems, which primarily facilitate data transmission over telephone lines or networks, codecs optimize media file size and quality, enhancing user experience in platforms like YouTube, Skype, and Spotify. Your choice of codec directly impacts the clarity, latency, and bandwidth usage in everyday digital communications and entertainment.
Modem vs Codec: Pros and Cons
Modem technology excels in enabling long-distance data transmission by converting digital signals to analog and vice versa, making it essential for internet connectivity but often limited by slower speeds and susceptibility to noise. Codec specializes in compressing and decompressing audio and video data, improving storage efficiency and streaming quality, yet it can introduce latency and requires significant processing power. Understanding the pros and cons of modem versus codec helps optimize data communication strategies based on transmission needs and media types.
Choosing Between Modem and Codec
Choosing between a modem and a codec depends on the specific communication needs and application context. Modems primarily modulate and demodulate analog signals for internet or telephone data transmission, making them essential for broadband connectivity, while codecs encode and decode digital audio or video streams, optimizing media quality and compression. Evaluate whether your priority is data transmission over networks (modem) or media signal processing for audio/video communication and streaming (codec) to make an informed choice.
Modem vs Codec Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com