TDD (Time Division Duplex) and FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) are two distinct methods for managing uplink and downlink transmissions in wireless communication, where TDD uses a single frequency band alternated over time, and FDD employs separate frequency bands simultaneously. Understanding the strengths and limitations of both TDD and FDD can greatly enhance Your network design decisions; explore the rest of the article to learn how each technology impacts performance and application suitability.
Table of Comparison
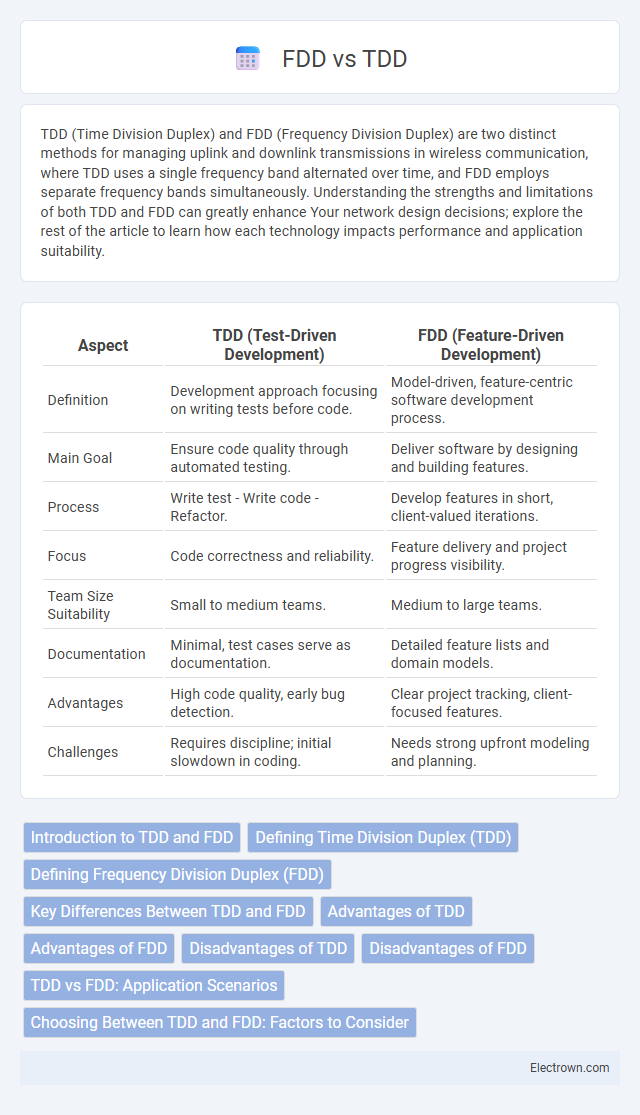
| Aspect | TDD (Test-Driven Development) | FDD (Feature-Driven Development) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development approach focusing on writing tests before code. | Model-driven, feature-centric software development process. |
| Main Goal | Ensure code quality through automated testing. | Deliver software by designing and building features. |
| Process | Write test - Write code - Refactor. | Develop features in short, client-valued iterations. |
| Focus | Code correctness and reliability. | Feature delivery and project progress visibility. |
| Team Size Suitability | Small to medium teams. | Medium to large teams. |
| Documentation | Minimal, test cases serve as documentation. | Detailed feature lists and domain models. |
| Advantages | High code quality, early bug detection. | Clear project tracking, client-focused features. |
| Challenges | Requires discipline; initial slowdown in coding. | Needs strong upfront modeling and planning. |
Introduction to TDD and FDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development process where developers write tests before coding functionality, ensuring code meets requirements and reduces bugs. Feature-Driven Development (FDD) centers on delivering client-valued features through a model-driven, iterative approach, emphasizing design and domain modeling. Both methodologies enhance software quality but differ in focus: TDD emphasizes early testing and code correctness, while FDD prioritizes feature delivery and project management.
Defining Time Division Duplex (TDD)
Time Division Duplex (TDD) is a communication method that transmits and receives data over the same frequency band by alternating time slots for uplink and downlink signals. TDD enables dynamic allocation of transmission time, optimizing network capacity based on traffic demands and improving spectral efficiency. This duplexing technique is widely used in modern wireless technologies such as 4G LTE and 5G NR due to its flexibility in handling asymmetric data flows.
Defining Frequency Division Duplex (FDD)
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) is a communication method that uses separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink, enabling simultaneous two-way data transmission. This separation reduces interference and is ideal for scenarios requiring continuous, real-time communication, such as voice calls. Your network performance may benefit from FDD's stable and predictable channel allocation, especially in environments with fixed bandwidth assignments.
Key Differences Between TDD and FDD
TDD (Time Division Duplex) and FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) differ primarily in how they allocate spectrum for uplink and downlink communication. TDD uses a single frequency band, alternating transmission and reception in different time slots, which allows dynamic adjustment of uplink and downlink ratios. FDD employs separate frequency bands for simultaneous uplink and downlink, providing consistent latency and interference isolation ideal for stable, continuous communication.
Advantages of TDD
TDD (Time Division Duplex) offers the advantage of using a single frequency band for both uplink and downlink, which simplifies spectrum allocation and reduces costs. It provides greater flexibility in adjusting uplink and downlink ratios dynamically based on traffic demands, improving network efficiency and user experience. TDD also enables better synchronization for massive MIMO and beamforming technologies, enhancing capacity and coverage in 5G networks.
Advantages of FDD
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) offers significant advantages such as continuous two-way communication with separate uplink and downlink frequency bands, which minimizes interference and enhances signal reliability. This method is ideal for applications requiring stable, consistent connections and is widely used in 4G LTE networks to support extensive mobile data traffic. Your network performance benefits from lower latency and improved spectrum efficiency, making FDD a robust choice for real-time voice and high-speed data transmission.
Disadvantages of TDD
TDD (Time Division Duplex) faces disadvantages such as increased latency due to the need for time-slot switching between uplink and downlink transmissions, which can limit real-time communication efficiency. It is also more susceptible to interference and signal fading in environments with unsynchronized users, leading to reduced reliability compared to FDD (Frequency Division Duplex). Furthermore, TDD systems require precise synchronization and guard times, increasing system complexity and overhead.
Disadvantages of FDD
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) faces limitations such as increased spectrum cost because it requires paired frequency bands, making it less efficient in spectrum utilization compared to Time Division Duplex (TDD). FDD is less flexible in handling asymmetric traffic loads since the uplink and downlink capacities are fixed, reducing adaptability to varying user demands. Furthermore, the complexity of designing separate transmit and receive hardware components raises both the initial deployment and maintenance costs for FDD systems.
TDD vs FDD: Application Scenarios
TDD (Time Division Duplex) is ideal for environments with symmetric traffic demands, such as video conferencing and live streaming, where uplink and downlink bandwidth are equally important. FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) performs better in scenarios with asymmetric traffic patterns, like traditional mobile broadband, where downlink traffic is significantly higher than uplink. Your choice between TDD and FDD should consider network topology, spectrum availability, and traffic requirements to optimize communication efficiency.
Choosing Between TDD and FDD: Factors to Consider
Choosing between TDD (Time Division Duplex) and FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) depends on factors such as spectrum availability, latency requirements, and deployment environment. TDD is ideal for asymmetric traffic patterns and dynamic spectrum use, while FDD offers lower latency and consistent performance in paired spectrum bands. Evaluating your network's traffic demands and regulatory constraints will help determine the optimal duplexing method for reliable wireless communication.
TDD vs FDD Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com