Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers up to 15.4 watts of power per device, while PoE+ increases the power output to 30 watts, enabling support for more demanding devices like PTZ cameras and VoIP phones. Explore this article to discover which option best suits your network needs and how to optimize your setup with the right technology.
Table of Comparison
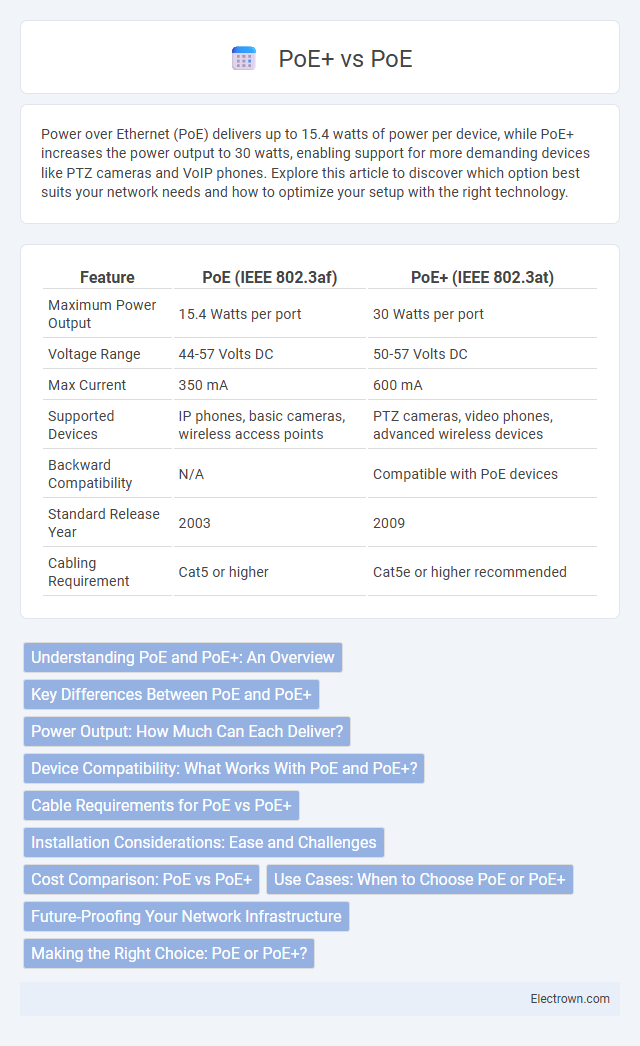
| Feature | PoE (IEEE 802.3af) | PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Power Output | 15.4 Watts per port | 30 Watts per port |
| Voltage Range | 44-57 Volts DC | 50-57 Volts DC |
| Max Current | 350 mA | 600 mA |
| Supported Devices | IP phones, basic cameras, wireless access points | PTZ cameras, video phones, advanced wireless devices |
| Backward Compatibility | N/A | Compatible with PoE devices |
| Standard Release Year | 2003 | 2009 |
| Cabling Requirement | Cat5 or higher | Cat5e or higher recommended |
Understanding PoE and PoE+: An Overview
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers up to 15.4 watts of power per port, enabling network devices like IP cameras and wireless access points to receive both data and power through a single Ethernet cable. PoE+ enhances this capability by supplying up to 30 watts per port, supporting devices with higher power demands such as PTZ cameras and advanced VoIP phones. Understanding the differences in power output and compatibility between PoE and PoE+ is essential for network design, ensuring adequate power delivery and efficient infrastructure deployment.
Key Differences Between PoE and PoE+
PoE (Power over Ethernet) delivers up to 15.4 watts of power per port, suitable for basic devices like IP phones and simple cameras, while PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) provides enhanced power up to 30 watts, supporting more demanding equipment such as pan-tilt-zoom cameras and wireless access points. PoE+ also features improved power management and efficiency, including better negotiation and detection protocols to optimize power delivery. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right technology to meet your network's power and performance requirements.
Power Output: How Much Can Each Deliver?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers up to 15.4 watts per port, suitable for low-power devices like IP cameras and VoIP phones. PoE+ significantly increases power output to 30 watts per port, enabling support for more demanding devices such as pan-tilt-zoom cameras and advanced wireless access points. The difference in power delivery capacity between PoE and PoE+ directly impacts device compatibility and network design decisions.
Device Compatibility: What Works With PoE and PoE+?
PoE (Power over Ethernet) supports devices requiring up to 15.4 watts per port, such as VoIP phones and basic wireless access points, while PoE+ provides up to 30 watts, compatible with more power-hungry devices like PTZ cameras and advanced wireless access points. PoE switches and injectors are backward compatible with PoE+ devices but limit the power to 15.4 watts, potentially causing underperformance or connection issues for high-power devices. Ensuring device compatibility involves matching power requirements with the appropriate PoE or PoE+ standard to optimize network performance and prevent power shortages.
Cable Requirements for PoE vs PoE+
PoE (Power over Ethernet) typically requires Cat5 cables to deliver up to 15.4 watts of power per port, while PoE+ demands higher quality cables like Cat5e or Cat6 to support increased power delivery up to 30 watts. These enhanced cable standards for PoE+ ensure minimal power loss and maintain optimal data transmission speeds, essential for powering more energy-intensive devices. When upgrading your network, selecting the correct cable type is crucial to maximize efficiency and device performance with PoE+ installations.
Installation Considerations: Ease and Challenges
PoE (Power over Ethernet) provides up to 15.4 watts per port, making it sufficient for basic devices and simplifying installation by reducing the need for separate power sources. PoE+ delivers up to 30 watts per port, supporting higher power devices but may require upgraded cabling and switches to handle increased current, introducing potential challenges in existing infrastructure. Choosing between PoE and PoE+ impacts installation ease, with PoE+ offering enhanced power capabilities at the cost of potentially more complex wiring and compatibility checks.
Cost Comparison: PoE vs PoE+
Power over Ethernet (PoE) offers a more cost-effective solution for low-power devices, with standard 802.3af delivering up to 15.4 watts per port, reducing cable and installation expenses. PoE+ (802.3at) supports higher power output up to 30 watts per port, which increases initial investment due to more robust switches and cabling requirements but accommodates power-hungry equipment like IP cameras and wireless access points. The cost differential between PoE and PoE+ is significant for large-scale deployments, making PoE preferable for budget-sensitive projects with minimal power needs.
Use Cases: When to Choose PoE or PoE+
PoE (Power over Ethernet) is ideal for low-power devices such as VoIP phones, basic wireless access points, and simple IP cameras, providing up to 15.4 watts per port. PoE+ offers higher power delivery, up to 30 watts per port, supporting more demanding devices like PTZ cameras, advanced wireless access points, and video phones requiring additional power for enhanced features. Selecting between PoE and PoE+ depends on the power requirements and functionality of the network equipment to ensure reliable performance and optimal energy use.
Future-Proofing Your Network Infrastructure
PoE+ (Power over Ethernet Plus) delivers up to 30 watts per port, nearly double the 15.4 watts offered by standard PoE, enabling support for more power-hungry devices like advanced IP cameras and wireless access points. Future-proofing your network infrastructure involves adopting PoE+ to accommodate growing power demands and ensure compatibility with emerging IoT technologies requiring higher wattage. Investing in PoE+ switches and cabling standards that support increased power and efficiency reduces the need for costly upgrades as network devices evolve.
Making the Right Choice: PoE or PoE+?
Choosing between PoE and PoE+ depends on your device power requirements and network infrastructure. PoE delivers up to 15.4 watts per port, ideal for devices like IP phones and simple wireless access points, while PoE+ supports up to 30 watts, tailored for power-hungry devices such as high-performance IP cameras and advanced Wi-Fi access points. Make sure your switch and equipment support the standard that matches your needs to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
PoE vs PoE+ Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com