VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) measures the efficiency of power transmission in a system by indicating the level of signal reflection, while Return Loss quantifies the amount of reflected signal lost due to impedance mismatch, expressed in decibels. Understanding these key differences can help you optimize your communication system's performance; explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively apply these concepts.
Table of Comparison
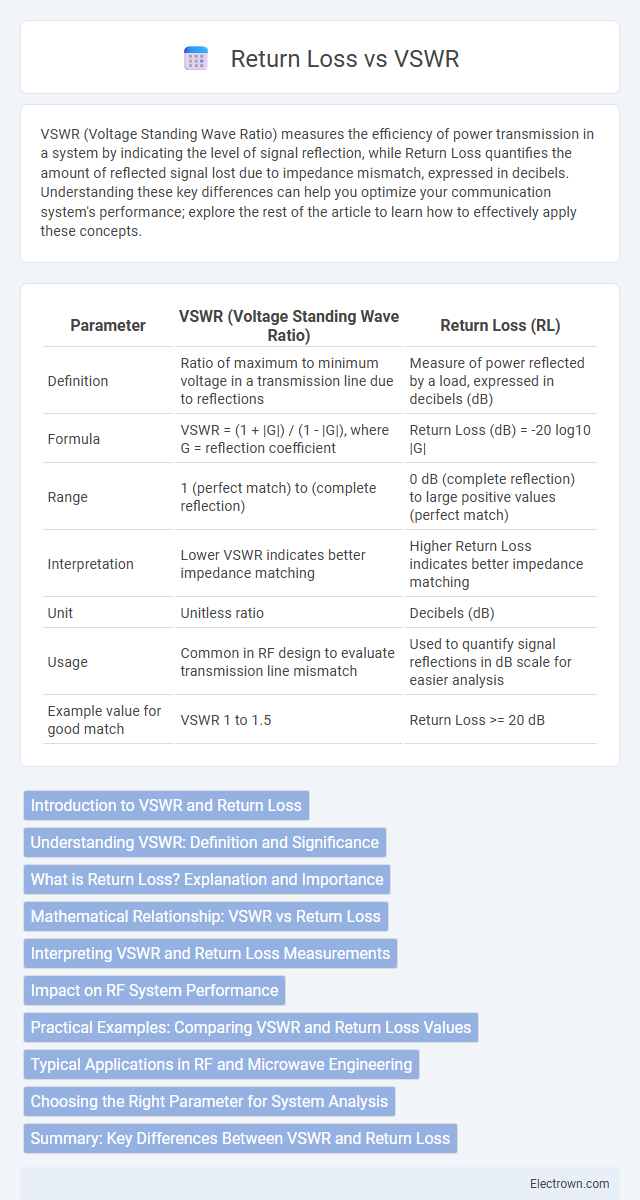
| Parameter | VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) | Return Loss (RL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of maximum to minimum voltage in a transmission line due to reflections | Measure of power reflected by a load, expressed in decibels (dB) |
| Formula | VSWR = (1 + |G|) / (1 - |G|), where G = reflection coefficient | Return Loss (dB) = -20 log10 |G| |
| Range | 1 (perfect match) to (complete reflection) | 0 dB (complete reflection) to large positive values (perfect match) |
| Interpretation | Lower VSWR indicates better impedance matching | Higher Return Loss indicates better impedance matching |
| Unit | Unitless ratio | Decibels (dB) |
| Usage | Common in RF design to evaluate transmission line mismatch | Used to quantify signal reflections in dB scale for easier analysis |
| Example value for good match | VSWR 1 to 1.5 | Return Loss >= 20 dB |
Introduction to VSWR and Return Loss
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) measures the efficiency of power transmission by comparing incident and reflected waves in a transmission line, indicating impedance matching quality. Return Loss quantifies the amount of power reflected back to the source in decibels, providing a direct measure of signal reflection and system performance. Understanding these parameters helps you optimize antenna systems and minimize signal loss for improved communication efficiency.
Understanding VSWR: Definition and Significance
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) quantifies the efficiency of power transmission by measuring the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage along a transmission line, indicating signal reflections caused by impedance mismatches. A lower VSWR value signifies better impedance matching and minimal signal loss, which is critical for optimizing antenna and RF system performance. Understanding VSWR helps you diagnose and minimize return loss, ensuring maximum energy transfer and improved communication reliability.
What is Return Loss? Explanation and Importance
Return Loss measures the amount of power reflected back from a transmission line, indicating how effectively the signal is transmitted without reflection. It is expressed in decibels (dB) and higher Return Loss values signify better impedance matching and less signal reflection. Understanding Return Loss is crucial for optimizing Your communication system's performance and minimizing signal degradation.
Mathematical Relationship: VSWR vs Return Loss
The mathematical relationship between VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) and Return Loss is defined by the equations: VSWR = (1 + |G|) / (1 - |G|) and Return Loss (dB) = -20 log10(|G|), where |G| represents the magnitude of the reflection coefficient. Return Loss quantifies how much power is reflected by the load, expressed in decibels, while VSWR measures the impedance matching quality on a linear scale. Understanding this relationship helps you interpret signal reflections and optimize transmission line performance effectively.
Interpreting VSWR and Return Loss Measurements
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) and Return Loss are critical parameters in assessing signal reflections in RF systems. VSWR values close to 1 indicate minimal reflections, while higher values suggest impedance mismatches that can degrade performance. Your interpretation of Return Loss, measured in dB, quantifies reflected power; higher Return Loss means better impedance matching and less signal reflection, ensuring efficient signal transmission.
Impact on RF System Performance
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) and Return Loss are critical parameters that directly impact RF system performance by indicating the efficiency of power transfer and signal reflection within the system. High VSWR values suggest significant signal reflections, leading to power loss, reduced transmitter efficiency, and potential damage to RF components. Your system's reliability improves with lower Return Loss, which signifies better impedance matching and minimal reflected signals, thus enhancing overall signal integrity and transmission quality.
Practical Examples: Comparing VSWR and Return Loss Values
A VSWR of 1.5 corresponds roughly to a return loss of 14 dB, indicating moderate signal reflection in RF systems. For instance, a VSWR of 2.0 aligns with a return loss of about 9.5 dB, often seen in practical antenna feed lines with minor mismatches. These values illustrate how lower VSWR and higher return loss represent better impedance matching and improved signal transmission efficiency.
Typical Applications in RF and Microwave Engineering
VSWR and Return Loss are critical parameters in RF and microwave engineering, commonly used to evaluate impedance matching in antennas, transmission lines, and RF components. Typical applications include ensuring efficient power transfer in wireless communication systems, radar systems, and satellite links, where low VSWR and high Return Loss indicate minimal signal reflection and improved system performance. Your RF design benefits from monitoring these metrics to optimize component integration and enhance signal integrity.
Choosing the Right Parameter for System Analysis
Return Loss provides a clearer measure of reflected power and is often preferred for assessing system performance in RF designs due to its logarithmic scale that simplifies interpretation of signal reflection. VSWR, expressed as a ratio, directly indicates impedance mismatch severity, making it useful for quick diagnostics in antenna and transmission line systems. Selecting between VSWR and Return Loss depends on whether precise quantification of reflected power or straightforward impedance mismatch assessment is prioritized in the specific RF system analysis.
Summary: Key Differences Between VSWR and Return Loss
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) measures the impedance matching quality in transmission lines by indicating the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage waves, while Return Loss quantifies the reflected signal power in decibels (dB), representing the efficiency of power transfer. A lower VSWR value close to 1 and higher Return Loss value indicate better impedance matching and minimal signal reflection. VSWR is a ratio without units, whereas Return Loss provides a logarithmic scale measurement, making it easier to interpret signal reflection performance in RF systems.
VSWR vs Return Loss Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com