NB-IoT offers extended coverage and low power consumption ideal for static, low-data IoT devices, while LTE-M supports higher data rates and mobility, making it suitable for real-time applications and mobile devices. Explore the rest of the article to understand which technology best fits Your IoT deployment needs.
Table of Comparison
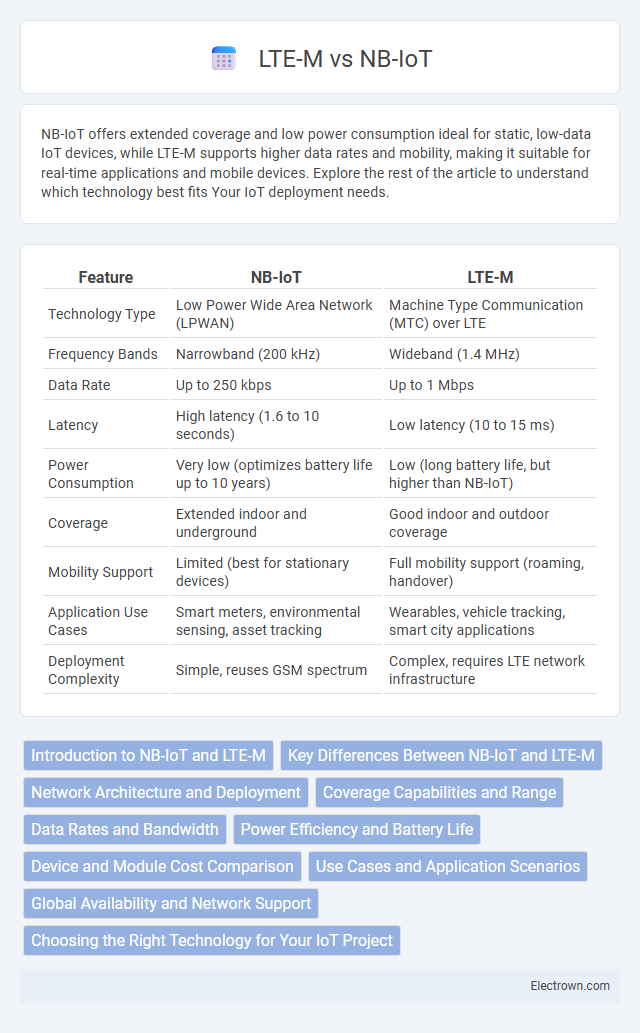
| Feature | NB-IoT | LTE-M |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) | Machine Type Communication (MTC) over LTE |
| Frequency Bands | Narrowband (200 kHz) | Wideband (1.4 MHz) |
| Data Rate | Up to 250 kbps | Up to 1 Mbps |
| Latency | High latency (1.6 to 10 seconds) | Low latency (10 to 15 ms) |
| Power Consumption | Very low (optimizes battery life up to 10 years) | Low (long battery life, but higher than NB-IoT) |
| Coverage | Extended indoor and underground | Good indoor and outdoor coverage |
| Mobility Support | Limited (best for stationary devices) | Full mobility support (roaming, handover) |
| Application Use Cases | Smart meters, environmental sensing, asset tracking | Wearables, vehicle tracking, smart city applications |
| Deployment Complexity | Simple, reuses GSM spectrum | Complex, requires LTE network infrastructure |
Introduction to NB-IoT and LTE-M
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things) and LTE-M (LTE Cat M1) are two prominent LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) technologies designed for IoT applications, offering optimized connectivity for low-power, wide-area devices. NB-IoT operates on a narrow bandwidth of 180 kHz, providing extended coverage and deep indoor penetration ideal for stationary sensors. LTE-M offers higher data rates up to 1 Mbps, supports mobility and voice, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate data throughput and device mobility.
Key Differences Between NB-IoT and LTE-M
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) operates on a narrowband spectrum of 200 kHz, optimizing for indoor coverage and long battery life, whereas LTE-M (LTE Cat-M1) supports wider bandwidths up to 1.4 MHz, enabling higher data rates and mobility. NB-IoT excels in low-cost, low-throughput applications with latency tolerance, while LTE-M supports real-time communication, voice (VoLTE), and handover for mobile IoT devices. Both technologies cater to massive IoT deployments but differ significantly in power consumption, bandwidth, latency, and mobility features.
Network Architecture and Deployment
NB-IoT utilizes a simplified network architecture with narrowband channels integrated into existing LTE infrastructure, enabling efficient deployment in coverage-limited areas through in-band, guard-band, or standalone modes. LTE-M supports full LTE functionality with wider bandwidth and mobility features, leveraging existing LTE networks for seamless connectivity and easier migration paths. Your choice between NB-IoT and LTE-M depends on deployment needs, with NB-IoT favoring deep indoor coverage and LTE-M excelling in mobility and throughput.
Coverage Capabilities and Range
NB-IoT offers superior coverage capabilities with a deeper indoor penetration and extended range, reaching up to 10 kilometers in rural areas, making it ideal for applications requiring wide-area connectivity. LTE-M provides moderate coverage with a range of around 1 to 5 kilometers, optimized for mobile IoT use cases and real-time data transmission. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize long-range, low-power coverage (NB-IoT) or better mobility and lower latency (LTE-M).
Data Rates and Bandwidth
NB-IoT offers lower data rates ranging from 20 to 250 kbps with narrow bandwidths of 180 kHz, making it ideal for simple, low-bandwidth IoT applications. LTE-M supports higher data rates up to 1 Mbps with wider bandwidths of 1.4 MHz, enabling more complex IoT use cases requiring faster transmission. Your choice between NB-IoT and LTE-M depends on the balance needed between data throughput and device energy efficiency.
Power Efficiency and Battery Life
NB-IoT offers superior power efficiency with extended battery life, often lasting up to 10 years on a single charge due to its low data rate and deep sleep modes. LTE-M supports higher data throughput but typically results in moderately shorter battery life, around 5 to 7 years, as it consumes more power during transmission. Your choice between NB-IoT and LTE-M should consider the balance between battery longevity and performance needs for your IoT application.
Device and Module Cost Comparison
NB-IoT modules typically offer lower device and module costs compared to LTE-M, making them ideal for large-scale deployments of simple sensors and low-bandwidth applications. LTE-M modules tend to be more expensive due to their support for higher data rates, mobility, and voice features like VoLTE. Cost differences impact choice based on application needs, with NB-IoT favoring low-cost, static devices and LTE-M suited for more complex, mobile IoT use cases.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios
NB-IoT excels in low-power, wide-area scenarios with infrequent data transmission such as smart metering, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking in dense urban environments. LTE-M supports applications requiring higher bandwidth and mobility, including real-time vehicle telematics, wearable devices, and smart city infrastructure with continuous data flow. Your choice depends on specific use case demands for power efficiency, data rates, and device mobility within the Internet of Things ecosystem.
Global Availability and Network Support
NB-IoT and LTE-M both offer extensive global availability, supported by major mobile network operators across regions including North America, Europe, and Asia. NB-IoT provides widespread coverage using existing LTE infrastructure with enhanced deep indoor penetration, making it ideal for stationary IoT devices. Your choice depends on network support in your target area, as LTE-M supports mobility and voice services, making it more suitable for applications requiring seamless roaming and real-time communication.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your IoT Project
NB-IoT offers ultra-low power consumption and superior indoor coverage, making it ideal for stationary IoT devices requiring long battery life and deep signal penetration. LTE-M supports higher data rates, mobility, and voice capabilities, suitable for applications like asset tracking and wearables demanding real-time communication. Assess device mobility, data transmission needs, and battery longevity to select the optimal LPWAN technology tailored to your IoT project's specific use case.
NB-IoT vs LTE-M Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com