HF (High Frequency) RFID operates at 13.56 MHz and is ideal for short-range applications like access control and payment systems, while UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID, operating between 860-960 MHz, offers longer read ranges and faster data transfer, making it suitable for inventory and asset tracking. Explore the rest of the article to understand which RFID technology best fits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
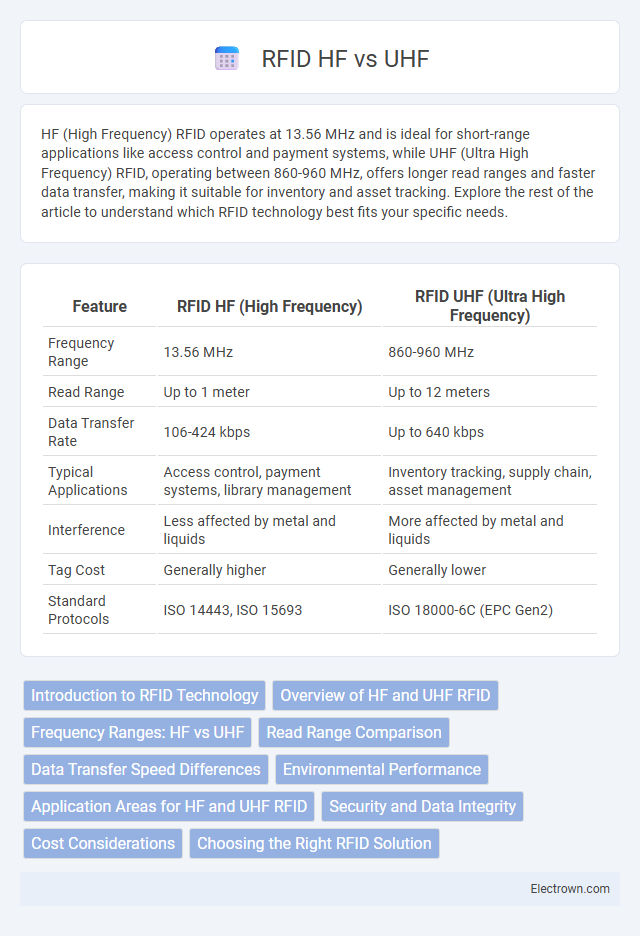
| Feature | RFID HF (High Frequency) | RFID UHF (Ultra High Frequency) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 13.56 MHz | 860-960 MHz |
| Read Range | Up to 1 meter | Up to 12 meters |
| Data Transfer Rate | 106-424 kbps | Up to 640 kbps |
| Typical Applications | Access control, payment systems, library management | Inventory tracking, supply chain, asset management |
| Interference | Less affected by metal and liquids | More affected by metal and liquids |
| Tag Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Standard Protocols | ISO 14443, ISO 15693 | ISO 18000-6C (EPC Gen2) |
Introduction to RFID Technology
RFID technology uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, with HF (High Frequency) operating at 13.56 MHz and UHF (Ultra High Frequency) ranging from 300 MHz to 3 GHz. HF RFID provides shorter read ranges up to 1 meter and excels in secure access control and payment systems, while UHF RFID offers longer read distances up to 12 meters, making it ideal for inventory management and supply chain logistics. Your choice between HF and UHF depends on the specific application requirements, including read range, data transfer speed, and environmental conditions.
Overview of HF and UHF RFID
HF (High Frequency) RFID operates at 13.56 MHz, offering short-range communication typically up to 10 cm to 1 meter, ideal for applications like access control and contactless payments. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID functions between 860 MHz and 960 MHz, enabling longer read ranges from 3 to 12 meters, well-suited for inventory management and asset tracking. Both HF and UHF RFID systems vary in read distance, data transfer speed, and susceptibility to interference, influencing their use in different environments.
Frequency Ranges: HF vs UHF
HF RFID operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, offering short-range communication typically up to 1 meter, making it ideal for applications like access control and contactless payments. UHF RFID functions between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, most commonly around 860-960 MHz, enabling longer read ranges up to 12 meters and faster data transfer rates suitable for inventory management and supply chain tracking. Your choice between HF and UHF depends primarily on the required reading distance and environmental conditions affecting signal propagation.
Read Range Comparison
HF RFID systems typically offer a read range of up to 1 meter, making them ideal for close-proximity applications such as access control and payment systems. UHF RFID technology extends this range significantly, often achieving 4 to 10 meters or more, which suits inventory management and asset tracking in large areas. Understanding the read range differences helps optimize Your choice based on operational environment and required scanning distances.
Data Transfer Speed Differences
HF RFID systems typically offer data transfer speeds ranging from 26.48 kbps to 424 kbps, suitable for applications requiring moderate speed and short read distances up to 10 cm. UHF RFID technology supports significantly higher data rates, often between 150 kbps and 640 kbps, enabling faster communication over longer distances, sometimes exceeding 12 meters. The increased data transfer speed of UHF RFID enhances efficiency in supply chain management and inventory tracking where rapid reading of multiple tags is critical.
Environmental Performance
RFID HF operates at 13.56 MHz and demonstrates superior performance in environments with metal and liquids, as its short range and lower frequency mitigate interference. UHF RFID, typically between 860-960 MHz, offers longer read ranges but is more susceptible to signal degradation near metal objects and water. Choosing between HF and UHF depends on specific environmental challenges, with HF favored for industrial, healthcare, and item-level tagging where environmental interference is prevalent.
Application Areas for HF and UHF RFID
HF RFID technology excels in applications requiring close-range communication such as access control, contactless payment, and smart cards due to its secure and interference-resistant characteristics. UHF RFID is widely used for asset tracking, inventory management, and supply chain logistics because of its longer read range and faster data transfer capabilities. Your choice between HF and UHF depends on the specific needs of operational range, read speed, and environmental factors in your application area.
Security and Data Integrity
RFID HF (High Frequency) systems operate at 13.56 MHz and offer enhanced security protocols such as ISO 14443 and ISO 15693, incorporating encryption and mutual authentication to protect data integrity against eavesdropping and cloning attacks. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID systems, operating between 860-960 MHz, generally provide longer read ranges but are more susceptible to interception and relay attacks due to weaker built-in security standards, although recent advancements introduce improved cryptographic methods like AES-based authentication. HF RFID's robust security features make it ideal for sensitive applications like access control and payment systems, while UHF is favored for inventory tracking where read range and speed are prioritized over advanced security.
Cost Considerations
RFID HF systems generally incur lower initial costs due to simpler reader designs and less expensive tags, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects. UHF RFID offers longer read ranges but comes with higher upfront investment and increased maintenance expenses due to more complex hardware and environmental sensitivity. Your choice between HF and UHF should weigh these cost factors alongside application requirements for optimal budget allocation.
Choosing the Right RFID Solution
When choosing the right RFID solution, consider that HF (High Frequency) RFID operates at 13.56 MHz and is ideal for short-range applications like access control and payment systems, offering reliable communication within 10 cm to 1 meter. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID, operating between 860-960 MHz, supports longer read ranges up to 12 meters and faster data transfer, making it suitable for inventory tracking and logistics. Your choice depends on factors such as read distance, environment, and data transfer needs to maximize efficiency and accuracy in your RFID deployment.
RFID HF vs UHF Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com