H.265 offers better compression efficiency than H.264, reducing file sizes while maintaining high video quality, which is ideal for streaming and storage. Explore the detailed comparison to understand how these codecs impact Your video playback experience.
Table of Comparison
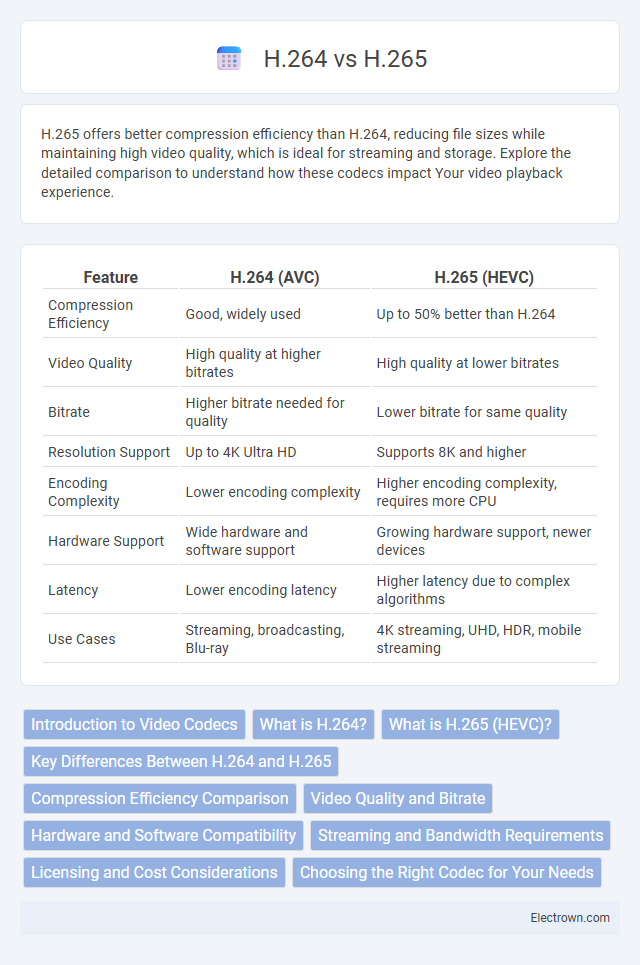
| Feature | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Efficiency | Good, widely used | Up to 50% better than H.264 |
| Video Quality | High quality at higher bitrates | High quality at lower bitrates |
| Bitrate | Higher bitrate needed for quality | Lower bitrate for same quality |
| Resolution Support | Up to 4K Ultra HD | Supports 8K and higher |
| Encoding Complexity | Lower encoding complexity | Higher encoding complexity, requires more CPU |
| Hardware Support | Wide hardware and software support | Growing hardware support, newer devices |
| Latency | Lower encoding latency | Higher latency due to complex algorithms |
| Use Cases | Streaming, broadcasting, Blu-ray | 4K streaming, UHD, HDR, mobile streaming |
Introduction to Video Codecs
H.264 and H.265 are advanced video codecs that compress digital video streams efficiently to reduce file size and bandwidth usage. H.265, also known as HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), offers approximately 50% better data compression compared to its predecessor H.264, enabling higher quality video at lower bit rates. These codecs are widely used in streaming platforms, video conferencing, and broadcasting to optimize video delivery across different devices and network conditions.
What is H.264?
H.264, also known as AVC (Advanced Video Coding), is a widely used video compression standard that efficiently reduces file size while maintaining high video quality, making it ideal for streaming, video conferencing, and Blu-ray discs. This codec balances performance and compatibility, supporting resolutions from standard definition to 4K and beyond, and is broadly supported across devices and platforms. Understanding H.264 helps you choose the right codec for your video encoding needs, especially when compatibility and bandwidth efficiency are priorities.
What is H.265 (HEVC)?
H.265, also known as High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is the successor to H.264 designed to deliver significantly improved video compression efficiency, enabling up to 50% better data compression at the same video quality. HEVC supports resolutions up to 8K UHD and enhances streaming performance by reducing bandwidth usage and storage requirements. This advanced codec uses improved motion compensation and prediction algorithms, making it ideal for modern high-resolution video applications and broadcasting.
Key Differences Between H.264 and H.265
H.264 and H.265 are video compression standards with H.265 offering approximately 50% better data compression than H.264 at the same video quality, enabling higher resolution streaming such as 4K and 8K with reduced bandwidth usage. H.265 uses more advanced algorithms including improved motion compensation and prediction, which results in higher efficiency but requires more processing power for encoding and decoding. When deciding between these codecs, your choice depends on device compatibility, desired video quality, and bandwidth constraints.
Compression Efficiency Comparison
H.265 (HEVC) offers significantly improved compression efficiency compared to H.264 (AVC), reducing video file sizes by approximately 50% at the same quality level. This improvement allows higher resolution streaming, such as 4K and 8K, with lower bandwidth requirements, optimizing your network usage. The enhanced algorithm in H.265 efficiently handles complex scenes and motion, resulting in better video quality even at lower bitrates.
Video Quality and Bitrate
H.265 (HEVC) offers significantly improved video quality at lower bitrates compared to H.264 (AVC), enabling sharper images with less data usage. This efficiency makes H.265 ideal for streaming high-resolution content like 4K and 8K videos, preserving your bandwidth while enhancing visual clarity. Choosing H.265 helps you achieve better compression without sacrificing video quality, optimizing playback across various devices and platforms.
Hardware and Software Compatibility
H.264 enjoys widespread hardware and software compatibility, supporting a vast range of devices including older smartphones, cameras, and video players, making it ideal for broad accessibility. H.265, or HEVC, offers superior compression efficiency but requires more advanced hardware decoding capabilities, often limiting compatibility to newer devices and software updates. Ensuring your device or platform supports H.265 is essential for leveraging its improved video quality and reduced bandwidth usage.
Streaming and Bandwidth Requirements
H.265, also known as HEVC, offers significantly improved compression efficiency compared to H.264, reducing bandwidth requirements by up to 50% for the same video quality. This efficiency makes H.265 ideal for streaming high-resolution content like 4K and 8K while maintaining smoother playback with lower data usage. Your streaming experience benefits from faster load times and less buffering, especially on networks with limited bandwidth.
Licensing and Cost Considerations
H.264, also known as AVC, has widespread adoption with more predictable and generally lower licensing fees compared to H.265 (HEVC), which involves more complex and fragmented patent pools leading to higher overall royalty costs. You should consider that H.265 delivers improved compression efficiency but may incur increased expenses due to multiple licensing bodies and stricter patent enforcement. Budget constraints and intended distribution scale play critical roles when choosing between H.264's cost-effectiveness and H.265's advanced but pricier technology.
Choosing the Right Codec for Your Needs
H.264 and H.265 are video compression standards where H.265 offers up to 50% better data compression at the same video quality compared to H.264, making it ideal for 4K and high-resolution streaming. Choosing the right codec depends on your device compatibility, bandwidth availability, and processing power, as H.265 requires more advanced hardware for encoding and decoding. For lower resolution content or older devices, H.264 remains widely supported and efficient, balancing quality and performance.
H.264 vs H.265 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com