32-bit audio provides a higher dynamic range and greater precision in sound processing compared to 64-bit, which primarily serves specialized professional applications requiring extensive data handling beyond typical listening needs. Understanding the differences can enhance your audio setup and performance; explore the rest of the article to learn how these formats impact your sound experience.
Table of Comparison
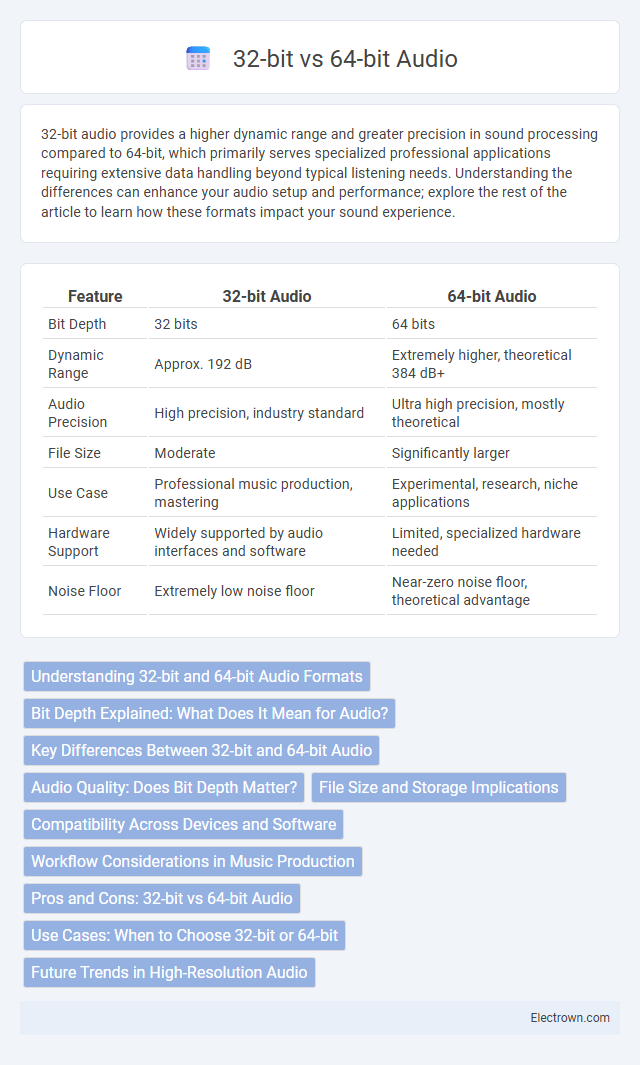
| Feature | 32-bit Audio | 64-bit Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Bit Depth | 32 bits | 64 bits |
| Dynamic Range | Approx. 192 dB | Extremely higher, theoretical 384 dB+ |
| Audio Precision | High precision, industry standard | Ultra high precision, mostly theoretical |
| File Size | Moderate | Significantly larger |
| Use Case | Professional music production, mastering | Experimental, research, niche applications |
| Hardware Support | Widely supported by audio interfaces and software | Limited, specialized hardware needed |
| Noise Floor | Extremely low noise floor | Near-zero noise floor, theoretical advantage |
Understanding 32-bit and 64-bit Audio Formats
32-bit and 64-bit audio formats refer to the bit depth used in digital audio processing, which directly impacts dynamic range and precision of sound representation. 32-bit audio offers a wider dynamic range and greater headroom than 16-bit or 24-bit formats, reducing noise and distortion during mixing, while 64-bit audio, primarily used in processing rather than playback, provides extremely high precision for audio editing and processing tasks. Your choice between 32-bit and 64-bit audio depends on whether you prioritize compatibility and file size or maximum audio fidelity and editing flexibility.
Bit Depth Explained: What Does It Mean for Audio?
Bit depth in audio refers to the number of bits used to represent each audio sample, directly impacting dynamic range and noise floor. A 32-bit depth offers a significantly higher dynamic range and lower distortion compared to a 64-bit depth, which is typically used for processing and calculation rather than final audio output. Your choice between 32-bit and 64-bit audio affects recording clarity, editing precision, and overall sound quality.
Key Differences Between 32-bit and 64-bit Audio
32-bit audio offers a dynamic range of 192 dB, allowing for extremely precise sound detail and less noise compared to 64-bit audio, which theoretically provides an even greater dynamic range and precision well beyond human hearing capabilities. The main difference lies in bit depth: 32-bit audio can capture and process more subtle variations in sound amplitude, improving audio quality for professional mixing and mastering, whereas 64-bit audio is primarily used in high-end digital signal processing and audio production software for complex calculations. Your choice should depend on whether you need top-tier audio precision for critical sound engineering or more advanced DSP computation that benefits from 64-bit floating-point accuracy.
Audio Quality: Does Bit Depth Matter?
Bit depth directly influences audio quality by determining the dynamic range and resolution of a digital audio signal, with 32-bit offering a theoretical dynamic range of 1920 dB compared to 96 dB in 16-bit and 144 dB in 24-bit audio, providing more detail and headroom. However, most human hearing cannot perceive differences beyond 24-bit depth in typical listening environments, making 32-bit audio primarily beneficial for post-production and processing rather than playback quality. The higher bit depth reduces quantization noise and allows for greater precision in audio editing, but it does not inherently improve the audible quality in consumer audio applications.
File Size and Storage Implications
64-bit audio offers significantly higher dynamic range and precision compared to 32-bit audio, but it results in larger file sizes that can quickly consume your storage capacity. While 32-bit audio files are more storage-efficient and easier to manage, 64-bit files require almost double the space, impacting hard drive utilization and backup requirements. Choosing between 32-bit and 64-bit audio depends on balancing your need for audio quality with your available storage resources.
Compatibility Across Devices and Software
32-bit audio files offer higher dynamic range and resolution but may face compatibility issues with older hardware and software primarily designed for 16-bit or 24-bit formats. Most modern devices and digital audio workstations (DAWs) support 64-bit processing internally, enhancing audio precision without requiring 64-bit audio files, which remain relatively rare and less universally supported. Ensuring optimal playback and editing compatibility often involves using 24-bit audio, striking a balance between quality and widespread device and software acceptance.
Workflow Considerations in Music Production
Choosing between 32-bit and 64-bit audio in music production significantly impacts workflow efficiency and resource management. 64-bit audio processing allows access to larger memory resources, enabling smoother handling of complex projects with numerous tracks and high-resolution plugins, reducing latency and enhancing real-time performance. However, 32-bit audio files ensure broader compatibility with legacy software and require less CPU power, making them suitable for smaller projects and hardware with limited capabilities.
Pros and Cons: 32-bit vs 64-bit Audio
32-bit audio offers higher dynamic range and finer detail in sound processing compared to 16-bit but can be limited by hardware compatibility and increased file sizes. 64-bit audio provides extraordinary precision and headroom for professional audio production and mixing, allowing for extensive manipulation without quality loss, but it demands more processing power and storage resources. Choosing between 32-bit and 64-bit audio depends on balancing the need for audio fidelity against system performance capabilities and application requirements.
Use Cases: When to Choose 32-bit or 64-bit
Choose 32-bit audio for standard music production and streaming, as it efficiently handles dynamic range and file sizes suitable for most consumer applications. Opt for 64-bit audio in professional audio editing, mastering, and sound design where extreme precision and headroom are critical for manipulating high-resolution audio without quality loss. Your decision depends on balancing performance needs against processing power and storage constraints.
Future Trends in High-Resolution Audio
32-bit audio offers a significantly higher dynamic range and greater detail compared to 64-bit audio, which mainly serves as an internal processing format rather than a common playback standard. Future trends in high-resolution audio emphasize 32-bit depth for capturing ultra-fine sound nuances, ensuring your audio experience maintains exceptional clarity and accuracy. Advances in DAC technology and streaming platforms will likely prioritize 32-bit audio support to meet the growing demand for immersive, studio-quality sound.
32-bit vs 64-bit Audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com