Coaxial cables offer reliable signal transmission with shielding that minimizes interference, making them ideal for traditional TV and internet connections, while optical cables provide faster data speeds and greater bandwidth by transmitting light signals, perfect for modern high-speed networks. Discover how to choose the best option for your specific needs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
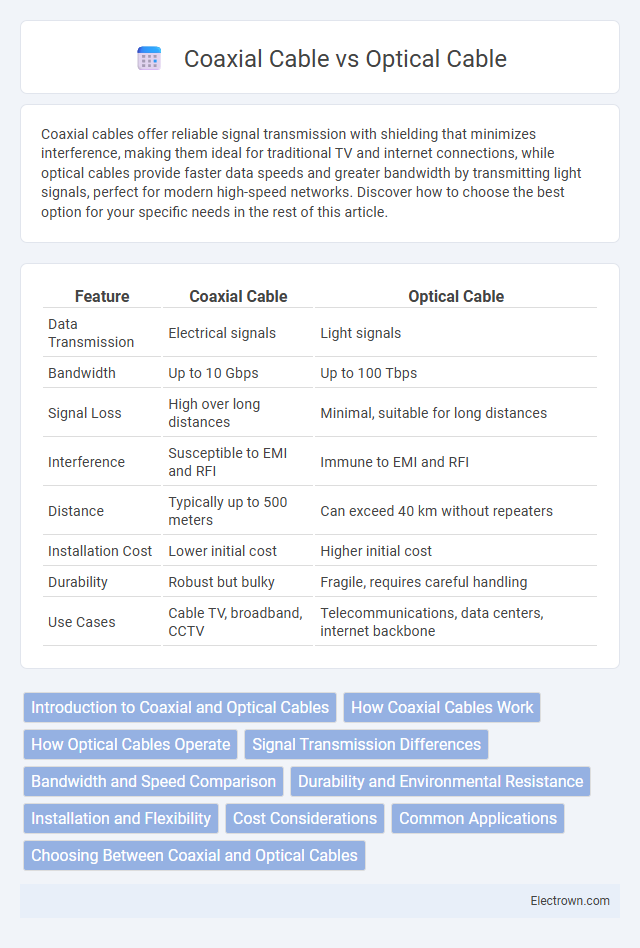
| Feature | Coaxial Cable | Optical Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission | Electrical signals | Light signals |
| Bandwidth | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 100 Tbps |
| Signal Loss | High over long distances | Minimal, suitable for long distances |
| Interference | Susceptible to EMI and RFI | Immune to EMI and RFI |
| Distance | Typically up to 500 meters | Can exceed 40 km without repeaters |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Robust but bulky | Fragile, requires careful handling |
| Use Cases | Cable TV, broadband, CCTV | Telecommunications, data centers, internet backbone |
Introduction to Coaxial and Optical Cables
Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, and outer jacket, enabling efficient transmission of radio frequency signals with minimal interference. Optical cables use thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light pulses, offering higher bandwidth, longer distance capabilities, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Both cables serve critical roles in telecommunications, broadband internet, and networking, with optical fibers increasingly preferred for high-speed data transfer and long-haul communication.
How Coaxial Cables Work
Coaxial cables transmit electrical signals through a central copper conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and a metallic shield, which minimizes electromagnetic interference and signal loss. The shield also protects against external noise, ensuring reliable data transmission over moderate distances. Your choice of cable depends on the required bandwidth, distance, and susceptibility to interference, with coaxial cables performing well in cable TV and broadband applications.
How Optical Cables Operate
Optical cables transmit data using light signals through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers, enabling high-speed communication with minimal signal loss over long distances. These cables employ total internal reflection to guide light pulses, allowing for greater bandwidth and immunity to electromagnetic interference compared to coaxial cables. Optical fibers support faster data rates and longer transmission ranges, making them ideal for modern broadband networks and telecommunications infrastructure.
Signal Transmission Differences
Coaxial cables transmit signals using electrical impulses through a copper core, which can experience signal degradation and electromagnetic interference over long distances. Optical cables use light pulses transmitted through glass or plastic fibers, enabling higher bandwidth and virtually no signal loss or interference over extended ranges. This fundamental difference makes optical cables superior for high-speed, long-distance data transmission compared to coaxial cables.
Bandwidth and Speed Comparison
Optical cables offer significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to coaxial cables, supporting up to terabits per second over long distances without signal degradation. Coaxial cables typically provide bandwidths up to several gigahertz, suitable for cable TV and basic internet, but experience more attenuation and interference over extended lengths. The superior frequency range and minimal signal loss of optical cables make them ideal for modern high-speed internet, data centers, and telecommunications networks.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Coaxial cables feature robust shielding and thick insulation, providing strong durability and resistance to physical damage, moisture, and electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for harsh environments. Optical cables, composed of glass or plastic fibers, excel in resisting electromagnetic interference and corrosion, but their fragility requires careful handling and environmental protection measures to maintain performance in physically demanding conditions. Both cable types offer environmental resistance, with coaxial cables better suited for rugged outdoor installations and optical cables preferred in settings requiring high immunity to electrical noise.
Installation and Flexibility
Coaxial cables are easier and quicker to install due to their rigid structure and compatibility with existing infrastructure, making them suitable for shorter distances and indoor applications. Optical cables, although more complex and requiring specialized tools for splicing and termination, offer greater flexibility with thinner, lighter design and superior resistance to electromagnetic interference, ideal for long-distance and high-speed data transmission. The choice between coaxial and optical cable installations depends on factors like environmental conditions, budget, and performance requirements.
Cost Considerations
Coaxial cables generally offer lower installation and material costs compared to optical cables, making them a more budget-friendly option for short-distance data transmission. Optical cables, while more expensive initially, provide greater long-term value through higher bandwidth capacity and lower maintenance requirements. Your decision should weigh upfront expenses against the need for future-proof performance and scalability.
Common Applications
Coaxial cables are commonly used for cable television distribution, internet connections in residential and commercial buildings, and closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems due to their ability to transmit television signals and broadband data efficiently. Optical cables, or fiber optic cables, are predominantly deployed in telecommunications networks, high-speed internet infrastructures, and long-distance data transmission because of their higher bandwidth capacity, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and longer transmission distances. Both cable types serve critical roles in network connectivity, with coaxial cables preferred for shorter-range applications and optical cables favored for high-performance, large-scale data transfer.
Choosing Between Coaxial and Optical Cables
Choosing between coaxial and optical cables depends on factors like data transmission speed, distance, and interference resistance. Optical cables offer higher bandwidth and longer reach with minimal signal loss, making them ideal for high-speed internet and large-scale networks. Your decision should consider installation cost, existing infrastructure compatibility, and future scalability requirements.
Coaxial Cable vs Optical Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com