GDDR6 offers higher data transfer rates and improved power efficiency compared to GDDR5, making it ideal for modern GPUs and gaming applications that demand faster memory performance. Discover how these advancements can impact your system's speed and responsiveness by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
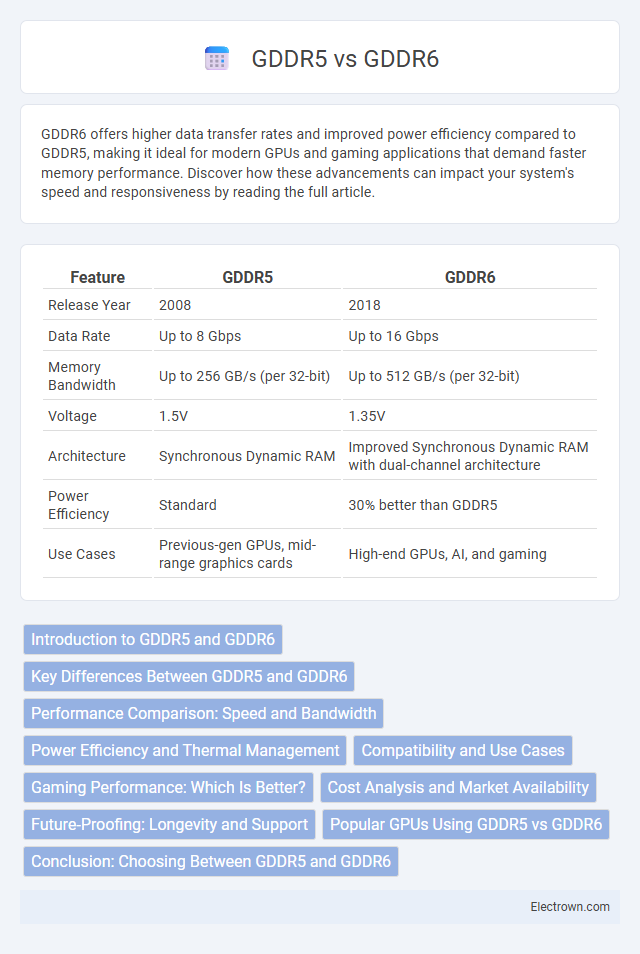
| Feature | GDDR5 | GDDR6 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 2008 | 2018 |
| Data Rate | Up to 8 Gbps | Up to 16 Gbps |
| Memory Bandwidth | Up to 256 GB/s (per 32-bit) | Up to 512 GB/s (per 32-bit) |
| Voltage | 1.5V | 1.35V |
| Architecture | Synchronous Dynamic RAM | Improved Synchronous Dynamic RAM with dual-channel architecture |
| Power Efficiency | Standard | 30% better than GDDR5 |
| Use Cases | Previous-gen GPUs, mid-range graphics cards | High-end GPUs, AI, and gaming |
Introduction to GDDR5 and GDDR6
GDDR5 (Graphics Double Data Rate 5) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) widely used in GPUs for enhanced bandwidth and efficient data transfer rates up to 8 Gbps. GDDR6, the successor of GDDR5, improves overall performance by doubling the data rate capability to 16 Gbps while offering better power efficiency and higher memory density. These advancements in GDDR6 make it ideal for high-end graphics processing tasks in gaming, professional rendering, and AI computations.
Key Differences Between GDDR5 and GDDR6
GDDR6 offers significantly higher data transfer rates, typically ranging from 14 to 16 Gbps, compared to GDDR5's 7 to 8 Gbps, making it ideal for demanding graphics workloads and gaming applications. Power efficiency improvements in GDDR6 reduce voltage usage to around 1.35V versus the 1.5V in GDDR5, helping lower overall system power consumption and heat output. You will also benefit from GDDR6's enhanced reliability features and increased memory density, allowing for larger VRAM capacities on modern GPUs.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Bandwidth
GDDR6 delivers significantly higher performance compared to GDDR5, with speeds reaching up to 16 Gbps per pin, whereas GDDR5 typically maxes out around 8 Gbps. The increased bandwidth of GDDR6, often doubling that of GDDR5, enables faster data transfer rates essential for gaming, video editing, and AI workloads. Choosing GDDR6 for Your graphics card ensures smoother rendering and improved overall system responsiveness.
Power Efficiency and Thermal Management
GDDR6 offers significant improvements in power efficiency compared to GDDR5, delivering up to 35% lower power consumption per bit transferred, thanks to its optimized voltage scaling and enhanced signaling technology. The reduced power draw in GDDR6 directly contributes to better thermal management, allowing GPUs to maintain lower operating temperatures under load, which can extend hardware lifespan and improve overall performance stability. Enhanced thermal efficiency in GDDR6 modules minimizes cooling requirements, making it a preferred choice for high-performance graphics cards and gaming systems where heat dissipation is critical.
Compatibility and Use Cases
GDDR5 and GDDR6 memory modules differ significantly in compatibility, with GDDR5 widely supported in older graphics cards, gaming consoles, and mainstream computing devices, while GDDR6 is primarily designed for newer GPUs demanding higher bandwidth and efficiency. Use cases for GDDR5 include budget-friendly gaming systems and mid-tier professional applications, whereas GDDR6 suits high-performance gaming, advanced AI workloads, and 4K or 8K ultra-high-definition rendering. GDDR6's enhanced data rates and lower power consumption make it ideal for modern devices requiring faster and more reliable memory performance.
Gaming Performance: Which Is Better?
GDDR6 offers significantly higher memory bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to GDDR5, resulting in smoother frame rates and faster load times for gaming. Your gaming experience benefits from increased data transfer speeds, enabling better support for high-resolution textures and complex game environments. This makes GDDR6 the superior choice for delivering optimal gaming performance on modern graphics cards.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
GDDR6 memory offers superior performance and efficiency compared to GDDR5 but comes at a higher cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and increased demand in high-end graphics cards. GDDR5 remains widely available and more affordable, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious users or mainstream applications. Your decision between these memory types should consider current market availability and price fluctuations influenced by supply chain conditions and technological adoption.
Future-Proofing: Longevity and Support
GDDR6 offers enhanced future-proofing compared to GDDR5 due to its higher data transfer rates, improved power efficiency, and greater memory density, making it better suited for upcoming graphics-intensive applications and gaming workloads. The widespread industry support and ongoing development around GDDR6 ensure longer-lasting compatibility with new GPU architectures and software standards. This results in extended device lifespan and reduced need for early hardware upgrades, providing better value over time.
Popular GPUs Using GDDR5 vs GDDR6
Popular GPUs using GDDR5 memory include the NVIDIA GTX 1060 and AMD RX 570, which offer solid performance for mid-range gaming and graphics tasks. In contrast, GPUs featuring GDDR6 memory, such as the NVIDIA RTX 3060 and AMD RX 6700 XT, deliver faster data rates and improved efficiency, enhancing your gaming and rendering experiences. Choosing a GPU with GDDR6 can provide noticeable benefits in bandwidth and future-proofing compared to GDDR5 models.
Conclusion: Choosing Between GDDR5 and GDDR6
GDDR6 outperforms GDDR5 in data transfer rates and power efficiency, making it the preferred choice for high-performance graphics cards and gaming applications. GDDR5 remains relevant in budget-friendly and mid-range devices where cost savings are prioritized over peak performance. Selecting between GDDR5 and GDDR6 depends on the specific needs for speed, power consumption, and budget constraints in the target system.
GDDR5 vs GDDR6 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com