Near Field Communication (NFC) enables quick data exchange and device pairing by simply bringing devices within close proximity, offering faster setup times compared to traditional Bluetooth pairing that requires device discovery and manual confirmation. Discover how these technologies differ in speed, convenience, and security to optimize Your wireless connections by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
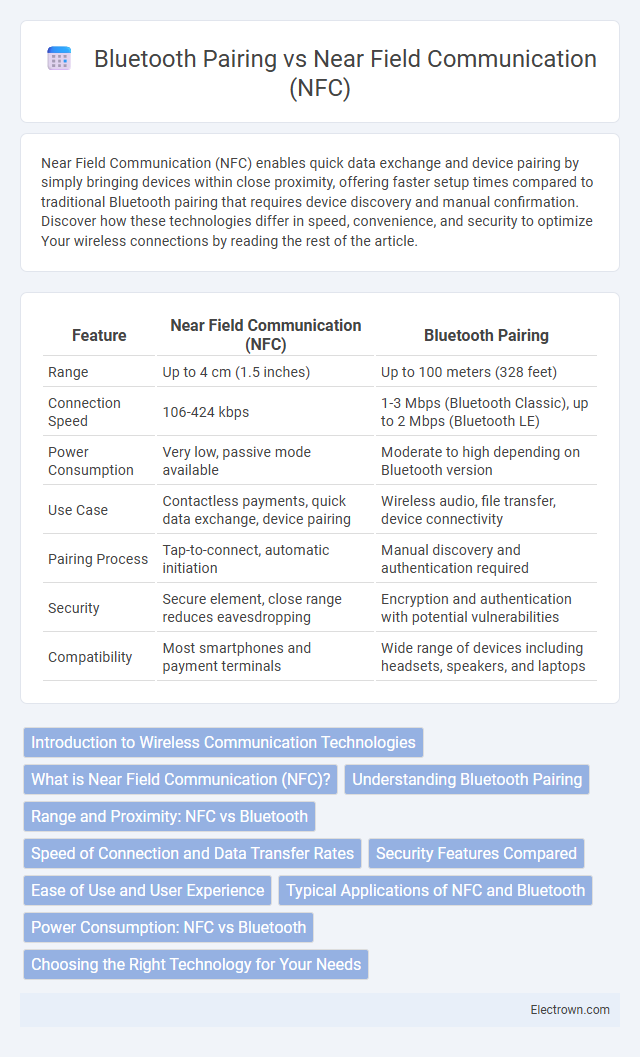
| Feature | Near Field Communication (NFC) | Bluetooth Pairing |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 4 cm (1.5 inches) | Up to 100 meters (328 feet) |
| Connection Speed | 106-424 kbps | 1-3 Mbps (Bluetooth Classic), up to 2 Mbps (Bluetooth LE) |
| Power Consumption | Very low, passive mode available | Moderate to high depending on Bluetooth version |
| Use Case | Contactless payments, quick data exchange, device pairing | Wireless audio, file transfer, device connectivity |
| Pairing Process | Tap-to-connect, automatic initiation | Manual discovery and authentication required |
| Security | Secure element, close range reduces eavesdropping | Encryption and authentication with potential vulnerabilities |
| Compatibility | Most smartphones and payment terminals | Wide range of devices including headsets, speakers, and laptops |
Introduction to Wireless Communication Technologies
Near Field Communication (NFC) enables secure, short-range wireless communication typically within 4 centimeters, facilitating instant device pairing and data exchange. Bluetooth pairing establishes longer-range connections, up to 100 meters, suitable for continuous data transfer and audio streaming between devices. Your choice between NFC and Bluetooth depends on the required range, speed, and ease of connection for wireless communication tasks.
What is Near Field Communication (NFC)?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless technology that enables two devices to exchange data when they are placed within a few centimeters of each other. Unlike Bluetooth pairing, NFC does not require manual setup or device discovery, making it faster and more convenient for initiating connections or transactions. Your smartphone or payment card equipped with NFC can instantly interact with compatible terminals for secure communication and contactless payments.
Understanding Bluetooth Pairing
Bluetooth pairing establishes a secure connection between devices by exchanging authentication keys, typically requiring manual confirmation through PIN codes or passkeys. This process enables longer-range communication compared to NFC, with Bluetooth devices pairing over distances up to 10 meters or more. Your Bluetooth-enabled gadgets rely on this pairing protocol for continuous wireless data transfer, making it essential for applications like audio streaming, file sharing, and peripheral connections.
Range and Proximity: NFC vs Bluetooth
Near Field Communication (NFC) operates within a very short range, typically up to 4 centimeters, ensuring secure and immediate device interactions ideal for contactless payments. Bluetooth pairing, on the other hand, offers a much broader range between 10 to 100 meters depending on the Bluetooth class, providing greater flexibility for connecting devices over longer distances. Your choice between NFC and Bluetooth should consider the balance between required proximity for security and the convenience of range for seamless connectivity.
Speed of Connection and Data Transfer Rates
NFC establishes connections instantly within milliseconds, making it ideal for quick pairing, but supports slower data transfer rates of around 424 kbps. Bluetooth pairing takes slightly longer, typically a few seconds to establish, yet offers significantly faster data transfer speeds, with Bluetooth 5.0 reaching up to 2 Mbps and Bluetooth 5.2 exceeding 3 Mbps. Your choice between NFC and Bluetooth pairing should consider whether rapid connection initiation or higher data transfer rates are more critical for your application.
Security Features Compared
Near Field Communication (NFC) offers enhanced security through its short operational range of typically 4 cm, limiting exposure to interception or unauthorized access. Bluetooth pairing employs various security modes, including Secure Simple Pairing (SSP), but remains more vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks and requires user interaction for device authentication. NFC's proximity-based connection reduces attack surfaces, making it more secure for sensitive transactions compared to Bluetooth's broader transmission range.
Ease of Use and User Experience
Near Field Communication (NFC) offers superior ease of use compared to Bluetooth pairing by enabling instant device connection through simple physical proximity, eliminating the need for manual discovery or passcode input. Bluetooth pairing often requires navigating device menus, selecting devices from a list, and entering PINs, which can complicate the user experience. NFC's fast, intuitive interaction enhances user satisfaction, especially in environments demanding quick and seamless connectivity.
Typical Applications of NFC and Bluetooth
NFC is commonly used for contactless payments, access control, and quick device pairing with smartphones due to its short range and ease of use. Bluetooth pairing excels in continuous data transfer applications like wireless headphones, speakers, and fitness trackers, offering longer range connectivity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize rapid, secure interactions (NFC) or sustained wireless communication (Bluetooth).
Power Consumption: NFC vs Bluetooth
NFC technology consumes significantly less power than Bluetooth, typically operating in passive mode with energy transferred from the reader to the tag, resulting in minimal battery drain. Bluetooth pairing requires a continuous connection and active radio communication, leading to higher power consumption, especially during data transfer. For energy-sensitive applications, NFC is more efficient due to its short-range, contactless communication design that conserves device battery life.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Near Field Communication (NFC) offers rapid, secure connections ideal for contactless payments and quick device pairing within a few centimeters, while Bluetooth pairing excels in longer-range data transfer and continuous audio streaming. Understanding your specific use case, such as short-range convenience with NFC or versatile connectivity with Bluetooth, ensures you select the technology that best fits your requirements. Your choice should balance ease of use, range, power consumption, and the type of data exchange for optimal performance.
Near Field Communication (NFC) vs Bluetooth Pairing Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com