eMMC offers basic internal storage with moderate speed and affordability, making it suitable for budget devices, while UFS provides faster data transfer rates and enhanced efficiency, ideal for high-performance smartphones and laptops. Discover the key differences and determine which storage technology best fits Your device's needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
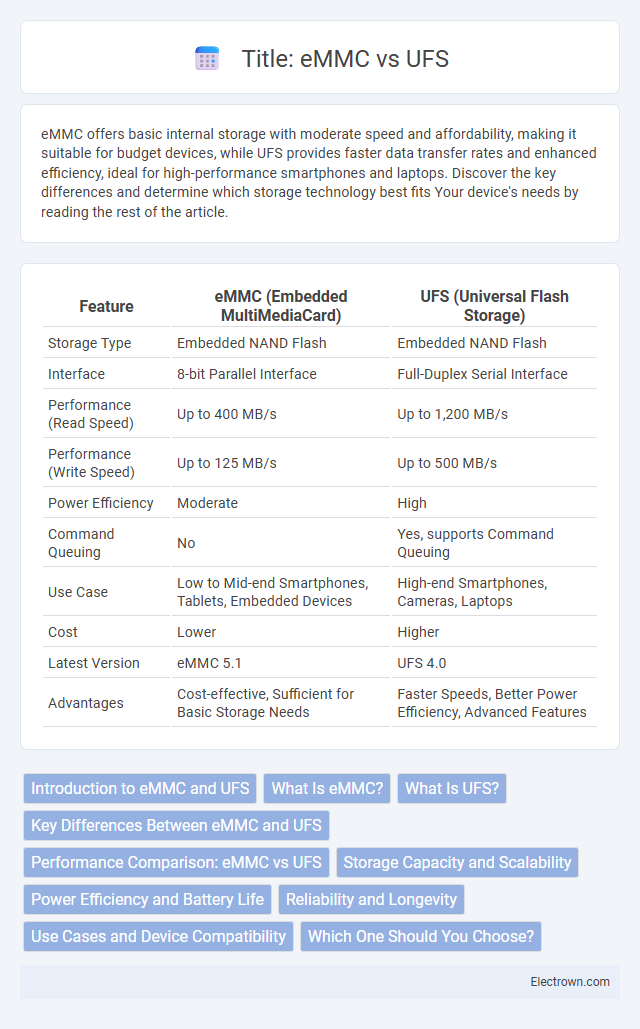
| Feature | eMMC (Embedded MultiMediaCard) | UFS (Universal Flash Storage) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Embedded NAND Flash | Embedded NAND Flash |
| Interface | 8-bit Parallel Interface | Full-Duplex Serial Interface |
| Performance (Read Speed) | Up to 400 MB/s | Up to 1,200 MB/s |
| Performance (Write Speed) | Up to 125 MB/s | Up to 500 MB/s |
| Power Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Command Queuing | No | Yes, supports Command Queuing |
| Use Case | Low to Mid-end Smartphones, Tablets, Embedded Devices | High-end Smartphones, Cameras, Laptops |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Latest Version | eMMC 5.1 | UFS 4.0 |
| Advantages | Cost-effective, Sufficient for Basic Storage Needs | Faster Speeds, Better Power Efficiency, Advanced Features |
Introduction to eMMC and UFS
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) and UFS (Universal Flash Storage) are advanced storage technologies commonly used in smartphones and other electronic devices. eMMC offers cost-effective, reliable flash memory with slower data transfer speeds, while UFS provides significantly faster read/write speeds and improved performance due to its full-duplex interface and command queuing. Understanding the differences between eMMC and UFS can help you choose the right storage solution tailored to your device's performance needs.
What Is eMMC?
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) is a type of non-volatile flash memory commonly used for storage in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices, integrating the memory and controller into a single package. It offers moderate performance and reliability with data transfer rates typically ranging from 250 MB/s to 400 MB/s, making it suitable for budget-friendly devices. Compared to UFS (Universal Flash Storage), eMMC has slower read/write speeds and less advanced command queuing, impacting multitasking and app loading efficiency.
What Is UFS?
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) is a high-performance flash storage standard designed for mobile devices, offering faster data transfer speeds and improved power efficiency compared to traditional eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) storage. UFS supports full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous read and write operations, which enhances overall device responsiveness and multitasking capabilities. Your device benefits from UFS with quicker app launches, smoother video playback, and faster file transfers, making it a superior choice for modern smartphones and tablets.
Key Differences Between eMMC and UFS
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) uses a parallel interface with lower data transfer speeds, typically maxing out around 400 MB/s, whereas UFS (Universal Flash Storage) employs a high-speed serial interface supporting speeds up to 2.9 GB/s, enabling faster read/write performance. UFS supports full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous read and write operations, while eMMC operates in half-duplex mode, limiting data throughput. Key differences also include advanced command queuing and power efficiency in UFS, making it ideal for high-performance mobile devices compared to the older, cost-effective eMMC technology.
Performance Comparison: eMMC vs UFS
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) offers significantly faster read and write speeds compared to eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard), delivering improved performance for smartphones and other devices. UFS supports full-duplex data transfer, enabling simultaneous read/write operations, whereas eMMC operates in half-duplex mode, limiting efficiency. Your device's overall responsiveness and app loading times benefit greatly from the advanced architecture and higher bandwidth provided by UFS technology.
Storage Capacity and Scalability
eMMC storage typically ranges from 4GB to 256GB, suitable for entry-level devices, while UFS offers higher capacities starting from 32GB up to 1TB, catering to high-performance smartphones and tablets. UFS supports scalable storage solutions with faster read/write speeds and better energy efficiency, enhancing overall device performance. Manufacturers favor UFS for its advanced architecture and future-proof scalability in emerging mobile and embedded systems.
Power Efficiency and Battery Life
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) offers significantly better power efficiency compared to eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard), resulting in longer battery life for mobile devices. UFS supports full-duplex data transfer and lower voltage operation, reducing energy consumption during read and write cycles. Devices utilizing UFS typically experience faster data access with less power drain, enhancing overall battery performance.
Reliability and Longevity
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) offers significantly higher reliability and longer longevity compared to eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) due to its advanced error correction algorithms and wear-leveling techniques. The faster data transfer rates and more efficient handling of read/write cycles in UFS reduce device degradation over time, ensuring consistent performance throughout your device's lifespan. Choosing UFS storage can enhance your device's durability and maintain data integrity during prolonged usage.
Use Cases and Device Compatibility
eMMC storage suits budget smartphones, tablets, and entry-level laptops where cost-effectiveness and moderate performance are priorities. UFS drives are preferred in high-end smartphones, gaming devices, and advanced automotive systems requiring faster data transfer speeds and improved multitasking capabilities. Your choice depends on device compatibility and performance needs, with UFS offering superior efficiency for intensive applications.
Which One Should You Choose?
UFS offers faster data transfer speeds and better energy efficiency compared to eMMC, making it ideal for high-performance smartphones and devices requiring quick read/write operations. eMMC remains a cost-effective solution suitable for budget devices or applications where speed is less critical. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize performance and future-proofing (UFS) or affordability and basic functionality (eMMC).
eMMC vs UFS Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com