HDMI ARC transmits audio and video signals through a single cable, supporting higher-quality sound formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD, while Optical Audio uses fiber optic cables limiting it to stereo and compressed surround formats. Understanding the differences helps you choose the best connection for your home theater setup; read on to explore which option suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
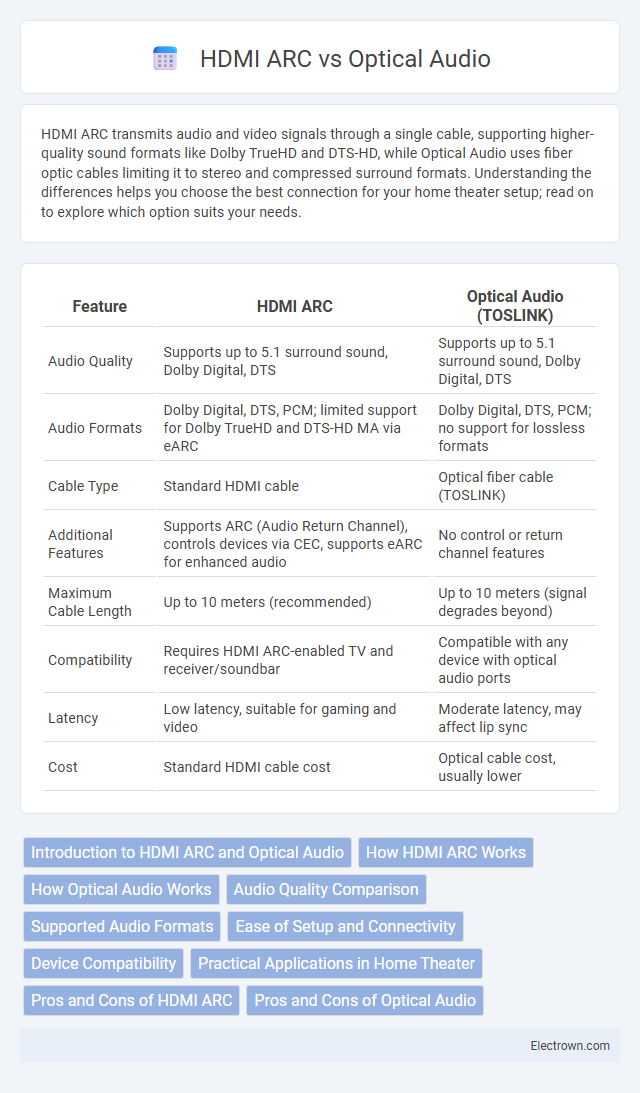
| Feature | HDMI ARC | Optical Audio (TOSLINK) |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Quality | Supports up to 5.1 surround sound, Dolby Digital, DTS | Supports up to 5.1 surround sound, Dolby Digital, DTS |
| Audio Formats | Dolby Digital, DTS, PCM; limited support for Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD MA via eARC | Dolby Digital, DTS, PCM; no support for lossless formats |
| Cable Type | Standard HDMI cable | Optical fiber cable (TOSLINK) |
| Additional Features | Supports ARC (Audio Return Channel), controls devices via CEC, supports eARC for enhanced audio | No control or return channel features |
| Maximum Cable Length | Up to 10 meters (recommended) | Up to 10 meters (signal degrades beyond) |
| Compatibility | Requires HDMI ARC-enabled TV and receiver/soundbar | Compatible with any device with optical audio ports |
| Latency | Low latency, suitable for gaming and video | Moderate latency, may affect lip sync |
| Cost | Standard HDMI cable cost | Optical cable cost, usually lower |
Introduction to HDMI ARC and Optical Audio
HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) enables two-way audio transmission between your TV and audio devices using a single HDMI cable, supporting high-quality digital sound formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. Optical audio, also known as TOSLINK, transmits digital audio signals via fiber-optic cables but lacks support for advanced audio formats and relies on separate cabling. Choosing between HDMI ARC and Optical Audio depends on your setup's compatibility and the desired audio quality.
How HDMI ARC Works
HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) transmits audio signals from a TV back to an AV receiver or soundbar using a single HDMI cable, simplifying connectivity and reducing cable clutter. It supports high-quality audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, enabling immersive home theater experiences without needing separate audio cables. HDMI ARC also allows devices to communicate for volume and power control via Consumer Electronics Control (CEC).
How Optical Audio Works
Optical audio transmits digital sound signals using light pulses through a fiber optic cable, ensuring minimal electromagnetic interference and high-quality audio output. It supports multi-channel audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS but lacks the bandwidth for advanced formats such as Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD Master Audio. Optical audio works by converting electrical audio signals into light signals at the source, which are then received and converted back into electrical signals by the audio device.
Audio Quality Comparison
HDMI ARC provides superior audio quality compared to Optical Audio by supporting higher bandwidths and advanced audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, delivering lossless surround sound. Optical Audio is limited to compressed formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, resulting in lower fidelity and fewer channel options. For the best audio experience, Your setup benefits more from HDMI ARC's enhanced capabilities and future-proof compatibility.
Supported Audio Formats
HDMI ARC supports advanced audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, and Dolby Atmos, enabling high-definition, immersive sound experiences for your home theater system. Optical audio is limited to compressed formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, which offer good quality but lack support for the latest high-resolution audio streams. Choosing HDMI ARC ensures compatibility with a wider range of audio formats for superior sound performance.
Ease of Setup and Connectivity
HDMI ARC offers simpler setup by using a single cable for both audio and video signals, reducing clutter and allowing automatic device recognition and control via HDMI-CEC. Optical audio requires a separate Toslink cable, which can complicate connections and often lacks support for control commands between devices. The direct HDMI ARC connection also supports higher bandwidth audio formats, enhancing overall convenience and performance.
Device Compatibility
HDMI ARC offers broader device compatibility by supporting both audio and video signals through a single cable, making it ideal for modern TVs, soundbars, and home theater systems equipped with HDMI ports. Optical Audio connections, while reliable for digital audio transmission, are limited to audio-only signals and may not work with devices lacking dedicated optical ports. Your choice should consider whether your devices support HDMI ARC for a more streamlined setup or if optical audio is your best option for older equipment.
Practical Applications in Home Theater
HDMI ARC supports both audio and video signals over a single cable, making it ideal for simplifying connections in your home theater setup. Optical audio offers high-quality sound transmission but is limited to audio only, requiring separate cables for video. Choosing HDMI ARC enhances practicality by enabling control of compatible devices with one remote and reducing cable clutter.
Pros and Cons of HDMI ARC
HDMI ARC supports both high-quality audio and control signals, enabling simplified connections and easier control of multiple devices with a single remote. It carries uncompressed audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, enhancing sound quality compared to optical audio's limited support for compressed formats. However, HDMI ARC may face compatibility issues between different brands and requires HDMI-compatible devices, whereas optical audio is more universally compatible and immune to electromagnetic interference.
Pros and Cons of Optical Audio
Optical audio cables provide high-quality digital sound transmission with immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for long-distance connections without signal degradation. However, optical audio supports only stereo and compressed surround formats, lacking compatibility with advanced audio formats like Dolby TrueHD or DTS:X, which limits its use for high-end home theater systems. Additionally, the fiber optic cables are fragile and can be easily damaged if bent excessively, posing a durability concern compared to HDMI ARC.
HDMI ARC vs Optical Audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com