Fast charging and quick charging both aim to reduce the time needed to power up your device, but they differ in technology and charging speeds depending on the battery capacity and charger specifications. Discover how these charging methods impact your device's performance and which option suits your needs best by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
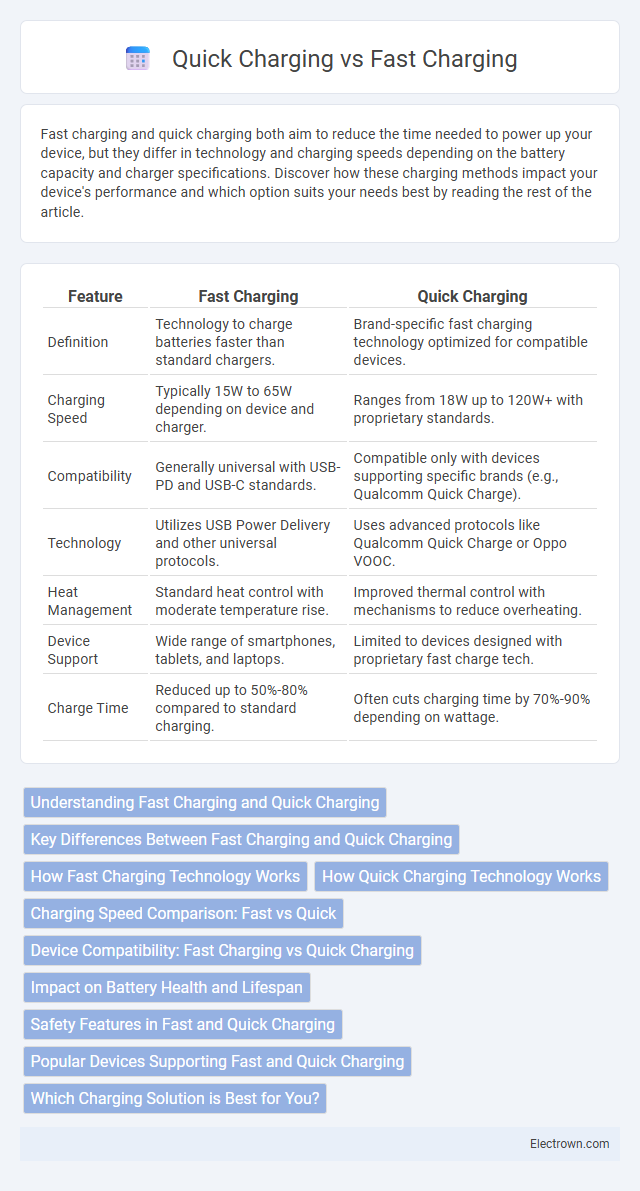
| Feature | Fast Charging | Quick Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology to charge batteries faster than standard chargers. | Brand-specific fast charging technology optimized for compatible devices. |
| Charging Speed | Typically 15W to 65W depending on device and charger. | Ranges from 18W up to 120W+ with proprietary standards. |
| Compatibility | Generally universal with USB-PD and USB-C standards. | Compatible only with devices supporting specific brands (e.g., Qualcomm Quick Charge). |
| Technology | Utilizes USB Power Delivery and other universal protocols. | Uses advanced protocols like Qualcomm Quick Charge or Oppo VOOC. |
| Heat Management | Standard heat control with moderate temperature rise. | Improved thermal control with mechanisms to reduce overheating. |
| Device Support | Wide range of smartphones, tablets, and laptops. | Limited to devices designed with proprietary fast charge tech. |
| Charge Time | Reduced up to 50%-80% compared to standard charging. | Often cuts charging time by 70%-90% depending on wattage. |
Understanding Fast Charging and Quick Charging
Fast Charging typically refers to charging technologies that deliver higher power levels, enabling a device to reach 50% or more battery capacity in approximately 30 minutes, often utilizing standards like USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) or Qualcomm Quick Charge. Quick Charging is a proprietary technology developed by Qualcomm, designed to increase charging speed by adjusting voltage and current dynamically based on the device's battery condition, optimizing efficiency and heat management. Both methods aim to reduce charging time significantly compared to traditional charging, but Quick Charging often requires compatible Qualcomm chipsets, whereas Fast Charging encompasses a broader range of standards and devices.
Key Differences Between Fast Charging and Quick Charging
Fast Charging delivers higher power output by increasing the voltage or current to reduce charging time, typically found in standards like USB Power Delivery; Quick Charging, often associated with Qualcomm Quick Charge technology, optimizes voltage levels dynamically for compatible devices. The key differences lie in protocol compatibility, power delivery mechanisms, and charging speed efficiency, with Fast Charging supporting broader device ecosystems while Quick Charging requires specific hardware support. Understanding these distinctions ensures your device charges safely and efficiently without overheating or battery damage.
How Fast Charging Technology Works
Fast charging technology increases the power delivered to your device by boosting voltage or current, enabling batteries to fill up more rapidly than with standard charging. Quick charging protocols, such as Qualcomm Quick Charge or USB Power Delivery, dynamically adjust voltage and current levels to optimize charging speed while protecting battery health. Understanding how these technologies manage energy flow can help you choose the best charger for efficient and safe power replenishment.
How Quick Charging Technology Works
Quick charging technology works by increasing the voltage and current delivered to the battery, allowing it to absorb power more rapidly without generating excessive heat. Advanced communication protocols between the charger and the device optimize power delivery, ensuring safety and efficiency during the charging process. Your device's battery management system manages this flow to protect battery health while achieving significantly reduced charging times compared to standard fast charging.
Charging Speed Comparison: Fast vs Quick
Fast charging typically delivers power at 15-30 watts, efficiently boosting your device's battery in around 1 to 1.5 hours, while quick charging technology can push this power output up to 65 watts or more, drastically reducing charging time to under 40 minutes. Fast charging suits everyday top-ups and moderate use, whereas quick charging is ideal for rapid battery replenishment during tight schedules. Understanding the power delivery capabilities and compatibility of your device ensures optimal charging speed and battery health.
Device Compatibility: Fast Charging vs Quick Charging
Fast Charging technology provides broad device compatibility by adapting charging speeds according to a device's battery capacity and supported voltage levels, making it suitable for various smartphones and tablets. Quick Charging, often associated with specific brands like Qualcomm Quick Charge, requires compatible hardware within both the charger and device to achieve accelerated power delivery, limiting its use to supported models. Understanding the compatibility differences helps consumers select chargers that maximize efficiency without risking battery damage.
Impact on Battery Health and Lifespan
Fast charging delivers higher power to reduce your device's charging time but generates more heat, which can accelerate battery degradation and reduce lifespan. Quick charging balances speed with optimized heat management to minimize stress on battery cells, helping maintain healthier battery performance over time. Choosing quick charging methods can extend your battery's longevity while still providing relatively fast recharge speeds.
Safety Features in Fast and Quick Charging
Fast Charging and Quick Charging both incorporate advanced safety features such as temperature control, over-voltage protection, and short-circuit prevention to protect your device during rapid power transfer. Fast Charging standards often include dynamic power adjustment to prevent overheating, while Quick Charging protocols prioritize efficient current management to maintain battery health. Understanding these safety mechanisms ensures your device charges swiftly without compromising long-term performance.
Popular Devices Supporting Fast and Quick Charging
Popular devices supporting fast charging include the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra, iPhone 14 Pro Max with MagSafe fast charging, and OnePlus 11, all equipped with chargers delivering up to 50W or higher power output. Quick charging is prominently supported by Qualcomm Quick Charge-enabled smartphones like the Xiaomi Redmi Note 12, Motorola Moto G Power, and LG V60 ThinQ, offering rapid battery replenishment through varying voltage levels for speeds typically around 18W to 30W. Both charging technologies are widely used in flagship and mid-range phones to minimize downtime and enhance user convenience.
Which Charging Solution is Best for You?
Fast charging delivers higher power output for rapid battery replenishment, ideal for users needing quick top-ups during short breaks. Quick charging optimizes charging speed based on device compatibility and battery health, ensuring efficient and safer power delivery over time. Your choice depends on device support and daily usage patterns, with fast charging benefiting urgent needs and quick charging offering balanced efficiency.
Fast Charging vs Quick Charging Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com