Edge detectors identify sudden changes in signal voltage indicating a transition or event, while level detectors monitor whether a signal has crossed a specific voltage threshold and maintain that status. Understanding the key differences between edge and level detectors can enhance your ability to design precise electronic circuits; continue reading to explore their applications and functionalities in detail.
Table of Comparison
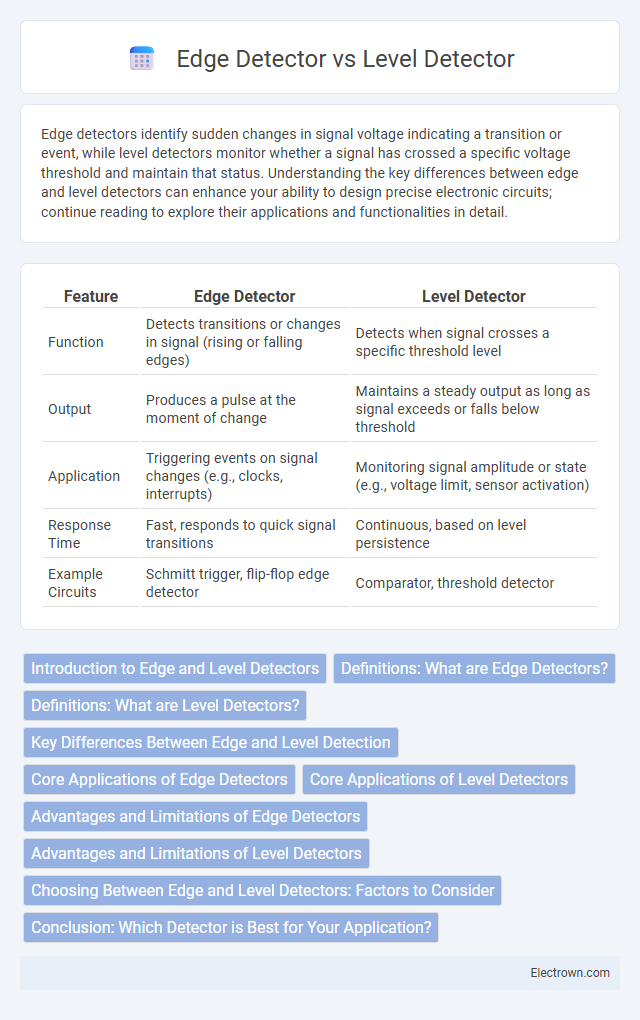
| Feature | Edge Detector | Level Detector |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects transitions or changes in signal (rising or falling edges) | Detects when signal crosses a specific threshold level |
| Output | Produces a pulse at the moment of change | Maintains a steady output as long as signal exceeds or falls below threshold |
| Application | Triggering events on signal changes (e.g., clocks, interrupts) | Monitoring signal amplitude or state (e.g., voltage limit, sensor activation) |
| Response Time | Fast, responds to quick signal transitions | Continuous, based on level persistence |
| Example Circuits | Schmitt trigger, flip-flop edge detector | Comparator, threshold detector |
Introduction to Edge and Level Detectors
Edge detectors identify signal transitions by capturing voltage changes at rising or falling edges, crucial for timing and synchronization applications. Level detectors monitor input signals relative to a defined threshold, generating outputs based on whether the signal voltage is above or below this level, essential in voltage monitoring and protection circuits. Understanding the differences helps optimize your design for specific signal processing needs in electronics and communication systems.
Definitions: What are Edge Detectors?
Edge detectors are electronic circuits or software algorithms designed to identify changes in signal levels, specifically detecting transitions such as rising or falling edges in digital signals. They are crucial in timing applications, triggering events precisely when the input changes from low to high (positive edge) or high to low (negative edge). Unlike level detectors that respond to a constant high or low voltage level, edge detectors focus solely on the moment a signal switches state.
Definitions: What are Level Detectors?
Level detectors are electronic circuits designed to sense when an input signal reaches a specific threshold voltage, producing an output that indicates whether the signal level is above or below this set point. These devices operate by comparing the input voltage to a predetermined reference voltage and remain steady as long as the input stays on one side of the threshold. Unlike edge detectors that respond to rapid changes or transitions in signals, level detectors provide continuous monitoring of signal amplitude relative to the threshold.
Key Differences Between Edge and Level Detection
Edge detectors identify transitions between signal states by capturing moments when the input changes from low to high or high to low, making them ideal for triggering actions on signal edges. Level detectors continuously monitor the signal voltage level, activating when the input remains above or below a predefined threshold, suited for detecting steady states. The primary difference lies in edge detectors responding to changes or pulses, while level detectors focus on sustained signal levels.
Core Applications of Edge Detectors
Edge detectors are primarily utilized in image processing and computer vision to identify object boundaries, enhancing feature extraction and scene segmentation accuracy. They play a crucial role in applications such as medical imaging, autonomous vehicle navigation, and industrial inspection by detecting abrupt intensity changes that signify edges. Level detectors, conversely, are more common in signal processing and electronic circuits for threshold-based event detection rather than spatial analysis.
Core Applications of Level Detectors
Level detectors are primarily used in applications requiring precise measurement of liquid levels in tanks, reservoirs, and pipelines to ensure safety and operational efficiency. These devices are crucial in industries such as water treatment, chemical processing, and oil and gas, where maintaining accurate liquid levels prevents overflows and equipment damage. Your monitoring systems benefit from level detectors' ability to provide continuous, reliable feedback, enabling real-time control and automation.
Advantages and Limitations of Edge Detectors
Edge detectors offer precise timing control by triggering on specific signal transitions, enabling accurate detection of rising or falling edges in digital circuits. Their advantages include sensitivity to signal changes, making them ideal for capturing short pulses or events, but they can be prone to noise, causing false triggering if signal integrity is compromised. Your choice between edge and level detectors should consider the need for timing accuracy versus stability in noisy environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Level Detectors
Level detectors excel at monitoring continuous signals, offering straightforward and reliable detection of signal thresholds, which is ideal for applications requiring consistent amplitude measurement. Their simplicity ensures low computational overhead and efficient implementation, but they struggle with noise sensitivity and cannot precisely determine rapid signal changes or timing information. You should consider these limitations when accuracy in transient detection or edge timing is critical in your system design.
Choosing Between Edge and Level Detectors: Factors to Consider
Choosing between edge detectors and level detectors depends on the nature of the signal and the specific application requirements. Edge detectors are ideal for capturing rapid changes or transitions in a signal, making them suitable for timing or pulse detection, while level detectors focus on maintaining a state when a signal crosses a predefined threshold, useful in control systems or alarms. Your decision should consider factors such as noise sensitivity, response speed, and the importance of detecting transitions versus sustaining signal levels.
Conclusion: Which Detector is Best for Your Application?
Edge detectors excel in identifying rapid signal transitions, making them ideal for applications requiring precise timing or triggering, such as pulse measurement and digital communication systems. Level detectors are better suited for monitoring continuous signal thresholds, often used in voltage monitoring, audio processing, and system protection circuits. The choice depends on whether the application demands detecting sudden changes or maintaining awareness of signal levels.
Edge detector vs level detector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com