EPROM and EEPROM differ primarily in their data retention and erase methods, with EPROM requiring ultraviolet light for erasure and EEPROM allowing electrical erasure and reprogramming on a byte level. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the right memory type for your electronic projects, so explore the rest of the article for a detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
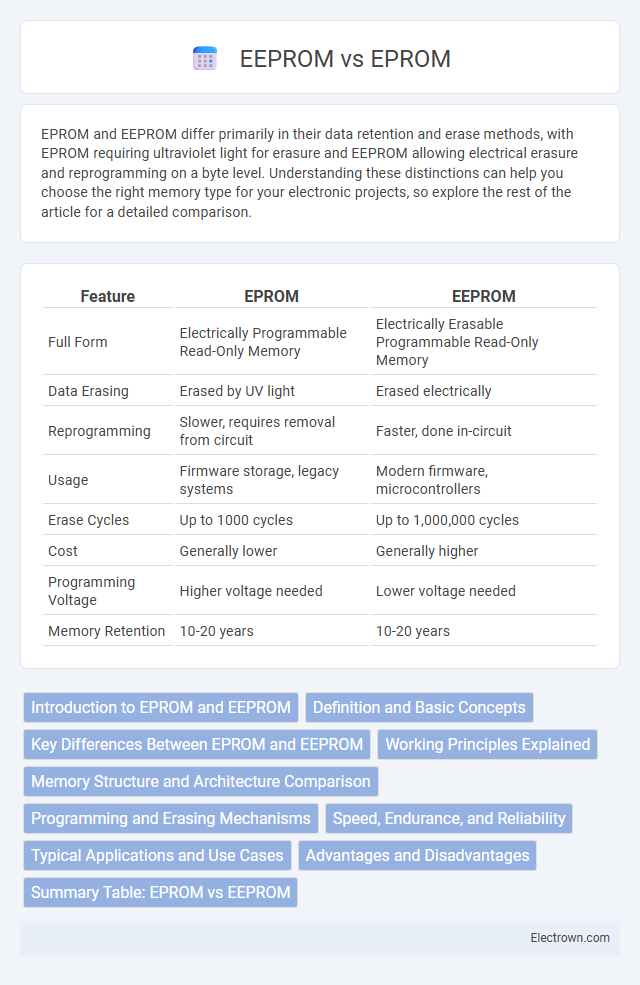
| Feature | EPROM | EEPROM |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Electrically Programmable Read-Only Memory | Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory |
| Data Erasing | Erased by UV light | Erased electrically |
| Reprogramming | Slower, requires removal from circuit | Faster, done in-circuit |
| Usage | Firmware storage, legacy systems | Modern firmware, microcontrollers |
| Erase Cycles | Up to 1000 cycles | Up to 1,000,000 cycles |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Programming Voltage | Higher voltage needed | Lower voltage needed |
| Memory Retention | 10-20 years | 10-20 years |
Introduction to EPROM and EEPROM
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) are non-volatile memory technologies used to store data that must be retained without power. EPROM requires ultraviolet light to erase data, while EEPROM allows electrical erasure and reprogramming at the byte level, making it more flexible for frequent updates. Both memory types are crucial in embedded systems, firmware storage, and applications where persistent data retention is essential.
Definition and Basic Concepts
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory that can be erased by exposing it to ultraviolet light and then reprogrammed. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed at the byte level without removing it from the device. Both EPROM and EEPROM store data persistently, but EEPROM offers more flexibility and convenience for rewrites compared to the ultraviolet-dependent erasure process of EPROM.
Key Differences Between EPROM and EEPROM
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) requires exposure to ultraviolet light for erasing data, while EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) allows data to be erased and rewritten electrically. EEPROM supports byte-level erasing and programming, offering greater flexibility compared to EPROM's block-level erasure process. Your choice depends on the need for frequent updates, with EEPROM favored in applications demanding in-circuit reprogramming and EPROM suited for stable, long-term data storage.
Working Principles Explained
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) stores data by trapping electrons in a floating gate transistor, requiring ultraviolet light exposure to erase stored information. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) utilizes electrically controlled tunneling to erase and rewrite data byte-by-byte without removing the chip from the circuit. This fundamental difference allows EEPROM to offer more flexible and precise data management compared to the bulk erasure method of EPROM.
Memory Structure and Architecture Comparison
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) features a memory structure where data is stored in floating-gate transistors that require ultraviolet light for erasing, making its architecture suitable for bulk erasing. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) uses a similar floating-gate transistor design but allows individual bytes to be electrically erased and rewritten, offering finer control and more flexible memory management. Your choice between EPROM and EEPROM depends on whether you need large-scale data erasure with simpler architecture or precise, byte-level modification capabilities.
Programming and Erasing Mechanisms
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) requires ultraviolet light exposure to erase data, making the process slower and less convenient compared to EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), which uses electrical signals for both programming and erasing. EEPROM allows byte-level erasing and reprogramming while EPROM typically requires full-chip erasure, affecting flexibility and efficiency in updates. Understanding these differences in programming and erasing mechanisms helps optimize memory use for your specific application needs.
Speed, Endurance, and Reliability
EEPROM offers faster read and write speeds compared to EPROM, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent data updates. Endurance of EEPROM is significantly higher, supporting around 1 million write/erase cycles, whereas EPROM typically handles about 100 cycles before degradation. Your choice between EPROM and EEPROM should consider EEPROM's superior reliability and flexibility for modern embedded systems.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
EPROM is typically used in firmware development and embedded systems where code is written once and rarely updated, such as in microcontrollers and industrial machines. EEPROM supports frequent data modifications and is ideal for applications requiring non-volatile memory with customizable storage, like configuration settings in consumer electronics and automotive control systems. Your choice between EPROM and EEPROM depends on the need for memory reprogramming flexibility and application-specific update requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages
EPROM offers the advantage of being cost-effective and reliable for read-intensive applications, but requires UV light for erasing, making in-system updates challenging. EEPROM allows byte-level erasure and writing electrically without removing the chip, enhancing flexibility and ease of reprogramming, though it generally has slower write speeds and higher cost. Your choice depends on the need for frequent updates and budget constraints, with EEPROM favored for modern, versatile applications and EPROM suitable for stable, long-term firmware storage.
Summary Table: EPROM vs EEPROM
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) requires UV light exposure to erase data, while EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) allows electrical erasure and reprogramming. EPROM offers faster read speeds but slower erase/write cycles compared to EEPROM, which supports byte-level erasing and rewriting. EEPROM is more flexible for frequent updates, making it ideal for applications needing frequent data modifications, unlike EPROM suited for less frequent changes.
EPROM vs EEPROM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com