Bus contention occurs when multiple devices attempt to use the bus simultaneously, causing data conflicts and system errors, whereas bus arbitration is the process used to control access to the bus, ensuring orderly communication and preventing contention. Understanding these mechanisms can help you optimize system performance; explore the rest of this article to learn how proper bus arbitration techniques prevent contention issues.
Table of Comparison
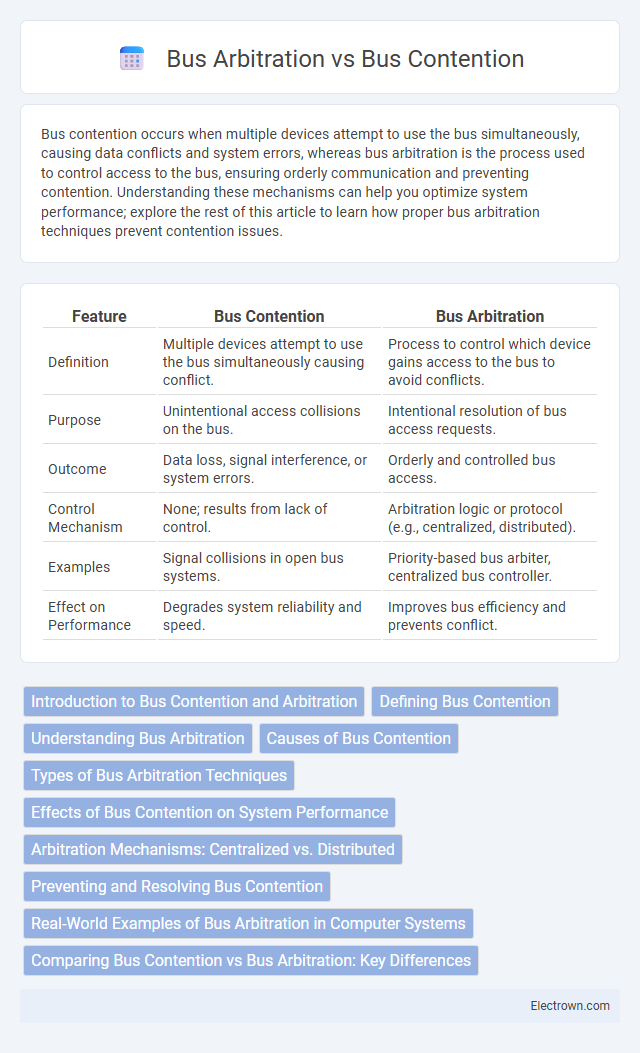
| Feature | Bus Contention | Bus Arbitration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple devices attempt to use the bus simultaneously causing conflict. | Process to control which device gains access to the bus to avoid conflicts. |
| Purpose | Unintentional access collisions on the bus. | Intentional resolution of bus access requests. |
| Outcome | Data loss, signal interference, or system errors. | Orderly and controlled bus access. |
| Control Mechanism | None; results from lack of control. | Arbitration logic or protocol (e.g., centralized, distributed). |
| Examples | Signal collisions in open bus systems. | Priority-based bus arbiter, centralized bus controller. |
| Effect on Performance | Degrades system reliability and speed. | Improves bus efficiency and prevents conflict. |
Introduction to Bus Contention and Arbitration
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices simultaneously attempt to use the same bus, leading to data conflicts and communication errors. Bus arbitration is the mechanism that manages and controls access to the bus, ensuring orderly and conflict-free data transfer by granting permission to one device at a time. Understanding the distinction between bus contention and bus arbitration helps you optimize system performance and prevent data transmission issues.
Defining Bus Contention
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices simultaneously attempt to control a shared bus, resulting in signal conflicts and data corruption risks. This simultaneous access leads to collisions that can disrupt communication and degrade system performance. Understanding bus contention helps you design effective bus arbitration mechanisms to prevent access conflicts and ensure reliable data transfer.
Understanding Bus Arbitration
Bus arbitration is a critical process in computer architecture that ensures orderly access to a shared communication bus among multiple devices, preventing bus contention and data collisions. It involves a control mechanism, such as centralized or distributed arbitration, that grants bus access to one device at a time based on priority schemes or request signals. Efficient bus arbitration enhances system performance by minimizing wait times and ensuring reliable data transfer across the bus.
Causes of Bus Contention
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices simultaneously attempt to control the data bus, causing signal conflicts and potential data corruption. Common causes include improper timing synchronization, faulty hardware design, and lack of an effective arbitration mechanism to manage access priority. Your system's performance can degrade significantly if bus arbitration protocols are not implemented to resolve contention and ensure orderly communication.
Types of Bus Arbitration Techniques
Bus arbitration techniques include centralized, distributed, and hybrid methods, each designed to resolve bus contention by controlling access among multiple devices. Centralized arbitration relies on a single arbiter to grant bus access, while distributed arbitration allows devices to self-coordinate through distributed control logic. Hybrid arbitration combines these approaches to optimize performance and fairness in managing your system's communication resources.
Effects of Bus Contention on System Performance
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices attempt to use the bus simultaneously, causing signal conflicts and data corruption. This leads to increased latency, data errors, and reduced overall system throughput, significantly degrading performance. Your system's efficiency depends on effective bus arbitration mechanisms to prevent contention and maintain smooth communication.
Arbitration Mechanisms: Centralized vs. Distributed
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices attempt to access the bus simultaneously, leading to conflicting data transfers. Arbitration mechanisms resolve these conflicts by determining which device gains control; centralized arbitration uses a single arbiter to manage bus access, ensuring orderly communication but potentially creating a bottleneck. Distributed arbitration allows devices to negotiate bus control collectively, improving scalability and fault tolerance while requiring more complex coordination protocols.
Preventing and Resolving Bus Contention
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices attempt to access the bus simultaneously, causing data conflicts and system errors. Bus arbitration is the mechanism that prevents this by assigning priority and controlling access, ensuring only one device communicates at a time. You can improve system reliability by implementing efficient bus arbitration protocols to resolve bus contention quickly and effectively.
Real-World Examples of Bus Arbitration in Computer Systems
Bus arbitration in computer systems ensures orderly access to a shared communication bus, preventing conflicts and data collisions common in bus contention scenarios. Real-world examples include PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) buses using centralized arbitration with a single arbiter to manage device requests, and CAN (Controller Area Network) buses where distributed arbitration prioritizes messages based on unique identifiers. Your system's stability and performance rely on efficient bus arbitration methods that coordinate multiple components accessing the bus simultaneously without contention.
Comparing Bus Contention vs Bus Arbitration: Key Differences
Bus contention occurs when multiple devices attempt to access the bus simultaneously, causing data conflicts and communication errors, whereas bus arbitration is the controlled process of managing access requests to ensure orderly and conflict-free bus usage. Bus arbitration utilizes algorithms or hardware controllers to prioritize and grant bus access, preventing contention by allowing only one device to communicate at a time. The key difference lies in contention being an undesirable conflict state, while arbitration is a preventive mechanism designed to maintain efficient and stable bus communication.
Bus Contention vs Bus Arbitration Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com