Open collector outputs allow multiple devices to share a line without damage by pulling the line low, while push-pull outputs actively drive the line both high and low for faster switching and stronger signals. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right output type for your circuit; read on to explore their specific applications and advantages.
Table of Comparison
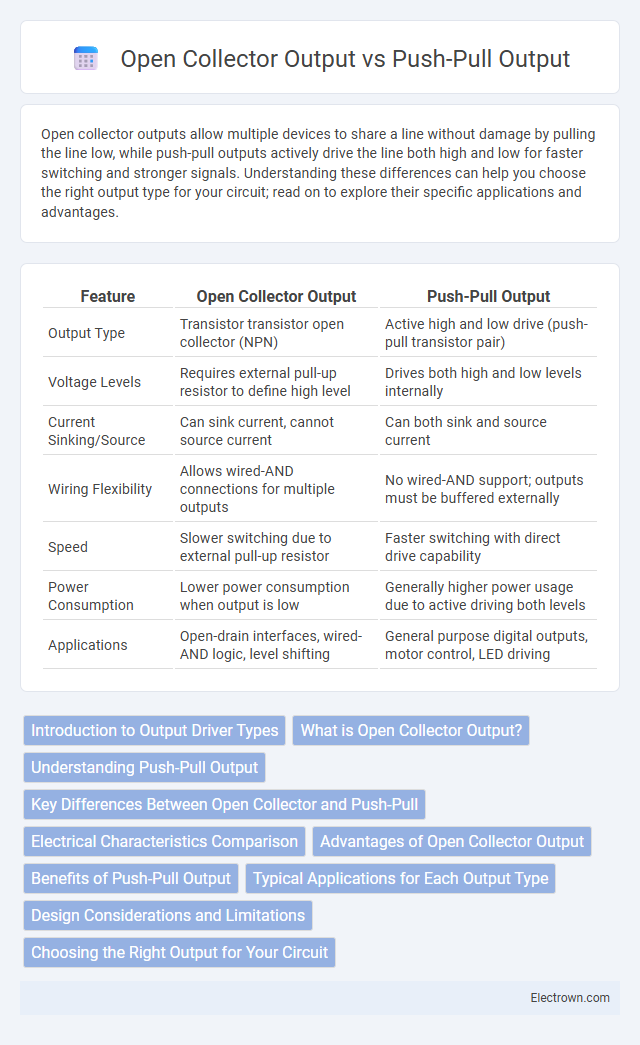
| Feature | Open Collector Output | Push-Pull Output |
|---|---|---|
| Output Type | Transistor transistor open collector (NPN) | Active high and low drive (push-pull transistor pair) |
| Voltage Levels | Requires external pull-up resistor to define high level | Drives both high and low levels internally |
| Current Sinking/Source | Can sink current, cannot source current | Can both sink and source current |
| Wiring Flexibility | Allows wired-AND connections for multiple outputs | No wired-AND support; outputs must be buffered externally |
| Speed | Slower switching due to external pull-up resistor | Faster switching with direct drive capability |
| Power Consumption | Lower power consumption when output is low | Generally higher power usage due to active driving both levels |
| Applications | Open-drain interfaces, wired-AND logic, level shifting | General purpose digital outputs, motor control, LED driving |
Introduction to Output Driver Types
Open collector output drivers use transistors that can only sink current, requiring an external pull-up resistor to provide a defined high level, making them ideal for wired-AND configurations and level shifting. Push-pull output drivers actively drive both high and low states, offering faster switching speeds and stronger output drive for digital circuits. Your choice between these output types depends on application requirements such as signal integrity, speed, and the need for multiple devices to share a common line.
What is Open Collector Output?
Open collector output is a type of digital output commonly used in electronic circuits where the transistor's collector is left open, allowing multiple outputs to be wired together to a single line for wired-AND logic functionality. This output requires an external pull-up resistor to a positive voltage supply, enabling the output to either pull the line low or leave it floating for high logic. Open collector outputs are ideal for interfacing with different voltage levels, driving LEDs, and enabling communication between devices with different ground references.
Understanding Push-Pull Output
Push-pull output provides both sourcing and sinking current capabilities, allowing the output to actively drive the line high or low with low impedance. This design improves switching speed and power efficiency by minimizing voltage drop and current leakage compared to open collector outputs. Your circuits benefit from more precise voltage levels and faster response times when using push-pull outputs in digital and analog applications.
Key Differences Between Open Collector and Push-Pull
Open collector outputs sink current by connecting the load to ground, requiring an external pull-up resistor to achieve a high state, which offers flexibility in voltage levels and ease of wired-AND configurations. Push-pull outputs actively drive both high and low states using complementary transistors, providing faster switching times and stronger drive capability without the need for external components. Your choice between open collector and push-pull depends on the required signal isolation, voltage compatibility, and speed for your specific application.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Open collector outputs allow current to flow only when the transistor is turned on, relying on an external pull-up resistor to define the high voltage level, typically resulting in slower rise times and lower current drive capability. Push-pull outputs actively drive both high and low states with internal transistors, providing faster switching speeds, higher current drive, and better noise immunity. Understanding these electrical characteristics helps you choose the appropriate output type for applications demanding speed, power efficiency, or specific voltage level control.
Advantages of Open Collector Output
Open collector output offers advantages such as the ability to interface with different voltage levels, allowing You to connect devices operating at varying logic voltages without damage. It provides flexible wiring configurations, enabling wired-AND logic and multiple outputs to be tied together safely. This output type also simplifies the integration with high-current loads, as the transistor can sink current directly without sourcing it.
Benefits of Push-Pull Output
Push-pull output provides faster switching speeds and better noise immunity compared to open-collector output, making it ideal for high-speed digital circuits. This configuration actively drives the output voltage both high and low, improving signal integrity and reducing power consumption. Your electronic designs will benefit from enhanced efficiency and improved performance when utilizing push-pull outputs.
Typical Applications for Each Output Type
Open collector outputs are commonly used in applications requiring wired-AND logic, level shifting, or interfacing with different voltage levels, such as in sensor inputs, I2C buses, and relay drives. Push-pull outputs are preferred in situations needing fast switching and strong drive capability, like driving LEDs, digital logic circuits, and microcontroller I/O pins. Your choice depends on whether you need simple, low-power signaling or robust, high-speed output performance.
Design Considerations and Limitations
Open collector outputs require an external pull-up resistor to define the high voltage level, which adds design complexity and can limit signal speed due to RC time constants. Push-pull outputs actively drive both high and low states, enabling faster switching and stronger output drive but can cause higher power consumption and potential damage if shorted. Your design choice should consider the load characteristics, required speed, and whether multiple outputs need to wire-AND together, with open collector favored for wired-logic and push-pull for speed and simplicity.
Choosing the Right Output for Your Circuit
Open collector output allows multiple outputs to be wired together for wired-AND logic and is ideal for interfacing with different voltage levels or creating simple communication buses. Push-pull output provides faster switching speeds and stronger drive capabilities, suitable for driving loads directly without external pull-up resistors. Selecting the right output depends on factors such as required load driving, voltage compatibility, speed, and circuit complexity, with open collector favored for flexibility and push-pull for efficiency.
Open Collector Output vs Push-Pull Output Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com