Serial communication transmits data one bit at a time over a single channel, offering simplicity and longer transmission distances with reduced electromagnetic interference, while parallel communication sends multiple bits simultaneously across multiple channels, enabling faster data transfer but often facing limitations in cable length and increased complexity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice between serial and parallel communication impacts system performance and application suitability.
Table of Comparison
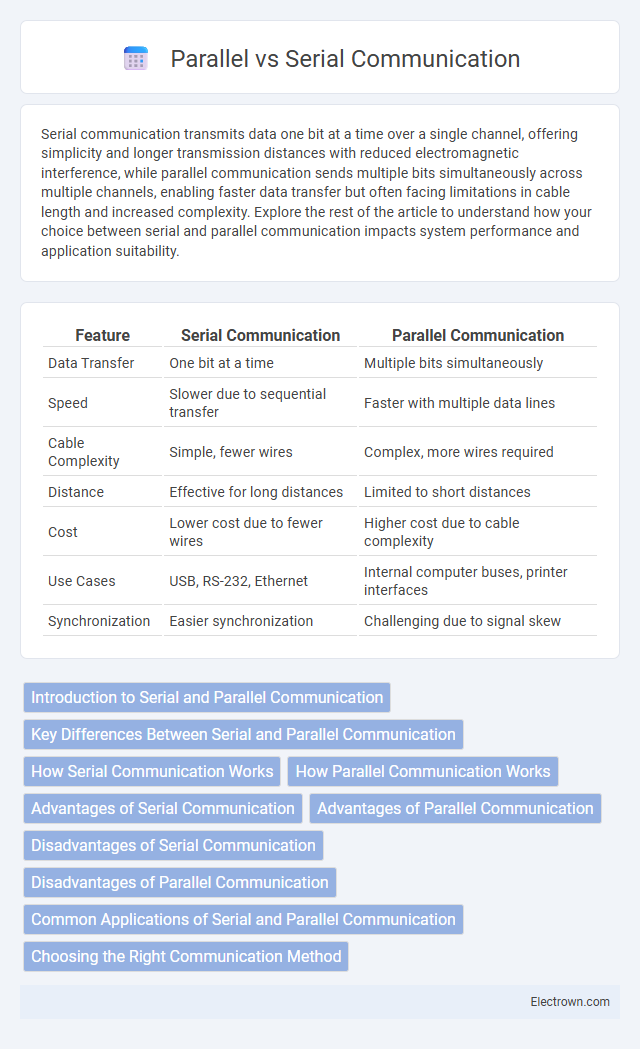
| Feature | Serial Communication | Parallel Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer | One bit at a time | Multiple bits simultaneously |
| Speed | Slower due to sequential transfer | Faster with multiple data lines |
| Cable Complexity | Simple, fewer wires | Complex, more wires required |
| Distance | Effective for long distances | Limited to short distances |
| Cost | Lower cost due to fewer wires | Higher cost due to cable complexity |
| Use Cases | USB, RS-232, Ethernet | Internal computer buses, printer interfaces |
| Synchronization | Easier synchronization | Challenging due to signal skew |
Introduction to Serial and Parallel Communication
Serial communication transmits data bits sequentially over a single channel, making it ideal for long-distance communication with minimal wiring. Parallel communication sends multiple bits simultaneously across multiple channels, providing faster data transfer rates but often limited by signal degradation over longer distances. Understanding the differences helps you choose the appropriate method based on speed, distance, and hardware complexity requirements.
Key Differences Between Serial and Parallel Communication
Serial communication transmits data one bit at a time over a single channel, making it ideal for long-distance and cost-effective transmission with reduced signal interference. Parallel communication sends multiple bits simultaneously across multiple channels, offering faster data rates but with increased complexity, higher costs, and limited distance due to signal degradation. Understanding your system's data requirements and distance constraints is crucial in choosing between serial and parallel communication for optimal performance.
How Serial Communication Works
Serial communication transmits data bit by bit over a single channel or wire, making it efficient for long-distance data transfer with reduced wiring complexity. Each bit is sent sequentially, synchronized by a clock signal or start and stop bits, allowing your devices to interpret the data accurately. This method contrasts with parallel communication by minimizing interference and improving signal integrity in communication systems.
How Parallel Communication Works
Parallel communication transmits multiple bits simultaneously across multiple channels or wires, each carrying a single bit in parallel. This method allows for faster data transfer rates compared to serial communication by sending entire words or bytes at once. However, it requires more physical connections and is susceptible to signal degradation and crosstalk over longer distances.
Advantages of Serial Communication
Serial communication offers advantages such as reduced wiring complexity and lower cost, as it requires fewer data lines compared to parallel communication. It supports longer transmission distances with less signal degradation and electromagnetic interference. The simplified synchronization process in serial communication enhances reliability and efficiency in data transfer.
Advantages of Parallel Communication
Parallel communication offers significant advantages in speed and efficiency by transmitting multiple bits simultaneously across multiple channels, making it ideal for short-distance data transfer within devices like computer memory and processors. This method reduces latency and increases data throughput compared to serial communication, which sends data sequentially. Your systems can benefit from enhanced performance and faster data exchange when using parallel communication in appropriate contexts.
Disadvantages of Serial Communication
Serial communication suffers from slower data transfer rates compared to parallel communication due to the sequential transmission of bits, which can create bottlenecks in high-speed applications. Error detection and correction mechanisms in serial communication often require additional overhead, leading to increased latency and reduced efficiency. Furthermore, the dependence on precise timing and synchronization in serial communication makes it more vulnerable to transmission errors in noisy environments.
Disadvantages of Parallel Communication
Parallel communication suffers from signal skew and crosstalk due to simultaneous transmission over multiple channels, limiting data integrity and speed over longer distances. The increased complexity and cost of parallel cables and connectors make them less efficient for modern high-speed data transfer applications. Your devices may experience synchronization issues and electromagnetic interference, reducing the reliability of parallel communication compared to serial communication.
Common Applications of Serial and Parallel Communication
Serial communication is commonly used in long-distance data transfer applications such as USB devices, RS-232, and network communication due to its lower cost and reduced signal interference. Parallel communication finds frequent use in short-distance scenarios like computer buses, printers, and internal data transfer within CPUs where high data transfer rates are critical. Each method suits specific environments based on factors like distance, speed, and complexity of data transmission.
Choosing the Right Communication Method
Choosing the right communication method depends on factors like data transfer speed, distance, and hardware complexity. Serial communication suits long-distance transmission with fewer wires and lower cost, while parallel communication offers faster data transfer for short distances due to multiple simultaneous data lines. Evaluating your system's requirements for speed, reliability, and cost helps determine the optimal communication protocol.
Serial vs parallel communication Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com