Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) use linear functions to generate predictable and periodic sequences, making them suitable for applications like error detection and simple cryptography. Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) introduce complex feedback functions that enhance security by producing less predictable sequences, ideal for advanced encryption systems; discover the key differences and which best fits Your cryptographic needs by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
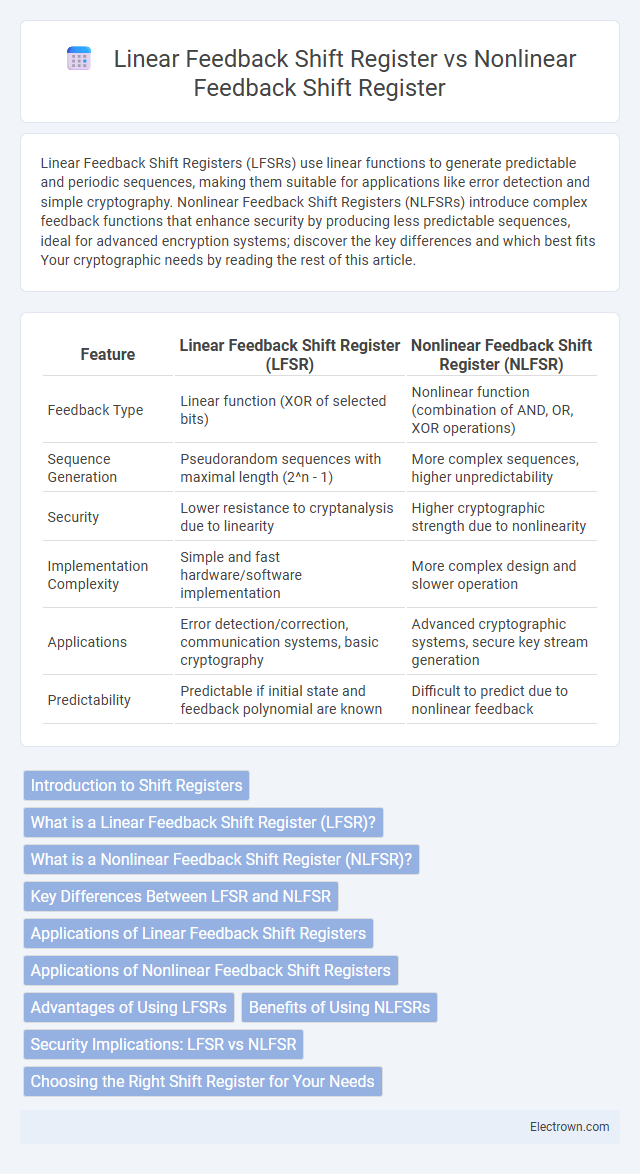
| Feature | Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) | Nonlinear Feedback Shift Register (NLFSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback Type | Linear function (XOR of selected bits) | Nonlinear function (combination of AND, OR, XOR operations) |
| Sequence Generation | Pseudorandom sequences with maximal length (2^n - 1) | More complex sequences, higher unpredictability |
| Security | Lower resistance to cryptanalysis due to linearity | Higher cryptographic strength due to nonlinearity |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple and fast hardware/software implementation | More complex design and slower operation |
| Applications | Error detection/correction, communication systems, basic cryptography | Advanced cryptographic systems, secure key stream generation |
| Predictability | Predictable if initial state and feedback polynomial are known | Difficult to predict due to nonlinear feedback |
Introduction to Shift Registers
Shift registers are fundamental digital circuits used for data storage and transfer, where Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) generate sequences based on linear feedback functions derived from exclusive OR operations. Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) utilize nonlinear feedback functions to produce more complex and less predictable sequences, enhancing cryptographic strength. While LFSRs offer simplicity and efficient implementation, NLFSRs provide increased security at the cost of higher design complexity and computational overhead.
What is a Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR)?
A Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) is a sequential shift register used in digital circuits to generate pseudorandom binary sequences based on linear feedback functions derived from its previous state bits. Its operation relies on a characteristic polynomial over the finite field GF(2), enabling efficient implementation for applications in cryptography, error detection, and digital signal processing. LFSRs produce sequences with maximal length and good statistical properties but are vulnerable to linear analysis attacks due to their deterministic linear structure.
What is a Nonlinear Feedback Shift Register (NLFSR)?
A Nonlinear Feedback Shift Register (NLFSR) is a shift register where the feedback function involves nonlinear operations, unlike the linear functions used in Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs). NLFSRs provide enhanced cryptographic security and complexity due to their nonlinear feedback mechanisms, making them suitable for pseudorandom number generation and stream cipher design. Understanding how NLFSRs differ from LFSRs can help you select the most secure and efficient register type for your cryptographic applications.
Key Differences Between LFSR and NLFSR
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) generate pseudo-random sequences using linear functions based on XOR operations, making them simpler and faster but predictable and less secure. Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) employ nonlinear functions, enhancing cryptographic strength and resistance to linear attacks by producing more complex and less predictable sequences. The key differences lie in their feedback functions, with LFSRs offering efficient hardware implementation and NLFSRs providing improved security for encryption and sequence generation applications.
Applications of Linear Feedback Shift Registers
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) are widely used in cryptography for stream cipher key generation, error detection and correction in communication systems, and pseudorandom number generation. Their ability to produce long sequences with good statistical properties and simple hardware implementation makes them ideal for applications in digital signal processing and spread spectrum systems. Unlike Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs), which enhance security through complexity, LFSRs excel in efficiency and speed for error checking and sequence generation tasks.
Applications of Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers
Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) are primarily applied in cryptographic systems requiring enhanced security, such as stream ciphers and pseudo-random number generators, due to their resistance to linear attacks. They generate more complex and unpredictable sequences compared to Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs), making them suitable for secure communications and encryption protocols. NLFSRs also find use in hardware implementations of secure key generation and authentication mechanisms in wireless sensor networks and embedded devices.
Advantages of Using LFSRs
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) offer advantages such as simplicity in implementation, fast operation, and low hardware cost, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient pseudorandom number generation or sequence scrambling. They provide predictable periodicity and excellent statistical properties, facilitating error detection and cryptographic functions with less computational overhead. The linearity of LFSRs enables straightforward analysis and easy design of circuits compared to complex nonlinear feedback shift registers (NFSRs).
Benefits of Using NLFSRs
Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) offer enhanced security features compared to Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) due to their complex feedback functions, making them resistant to linear cryptanalysis and prediction attacks. NLFSRs can generate sequences with higher linear complexity and better statistical properties, which are crucial in cryptographic applications such as stream ciphers and secure key generation. The increased unpredictability and improved randomness quality of NLFSR outputs make them ideal for robust encryption systems in modern communication protocols.
Security Implications: LFSR vs NLFSR
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) are vulnerable to cryptanalysis due to their predictable linear structure, making them less secure for cryptographic applications. Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NLFSRs) enhance security by employing nonlinear functions, which significantly increase resistance against correlation and algebraic attacks. The complexity of NLFSRs' state space and output sequences provides stronger defense mechanisms, crucial for robust stream cipher designs.
Choosing the Right Shift Register for Your Needs
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) are ideal for applications requiring high-speed, simple implementation with predictable pseudo-random sequences, commonly used in error detection and cryptography. Nonlinear Feedback Shift Registers (NFSRs) provide enhanced security and complexity, making them suitable for cryptographic applications demanding resistance against linear attacks. Choosing the right shift register depends on balancing your need for speed, security, and implementation complexity.
Linear Feedback Shift Register vs Nonlinear Feedback Shift Register Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com