PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controls signal by varying the pulse duration while keeping frequency constant, ideal for applications needing precise power delivery. PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) shifts pulse positions without changing pulse width, useful in communication systems to reduce noise interference; explore the article to understand which modulation suits your needs best.
Table of Comparison
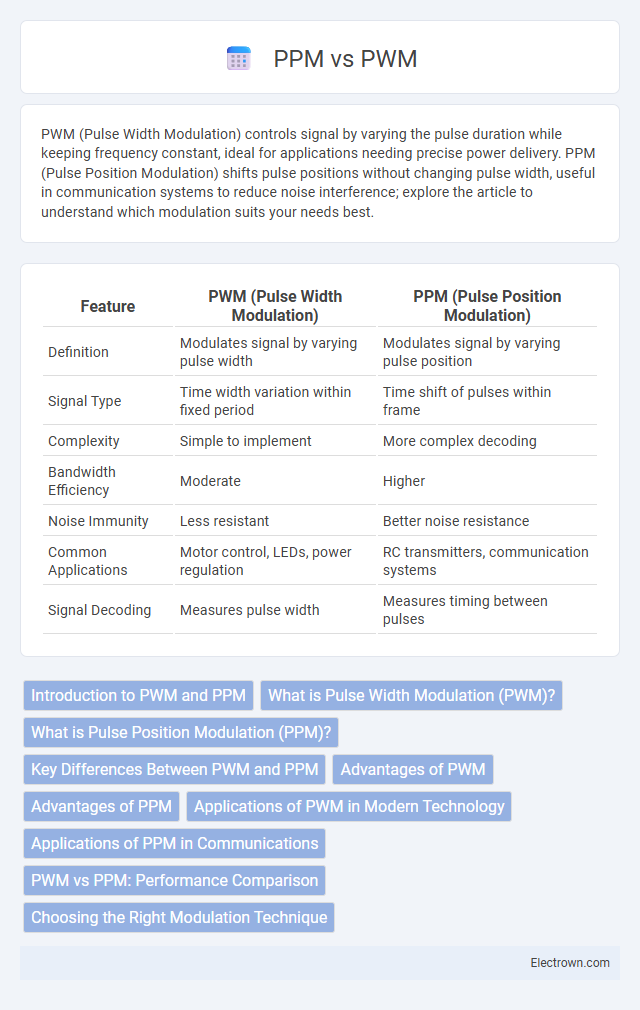
| Feature | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) | PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modulates signal by varying pulse width | Modulates signal by varying pulse position |
| Signal Type | Time width variation within fixed period | Time shift of pulses within frame |
| Complexity | Simple to implement | More complex decoding |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | Moderate | Higher |
| Noise Immunity | Less resistant | Better noise resistance |
| Common Applications | Motor control, LEDs, power regulation | RC transmitters, communication systems |
| Signal Decoding | Measures pulse width | Measures timing between pulses |
Introduction to PWM and PPM
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls devices by varying the duration of each pulse within a fixed frequency, commonly used in motor speed regulation and LED dimming. Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) encodes information by shifting the timing of pulses relative to a reference, often applied in radio control systems for model aircraft. Understanding the distinctions between PWM and PPM helps you choose the right modulation technique for precise signal control and communication.
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)?
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control the amount of power delivered to an electronic device by varying the width of the pulses in a continuous signal. This modulation allows precise control of motors, LEDs, and other devices by adjusting the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the pulse duration to the total period. Understanding PWM helps you optimize power efficiency and performance in applications like motor speed control and light dimming.
What is Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)?
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) is a digital modulation technique where the position of each pulse within a time frame varies to represent information. PPM encodes data by shifting the timing of pulses relative to a reference clock, improving noise immunity compared to PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). It is commonly used in communication systems, remote controls, and signal processing for its high efficiency in bandwidth and robustness against amplitude variations.
Key Differences Between PWM and PPM
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controls the duration of on-time within a fixed period to regulate power delivery, while PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) varies the position of pulses within a time frame to encode information. PWM is commonly used in motor speed control and LED dimming due to its efficient power modulation, whereas PPM excels in radio communication systems by enabling precise timing synchronization. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate modulation technique based on your application's needs for power efficiency or signal accuracy.
Advantages of PWM
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) offers precise control over motor speed and brightness due to its varying duty cycle, enabling efficient energy use and smooth operation. PWM signals reduce electromagnetic interference and heat generation compared to other modulation methods, increasing device lifespan. Its compatibility with a wide range of electronic components makes PWM optimal for applications requiring fine control and reliability.
Advantages of PPM
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) offers several advantages over Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), including better noise immunity and reduced signal interference due to its modulation of pulse timing rather than pulse width. PPM signals provide more precise synchronization for radio control applications, leading to improved reliability in transmitting multiple channels simultaneously. For your remote control or communication system, PPM ensures clearer signal decoding and greater resistance to signal distortion.
Applications of PWM in Modern Technology
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is widely used in modern technology for controlling the brightness of LED lights, regulating motor speeds in robotics, and managing power delivery in renewable energy systems. Its precise control over voltage and current makes it ideal for applications requiring efficient energy use and rapid response times. Your electronic devices benefit from PWM by achieving better performance and energy efficiency through these varied applications.
Applications of PPM in Communications
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) is widely used in optical communication systems due to its high noise immunity and efficient bandwidth usage. Applications of PPM include infrared remote controls, free-space optical links, and fiber-optic communications where precise timing in pulse transmission enhances data integrity. Your communication system benefits from PPM's reduced error rates and power efficiency in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
PWM vs PPM: Performance Comparison
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) offers precise control of motor speed and servo positioning through variable pulse durations within a fixed frequency, resulting in smooth and reliable performance. PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) encodes multiple channels into a single pulse sequence by varying pulse positions, enabling efficient multiplexing but with slightly increased latency and complexity in decoding. Performance-wise, PWM provides faster response times and finer resolution for individual channel control, while PPM excels in reducing wiring and improving synchronization for multi-channel systems.
Choosing the Right Modulation Technique
Selecting the right modulation technique between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) depends on the specific application requirements such as noise immunity, signal resolution, and synchronization needs. PWM excels in controlling power delivery and motor speed due to its straightforward implementation and precise duty cycle control, while PPM offers superior timing accuracy and reduced susceptibility to amplitude noise, making it ideal for sensitive communication systems. Evaluating factors like bandwidth efficiency, error tolerance, and hardware complexity ensures the optimal choice for robust and efficient signal transmission.
PWM vs PPM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com