A multiplexer selects one input from multiple data inputs and forwards it to a single output line based on select signals, while an encoder converts multiple input lines into a smaller number of output lines representing the binary code of the active input. Understanding the differences between these components can enhance your digital circuit design skills; explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
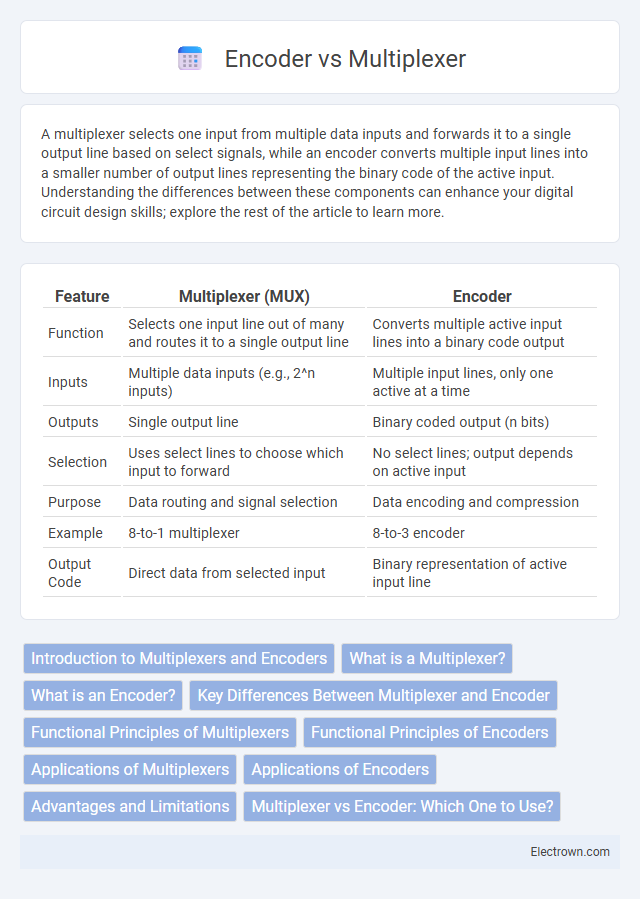
| Feature | Multiplexer (MUX) | Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Selects one input line out of many and routes it to a single output line | Converts multiple active input lines into a binary code output |
| Inputs | Multiple data inputs (e.g., 2^n inputs) | Multiple input lines, only one active at a time |
| Outputs | Single output line | Binary coded output (n bits) |
| Selection | Uses select lines to choose which input to forward | No select lines; output depends on active input |
| Purpose | Data routing and signal selection | Data encoding and compression |
| Example | 8-to-1 multiplexer | 8-to-3 encoder |
| Output Code | Direct data from selected input | Binary representation of active input line |
Introduction to Multiplexers and Encoders
Multiplexers are digital devices that select one input line from multiple inputs and forward it to a single output line based on select signals, optimizing data transmission and reducing wiring complexity. Encoders convert multiple active input signals into a coded binary output, often used to reduce the number of lines required for data processing. Both components play crucial roles in digital circuits for efficient data routing and signal encoding, enhancing overall system performance.
What is a Multiplexer?
A multiplexer is a digital switch that selects one input from multiple data lines and directs it to a single output line based on select signals. It efficiently manages data routing in communication systems and digital circuits by reducing the number of data paths required. Your system's performance can be enhanced by using a multiplexer to streamline signal processing and minimize hardware complexity.
What is an Encoder?
An encoder is a digital circuit that converts multiple input lines into a smaller number of output lines, representing the binary code of the active input. It simplifies complex signals into binary format, facilitating easier data processing and transmission. Your digital system uses encoders to efficiently reduce the number of data lines while preserving essential information.
Key Differences Between Multiplexer and Encoder
A multiplexer selects one input from multiple signal sources and forwards it to a single output line, effectively channeling data based on a select signal. An encoder, however, converts multiple input lines into a binary code, representing the active input with fewer output lines for simplified data representation. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize digital circuit design by choosing the correct component for signal selection or data encoding tasks.
Functional Principles of Multiplexers
Multiplexers function by selecting one input signal from multiple data inputs and routing it to a single output line based on select lines, enabling efficient data channel sharing in digital circuits. This selection process reduces hardware complexity by consolidating multiple signals into one line, controlled by binary select inputs that determine which data input is transmitted. Your systems benefit from improved signal management and reduced wiring through this fundamental principle of multiplexers.
Functional Principles of Encoders
Encoders convert multiple input signals into a coded output, simplifying data transmission by reducing the number of data lines required. Unlike multiplexers that select a single input line to send to the output, encoders provide a binary representation of active inputs, enhancing signal processing efficiency. Understanding your encoder's functionality ensures effective integration in digital circuits where encoding priority and input activation play key roles.
Applications of Multiplexers
Multiplexers play a crucial role in communication systems by enabling multiple data signals to share a single transmission channel, optimizing bandwidth usage in telecommunication networks. They are widely used in digital circuits for selecting one of many input signals and forwarding the chosen input into a single line, enhancing the efficiency of data routing in computer memory and processor systems. In industrial automation, multiplexers facilitate sensor data management by consolidating outputs from various sensors into a single output line for streamlined processing and monitoring.
Applications of Encoders
Encoders are widely used in digital systems for data compression and selection, translating multiple input signals into a smaller number of output lines. Common applications include priority encoders in interrupt systems, rotary encoders in position sensing for robotics and industrial automation, and optical encoders for motion detection in automotive and elevator controls. Their ability to efficiently encode input data into binary form makes them essential in communication systems and data routing.
Advantages and Limitations
Multiplexers offer efficient data transmission by selecting one input from multiple signals, reducing the number of data lines required, which optimizes bandwidth and hardware usage. However, limitations include increased complexity and propagation delay as the number of input lines grows, impacting performance in high-speed applications. Encoders excel in converting multiple input lines into binary code with fewer output lines, simplifying the design, but they are restricted by errors if multiple inputs are active simultaneously and are less effective for complex data routing compared to multiplexers.
Multiplexer vs Encoder: Which One to Use?
Choosing between a multiplexer and an encoder depends on your specific application needs; multiplexers select one input from multiple data lines for transmission on a single line, ideal for data routing and communication efficiency. Encoders convert multiple input lines into a coded output, primarily used for simplifying signal processing and reducing the number of input lines. Your decision should consider whether you need data selection with minimal wiring or compact signal representation.
Multiplexer vs Encoder Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com