Pluggable modules offer flexibility and easy replacement, ideal for prototypes and devices requiring frequent upgrades, while soldered components provide more reliable connections and better mechanical stability for permanent assemblies. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits Your specific electronics project needs.
Table of Comparison
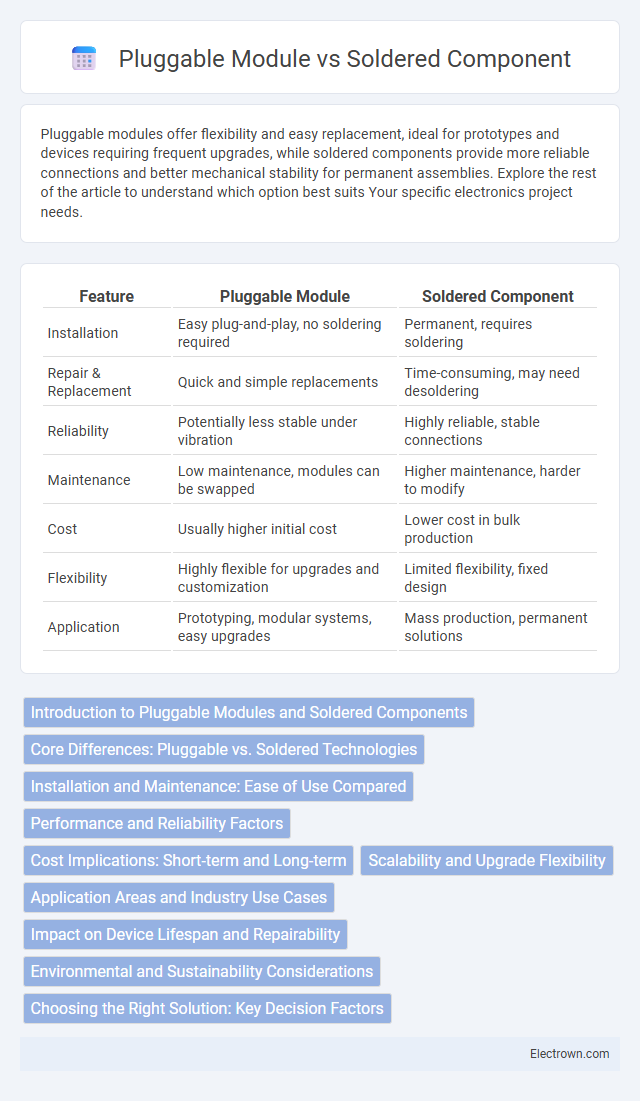
| Feature | Pluggable Module | Soldered Component |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Easy plug-and-play, no soldering required | Permanent, requires soldering |
| Repair & Replacement | Quick and simple replacements | Time-consuming, may need desoldering |
| Reliability | Potentially less stable under vibration | Highly reliable, stable connections |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, modules can be swapped | Higher maintenance, harder to modify |
| Cost | Usually higher initial cost | Lower cost in bulk production |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for upgrades and customization | Limited flexibility, fixed design |
| Application | Prototyping, modular systems, easy upgrades | Mass production, permanent solutions |
Introduction to Pluggable Modules and Soldered Components
Pluggable modules are electronic components designed for easy insertion and removal from a host system, allowing rapid upgrades and maintenance without soldering. Soldered components are permanently affixed to a circuit board, providing robust mechanical and electrical connections essential for long-term reliability. Comparing these two highlights the trade-off between modular flexibility and structural stability in electronic device design.
Core Differences: Pluggable vs. Soldered Technologies
Pluggable modules enable easy replacement and upgrades without desoldering, enhancing flexibility in system design and maintenance. Soldered components provide stronger mechanical stability and lower electrical resistance, ensuring reliable long-term performance under harsh conditions. The core difference lies in pluggable modules' modularity versus soldered components' fixed integration, influencing repairability, manufacturing complexity, and application suitability.
Installation and Maintenance: Ease of Use Compared
Pluggable modules offer straightforward installation and simplified maintenance, allowing you to quickly replace or upgrade components without specialized tools or desoldering skills. Soldered components, while providing a more permanent and reliable connection, require skilled technicians and more time-consuming procedures for installation and repairs. This distinction makes pluggable modules highly suitable for environments demanding frequent updates or minimal downtime.
Performance and Reliability Factors
Pluggable modules offer easier replacement and upgradeability but may introduce slight contact resistance and signal integrity issues affecting high-frequency performance. Soldered components provide superior mechanical stability and lower electrical resistance, resulting in enhanced reliability under thermal and vibration stress. Careful consideration of the application's environmental conditions and performance requirements determines the optimal choice between pluggable and soldered options.
Cost Implications: Short-term and Long-term
Pluggable modules generally have higher short-term costs due to additional connectors and modular design but offer long-term savings through easier maintenance and upgrades. Soldered components reduce initial expenses with simpler assembly processes but can incur higher long-term costs from increased repair complexity and full board replacements. Choosing between the two impacts total cost of ownership, depending on maintenance frequency and product lifecycle expectations.
Scalability and Upgrade Flexibility
Pluggable modules offer superior scalability by enabling quick, tool-less upgrades and easy component swaps, allowing systems to adapt to evolving performance demands without extensive downtime. Soldered components, by contrast, limit upgrade flexibility due to permanent installation, requiring specialized skills and hardware for modifications or replacements. This makes pluggable modules ideal for environments prioritizing modular growth and efficient system maintenance.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
Pluggable modules are widely used in telecommunications, data centers, and industrial automation due to their ease of replacement and upgrade, supporting high-speed data transfer and flexible system configurations. Soldered components are preferred in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries where durability, miniaturization, and cost-efficiency are critical for mass production and long-term reliability. Both technologies enable tailored solutions across sectors, optimizing performance and maintenance based on specific operational demands.
Impact on Device Lifespan and Repairability
Pluggable modules significantly enhance device lifespan by allowing easy replacement of faulty components, reducing electronic waste and repair costs. Soldered components, while offering a compact design, limit repair options and often lead to complete device replacement when failures occur. Your choice between them directly affects long-term maintenance ease and overall device durability.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Pluggable modules offer enhanced environmental benefits by enabling easier repairs and upgrades, reducing electronic waste compared to soldered components that often require full board replacements. This modularity supports longer device lifespans and facilitates recycling processes by allowing individual parts to be separated and processed efficiently. Your choice of pluggable modules can directly contribute to more sustainable electronics practices by minimizing resource consumption and promoting circular economy principles.
Choosing the Right Solution: Key Decision Factors
Selecting between pluggable modules and soldered components depends heavily on maintenance needs, production volume, and long-term flexibility. Pluggable modules offer easy replacement and upgrades, ideal for prototypes and modular systems, while soldered components provide reliability and cost-efficiency in high-volume, stable designs. Key decision factors include repairability, signal integrity, mechanical robustness, and lifecycle requirements specific to the application environment.
Pluggable module vs soldered component Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com